
In organic chemistry, an ethyl group is an alkyl substituent with the formula −CH2CH3, derived from ethane. Ethyl is used in the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry's nomenclature of organic chemistry for a saturated two-carbon moiety in a molecule, while the prefix "eth-" is used to indicate the presence of two carbon atoms in the molecule.

Ethyl acetate is the organic compound with the formula CH3CO2CH2CH3, simplified to C4H8O2. This colorless liquid has a characteristic sweet smell and is used in glues, nail polish removers, and in the decaffeination process of tea and coffee. Ethyl acetate is the ester of ethanol and acetic acid; it is manufactured on a large scale for use as a solvent.
Stearyl heptanoate, the ester of stearyl alcohol and heptanoic acid, is found in most cosmetic eyeliner. It is prepared from stearyl alcohol, which may be derived from sperm whale oil or from vegetable sources.
Enanthic acid, also called heptanoic acid, is an organic compound composed of a seven-carbon chain terminating in a carboxylic acid functional group. It is a colorless oily liquid with an unpleasant, rancid odor. It contributes to the odor of some rancid oils. It is slightly soluble in water, but very soluble in ethanol and ether. Salts and esters of enanthic acid are called enanthates or heptanoates.

Testosterone enanthate is an androgen and anabolic steroid (AAS) medication which is used mainly in the treatment of low testosterone levels in men. It is also used in hormone therapy for transgender men. It is given by injection into muscle or subcutaneously usually once every one to four weeks.

Ethyl loflazepate is a drug which is a benzodiazepine derivative. It possesses anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, sedative and skeletal muscle relaxant properties. In animal studies it was found to have low toxicity, although in rats evidence of pulmonary phospholipidosis occurred with pulmonary foam cells developing with long-term use of very high doses. Its elimination half-life is 51–103 hours. Its mechanism of action is similar to other benzodiazepines. Ethyl loflazepate also produces an active metabolite which is stronger than the parent compound. Ethyl loflazepate was designed to be a prodrug for descarboxyloflazepate, its active metabolite. It is the active metabolite which is responsible for most of the pharmacological effects rather than ethyl loflazepate. The main metabolites of ethyl loflazepate are descarbethoxyloflazepate, loflazepate and 3-hydroxydescarbethoxyloflazepate. Accumulation of the active metabolites of ethyl loflazepate are not affected by those with kidney failure or impairment. The symptoms of an overdose of ethyl loflazepate include sleepiness, agitation and ataxia. Hypotonia may also occur in severe cases. These symptoms occur much more frequently and severely in children. Death from therapeutic maintenance doses of ethyl loflazepate taken for 2 – 3 weeks has been reported in 3 elderly patients. The cause of death was asphyxia due to benzodiazepine toxicity. High doses of the antidepressant fluvoxamine may potentiate the adverse effects of ethyl loflazepate.
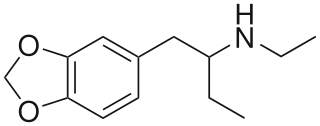
Ethylbenzodioxolylbutanamine is a lesser-known entactogen, stimulant, and psychedelic. It is the N-ethyl analogue of benzodioxylbutanamine, and also the α-ethyl analogue of methylenedioxyethylamphetamine.
The molecular formula C9H18O2 (molar mass: 158.24 g/mol) may refer to:
Propyl hexanoate (C9H18O2), also known as propyl caproate, is an ester formed by the reaction of propanol with hexanoic acid. Although it is a completely different ester, propyl hexanoate shares the same chemical formula with methyl octanoate, ethyl heptanoate, butyl pentanoate, etc. because they all have the same total carbon chain length. The scent of this ester can be described as that of blackberries, pineapple, cheese or wine.

Hydroxyprogesterone heptanoate (OHPH), also known as hydroxyprogesterone enanthate (OHPE) and sold under the brand names H.O.P., Lutogil A.P., and Lutogyl A.P. among others, is a progestin medication used for progestogenic indications. It has been formulated both alone and in together with estrogens, androgens/anabolic steroids, and other progestogens in several combination preparations. OHPH is given by injection into muscle at regular intervals.

