
Halomonadaceae is a family of halophilic Pseudomonadota.

Cupriavidus is a genus of bacteria that includes the former genus Wautersia. They are characterized as Gram-negative, motile, rod-shaped organisms with oxidative metabolism. They possess peritrichous flagella, are obligate aerobic organisms, and are chemoorganotrophic or chemolithotrophic. Resistance to metals has been described. These organisms have been found in both soil and in clinical isolates.
Halopiger is a genus of archaeans in the family Natrialbaceae that have high tolerance to salinity.
In taxonomy, Halovivax is a genus of the Natrialbaceae. Some species of Halovivax are halophiles and have been found in Iran's Aran-Bidgol hypersaline lake.
Companilactobacillus kimchii is a bacteriocin-producing lactic acid bacterium of the genus Companilactobacillus. It is named for and found in the Korean fermented-vegetable food kimchi.
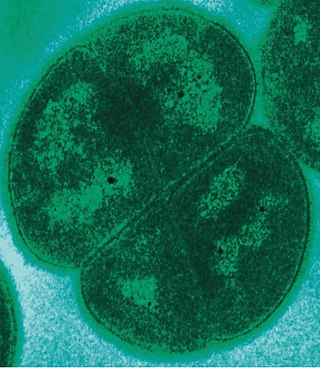
Deinococcus is in the monotypic family Deinococcaceae, and one genus of three in the order Deinococcales of the bacterial phylum Deinococcota highly resistant to environmental hazards. These bacteria have thick cell walls that give them Gram-positive stains, but they include a second membrane and so are closer in structure to Gram-negative bacteria. Deinococcus survive when their DNA is exposed to high doses of gamma and UV radiation. Whereas other bacteria change their structure in the presence of radiation, such as by forming endospores, Deinococcus tolerate it without changing their cellular form and do not retreat into a hardened structure. They are also characterized by the presence of the carotenoid pigment deinoxanthin that give them their pink color. They are usually isolated according to these two criteria. In August 2020, scientists reported that bacteria from Earth, particularly Deinococcus bacteria, were found to survive for three years in outer space, based on studies conducted on the International Space Station. These findings support the notion of panspermia, the hypothesis that life exists throughout the Universe, distributed in various ways, including space dust, meteoroids, asteroids, comets, planetoids or contaminated spacecraft.
Polynucleobacter is a genus of bacteria, originally established by Heckmann and Schmidt (1987) to exclusively harbor obligate endosymbionts of ciliates belonging to the genus Euplotes.
Caballeronia grimmiae is a gram-negative, non-spore-forming, rod-shaped bacterium from the genus of Caballeronia and the family of Burkholderiaceae which was isolated from the xerophilous moss Grimmia montana in China.
Shinella is a genus of bacteria from the family Rhizobiaceae.
Altererythrobacter is a bacterial genus from the family Erythrobacteraceae.
Pontixanthobacter luteolus is a Gram-negative, halophilic and non-spore-forming bacterium from the genus Pontixanthobacter which has been isolated from tidal flat from the Yellow Sea in Korea.
Paraurantiacibacter namhicola is a Gram-negative, aerobic and non-motile bacterium from the genus Paraurantiacibacter which has been isolated from seawater from the South Sea in Korea.
Alsobacter is a genus of Alphaproteobacteria.
Amorphaceae is a family of Alphaproteobacteria.
Ancalomicrobiaceae is a family of Alphaproteobacteria.
Emcibacteraceae is a family of bacteria.
Iodidimonas is a genus of bacteria.
The Temperatibacteraceae are a family of bacteria.
The Ignavibacteriales are an order of obligately anaerobic, non-photosynthetic bacteria that are closely related to the green sulfur bacteria.
The Holophagae is a class of Acidobacteriota.


