| Emission nebula | |
|---|---|
| Planetary nebula | |
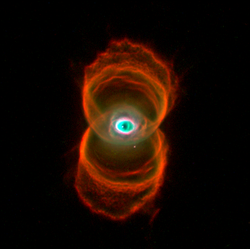 1996 Hubble Space Telescope image of the Hourglass Nebula | |
| Observation data: J2000 epoch | |
| Right ascension | 13h 39m 35.116s [1] |
| Declination | −67° 22′ 51.45″ [1] |
| Distance | 8,000 ly |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 13.0 [1] |
| Constellation | Musca |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Radius | 0.29 ly |
| Notable features | Resembles a human eye |
| Designations | ESO 97-1, [1] Engraved Hourglass Nebula, [1] Contents[1] , RCW 77 |
The Engraved Hourglass Nebula (also known as MyCn 18 [2] ) is a young planetary nebula in the southern constellation Musca. It was discovered by Annie Jump Cannon and Margaret W. Mayall during their work on an extended Henry Draper Catalogue (the catalogue was built between 1918 and 1924). At the time, it was designated simply as a small faint planetary nebula. Much improved telescopes and imaging techniques allowed the hourglass shape of the nebula to be discovered by Romano Coradi and Hugo Schwarz in images taken during 1991–1992 at the European Southern Observatory. [3] It is conjectured that MyCn 18's hourglass shape is produced by the expansion of a fast stellar wind within a slowly expanding cloud which is denser near its equator than its poles. The vivid colours given off by the nebula are the result of different 'shells' of elements being expelled from the dying star, in this case helium, nitrogen, oxygen and carbon. The central star of the nebula has a strong magnetic field https://www.esa.int/Science_Exploration/Space_Science/The_Hourglass_Nebula_MyCn-18
The Hourglass Nebula was photographed by the Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2 of the Hubble Space Telescope.
A less-famous "Hourglass Nebula" is located inside the Lagoon Nebula.