Estrapronicate, also known as estradiol nicotinate propionate is an estrogen medication and estrogen ester which was never marketed. It was studied as a component of the experimental tristeroid combination drug Trophobolene, which contained nandrolone decanoate, estrapronicate, and hydroxyprogesterone heptanoate.

Androstanolone enanthate, also known as stanolone enanthate or dihydrotestosterone heptanoate (DHTH), as well as 5α-androstan-17β-ol-3-one 17β-heptanoate, is a synthetic androgen and anabolic steroid and a dihydrotestosterone ester. It is used as an injectable and acts as a prodrug of androstanolone. The drug has been studied in and found to be effective in the treatment of gynecomastia in boys and adult men. The pharmacology of androstanolone enanthate has been studied.

Testosterone enantate benzilic acid hydrazone (TEBH), or testosterone 17β-enantate 3-benzilic acid hydrazone, is a synthetic, injected androgen/anabolic steroid and an androgen ester – specifically, the C17β enantate (heptanoate) ester and C3 benzilic acid hydrazone of testosterone. It was previously marketed in combination with estradiol benzoate and estradiol dienantate under the brand names Climacteron, Lactimex, and Lactostat. Clinical studies have assessed this formulation. TEBH was first described in the scientific literature in 1959. It is a very long-lasting prodrug of testosterone when administered in oil via intramuscular injection.

Trestolone enanthate, also known as 7α-methyl-19-nortestosterone 17β-enanthate, is an androgen and anabolic steroid (AAS) and progestogen which was never marketed. It is an androgen ester; specifically, it is the C17β enanthate (heptanoate) ester of trestolone (7α-methylestr-4-en-17β-ol-3-one). Trestolone enanthate has low affinity for sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG), similarly to testosterone enanthate.

Estradiol dibutyrate (EDBu), or estradiol dibutanoate, is an estrogen medication and an estrogen ester – specifically, a diester of estradiol – which is no longer used. It was a component of Triormon Depositum, a combination formulation of estradiol dibutyrate, testosterone caproate, and hydroxyprogesterone heptanoate which was developed in the 1950s.
Progesterone/hydroxyprogesterone heptanoate/α-tocopherol palmitate (P4/OHPH/VE), sold under the brand name Tocogestan, is a combination medication of progesterone (P4), a short-acting progestogen, hydroxyprogesterone heptanoate (OHPH), a long-acting progestogen, and α-tocopherol palmitate, a prodrug of α-tocopherol and form of vitamin E, which was previously used in France to support pregnancy in women but is no longer available. It contained 50 mg P4, 200 mg OHPH, and 250 mg in 2 mL oil solution, was provided in the form of 2 mL ampoules, and was administered by intramuscular injection.
Estradiol dibutyrate/hydroxyprogesterone heptanoate/testosterone caproate (EDBu/OHPH/TCa), sold under the brand name Triormon Depositum, is an injectable combination medication of estradiol dibutyrate (EDBu), an estrogen, hydroxyprogesterone heptanoate (OHPH), a progestogen, and testosterone caproate (TCa), an androgen/anabolic steroid, which was used in the treatment of menopausal symptoms in women. It contained 3 mg EDBu, 30 mg OHPH, and 50 mg TCa in oil solution and was administered by intramuscular injection. The medication was developed by 1957. It is no longer available.

Hydroxyprogesterone heptanoate benzilic acid hydrazone (OHPHBH), also known as 17α-hydroxyprogesterone 17α-heptanoate 3-benzilic acid hydrazone, is a progestin medication which was never marketed. It is the C3 benzilic acid hydrazone of hydroxyprogesterone heptanoate (OHPH). The medication has a longer duration of action than OHPH when administered by subcutaneous injection in animals.












