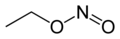
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name Ethyl nitrite | |||
| Other names 1-Nitrosooxyethane Ethyl alcohol nitrite Nitrous acid Nitrous ether Ethyl ester Nitrethyl | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.385 | ||
PubChem CID | |||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C2H5NO2 | |||
| Molar mass | 75.067 g·mol−1 | ||
| Boiling point | 17 °C (63 °F; 290 K) | ||
| 5.07 g/100 ml | |||
| Hazards | |||
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |||
Main hazards | [1] | ||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
The chemical compound ethyl nitrite is an alkyl nitrite with a chemical formula C2H5NO2. It may be prepared from ethanol. [2]