
Castilleja, commonly known as paintbrush, Indian paintbrush, or prairie-fire, is a genus of about 200 species of annual and perennial herbaceous plants native to the west of the Americas from Alaska south to the Andes, northern Asia, and one species as far west as the Kola Peninsula in northwestern Russia. These plants are classified in the broomrape family Orobanchaceae. They are hemiparasitic on the roots of grasses and forbs. The generic name honors Spanish botanist Domingo Castillejo.

Plantago lanceolata is a species of flowering plant in the plantain family Plantaginaceae. It is known by the common names ribwort plantain, narrowleaf plantain, English plantain, ribleaf, lamb's tongue, and buckhorn. It is a common weed on cultivated or disturbed land.

Junonia coenia, known as the common buckeye or buckeye, is a butterfly in the family Nymphalidae. Its range covers much of North America and some of Central America, including most of the eastern half of the US, the lower to middle Midwest, the Southwest, southern Canada, and Mexico. Its habitat is open areas with low vegetation and some bare ground. Its original ancestry has been traced to Africa, which then experiences divergence in Asia. The species Junonia grisea, the gray buckeye, is found west of the Rocky Mountains and was formerly a subspecies of Junonia coenia.

The marsh fritillary is a butterfly of the family Nymphalidae. Commonly distributed in the Palearctic region, the marsh fritillary's common name derives from one of its several habitats, marshland. The prolonged larval stage lasts for approximately seven to eight months and includes a period of hibernation over the winter. The larvae are dependent on the host food plant Succisa pratensis not only for feeding but also for hibernation, because silken webs are formed on the host plant as the gregarious larvae enter hibernation. Females lay eggs in batches on the host plant and are, like other batch-layers, selective about the location of oviposition because offspring survivorship levels for batch-layers are more tied to location selection than they are for single-egg layers.

Iridoids are a type of monoterpenoids in the general form of cyclopentanopyran, found in a wide variety of plants and some animals. They are biosynthetically derived from 8-oxogeranial. Iridoids are typically found in plants as glycosides, most often bound to glucose.

Scrophularia californica is a flowering plant in the figwort family which is known by the common names California figwort and California bee plant.

Chelone glabra, or white turtlehead, is a herbaceous species of plant native to North America. Its native range extends from Georgia to Newfoundland and Labrador and from Mississippi to Manitoba. Its common name comes from the appearance of its flower petals, which resemble the head of a tortoise. In fact, in Greek, chelone means "tortoise" and was the name of a nymph who refused to attend the wedding of Zeus and was turned into a turtle as punishment. Its natural habitat is wet areas, such as riparian forests and swamps.

The variable checkerspot or Chalcedon checkerspot is a butterfly in the family Nymphalidae. It is found in western North America, where its range stretches from Alaska in the north to Baja California in the south and extends east through the Rocky Mountains into Colorado, Montana, New Mexico and Wyoming. The butterfly is usually brown or black with extensive white and yellow checkering and some red coloration on the dorsal wing. Adult wingspan is 3.2–5.7 cm (1.3–2.2 in). Adult butterflies feed on nectar from flowers while larvae feed on a variety of plants including snowberry (Symphoricarpos), paintbrush (Castilleja), Buddleja, Diplacus aurantiacus and Scrophularia californica.

Plantago erecta is a flowering plant in the plantain family, commonly known as the California plantain, foothill plantain, dot-seed plantain, English plantain, and dwarf plantain. Plantago erecta is a small, unassuming annual herb with needle-like leaves and translucent flowers clustered on a stalk. It grows in sandy, clay, or serpentine soils, on grassy slopes and flats or open woodland, found in Baja California, California and Oregon. Plantago erecta is a host species for the Edith's checkerspot butterfly.
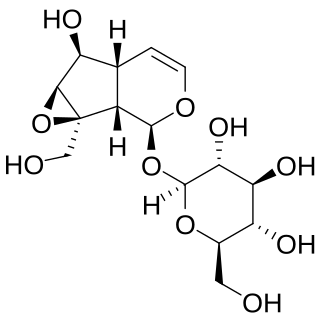
Catalpol is an iridoid glucoside. This natural product falls in the class of iridoid glycosides, which are simply monoterpenes with a glucose molecule attached.

The Baltimore checkerspot is a North American butterfly of the family Nymphalidae. It has been the official state insect of the U.S. State of Maryland since 1973. The Baltimore checkerspot was named for the first Lord Baltimore due to its similarity of colors in the family crest. Despite the species status as Maryland state insect, the population in Maryland has faced significant decline and is currently listed by the Maryland Department of Natural Resources as "rare, threatened, and endangered" animal list.

The Quino checkerspot is a butterfly native to southern California and northwestern Baja California. It is a subspecies of the common Edith's checkerspot and the second such subspecies to be listed under the federal Endangered Species Act.

Edith's checkerspot is a species of butterfly in the family Nymphalidae. It is a resident species of western North America and among the subspecies, entomologists have long been intrigued by their many phenotypic variations in coloration, wing length, and overall body size. Most populations are monophagous and rely on plants including Plantago erecta and Orthocarpus densiflorus as their host species in developing from eggs through to larvae, pupae, and mature butterflies. Males exhibit polygyny whereas females rarely mate more than once. Males devote most of their attention to mate acquisition, and such mate locating strategies such as hilltopping behavior have developed. Climate change and habitat destruction have impacted certain subspecies. Three subspecies in particular, Euphydryas editha quino, Euphydryas editha bayensis and Euphydryas editha taylori, are currently under protection via the Endangered Species Act.

Plantago patagonica is a species of plantain known by the common name woolly plantain. It is native to much of North America, including the southern half of Canada, the western and central United States, and northern Mexico, and parts of southern South America. It grows in many types of habitat, including grassland and woodlands. It is a hairy annual herb producing linear or very narrowly lance-shaped basal leaves up to 10 centimetres (4 in) long. There are usually many stemlike inflorescences growing erect to a maximum height of around 15 cm (6 in). Atop the peduncle of the inflorescence is a dense cylindrical or somewhat conical spike of several tiny flowers and bracts. The spike is very woolly.

Castilleja levisecta is a rare species of flowering plant in the family Orobanchaceae known by the common name golden paintbrush, or golden Indian paintbrush, listed under the Endangered Species Act in 1997. It is native to British Columbia and Washington, where it is known from eleven remaining populations. It occurred in Oregon but all natural occurrences there have been extirpated. It has been reintroduced to a few areas in Oregon, but it remains to be seen if the plants will survive. The plant is a federally listed endangered species of Canada and was listed as threatened in the United States in 1997. On June 30, 2021, the plant was proposed for delisting due to recovery. Effective August 18, 2023, the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service issued a rule removing golden paintbrush from the Federal List of Endangered and Threatened Plants

Icaricia icarioides blackmorei, the Puget blue, is a butterfly native to the Puget Sound area in the northwestern U.S. state of Washington. It is a subspecies of Boisduval's blue.

Chlosyne leanira, the leanira checkerspot, is a butterfly of the family Nymphalidae. It is found in North America from western Oregon south to California, Nevada, Utah and western Colorado, as well as Baja California. The wingspan is 33–40 mm. Generally, females are larger than males, but males have a more apparent red color to their wings.

The Bay checkerspot is a butterfly endemic to the San Francisco Bay region of the U.S. state of California. It is a federally threatened species, as a subspecies of Euphydryas editha.
Robert F. Sternitzky was a United States lepidopterist and illustrator. Butterfly and moth specimens he collected are in a number of collections, including those of the Harvard Museum of Natural History, the Essig Museum of Entomology, Manitoba Museum, and the Smithsonian National Museum of Natural History. He collected primarily in California and Arizona.

Castilleja hispida is a species of flowering plant in the family Orobanchaceae, also known by the common name harsh paintbrush, or harsh Indian paintbrush. It is native to British Columbia, Alberta, Washington, Idaho, Montana, and Oregon.























