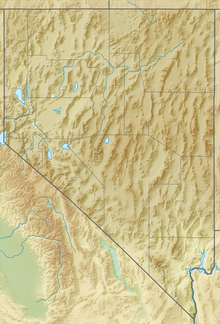
The Sierra Nevada is a mountain range in the Western United States, between the Central Valley of California and the Great Basin. The vast majority of the range lies in the state of California, although the Carson Range spur lies primarily in Nevada. The Sierra Nevada is part of the American Cordillera, an almost continuous chain of mountain ranges that forms the western "backbone" of the Americas.
Excelsior, a Latin comparative word often translated as "ever upward" or "even higher", may refer to:
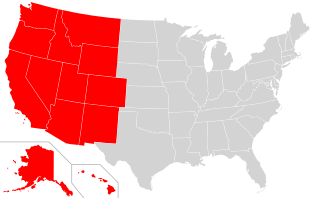
The Western United States is the region comprising the westernmost states of the United States. As American settlement in the U.S. expanded westward, the meaning of the term the West changed. Before about 1800, the crest of the Appalachian Mountains was seen as the western frontier. The frontier moved westward and eventually the lands west of the Mississippi River were considered the West.
Sierra may refer to the following:

The Humboldt–Toiyabe National Forest (HTNF) is the principal U.S. National Forest in the U.S. state of Nevada, and has a smaller portion in Eastern California. With an area of 6,289,821 acres (25,454.00 km2), it is the largest U.S. National Forest outside of Alaska.

The Great Basin is the largest area of contiguous endorheic watersheds, those with no outlets, in North America. It spans nearly all of Nevada, much of Utah, and portions of California, Idaho, Oregon, Wyoming, and Baja California. It is noted for both its arid climate and the basin and range topography that varies from the North American low point at Badwater Basin in Death Valley to the highest point of the contiguous United States, less than 100 miles (160 km) away at the summit of Mount Whitney. The region spans several physiographic divisions, biomes, ecoregions, and deserts.

The Pacific Coast Ranges are the series of mountain ranges that stretch along the West Coast of North America from Alaska south to Northern and Central Mexico. Although they are commonly thought to be the westernmost mountain range of the continental United States and Canada, the geologically distinct Insular Mountains of Vancouver Island lie further west.

The Basin and Range Province is a vast physiographic region covering much of the inland Western United States and northwestern Mexico. It is defined by unique basin and range topography, characterized by abrupt changes in elevation, alternating between narrow faulted mountain chains and flat arid valleys or basins. The physiography of the province is the result of tectonic extension that began around 17 million years ago in the early Miocene epoch.
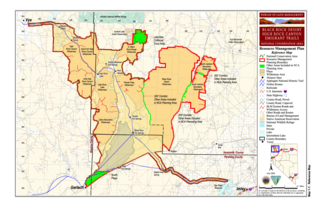
The Black Rock Desert is a semi-arid region of lava beds and playa, or alkali flats, situated in the Black Rock Desert–High Rock Canyon Emigrant Trails National Conservation Area, a silt playa 100 miles (160 km) north of Reno, Nevada that encompasses more than 300,000 acres (120,000 ha) of land and contains more than 120 miles (200 km) of historic trails. It is in the northern Nevada section of the Great Basin with a lakebed that is a dry remnant of Pleistocene Lake Lahontan.

The Inyo Mountains are a short mountain range east of the Sierra Nevada in eastern California in the United States. The range separates the Owens Valley to the west from Saline Valley to the east, extending for approximately 70 miles (110 km) south-southeast from the southern end of the White Mountains, from which they are separated by Westgard Pass, to the east of Owens Lake.
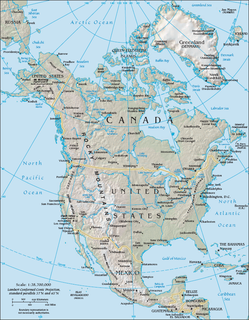
The North American Cordillera, sometimes also called the Western Cordillera of North America, the Western Cordillera or the Pacific Cordillera, is the North American portion of the American Cordillera, the mountain chain system (cordillera) along the western coast of the Americas. The North American Cordillera covers an extensive area of mountain ranges, intermontane basins and plateaus in Western/Northwestern Canada, Western United States and Mexico, including much of the territory west of the Great Plains.
The Monte Cristo Range is located in western Nevada in the United States. The range lies southeast of the Excelsior Mountains and east and north of Highway 95 in Esmeralda County. The Bureau of Land Management manages 99.9% of the range. Sagebrush scrub makes up 63.1% of the mountains, with Shadscale comprising 36.6%.

The Intermountain West, or Intermountain Region, is a geographic and geological region of the Western United States. It is located between the front ranges of the Rocky Mountains on the east and the Cascade Range and Sierra Nevada on the west.

The Currant Mountain Wilderness is a 47,357-acre (19,165 ha) wilderness area centered on Currant Mountain in the White Pine Range of Nye County and White Pine County, in the eastern section of the state of Nevada in the western United States.

The Calico Hills or Calico Mountains are a mountain range in northwestern Nevada. The range runs north to south along the western edge of the Black Rock Desert. This mountain range is located in western Humboldt County and the northwestern corner of Pershing County, approximately 30 miles north of the town of Gerlach, Nevada. The best access to the Calico Hills is located from the maintained Soldier Meadows Road that forms its eastern boundary.

The Trout Creek Mountains are a remote, semi-arid Great Basin mountain range mostly in southeastern Oregon and partially in northern Nevada in the United States. The range's highest point is Orevada View Benchmark, 8,506 feet (2,593 m) above sea level, in Nevada. Disaster Peak, elevation 7,781 feet (2,372 m), is another prominent summit in the Nevada portion of the mountains.

The Mountain States form one of the nine geographic divisions of the United States that are officially recognized by the United States Census Bureau. It is a subregion of the Western United States.
Excelsior is a ghost town in Elko County, in the U.S. state of Nevada.

Black Mountain is an 11,797-foot-elevation (3,596 meter) summit located in the Sierra Nevada mountain range, in Mono County of northern California, United States. The mountain is set within the Hoover Wilderness, on the common boundary shared by Inyo National Forest with Humboldt–Toiyabe National Forest, and 1.5 mile outside the boundary of Yosemite National Park. The peak is situated immediately southwest above Virginia Lakes, 1.8 miles (2.9 km) northeast of line parent Excelsior Mountain, and 1.8 miles (2.9 km) south of Dunderberg Peak. Topographic relief is significant as the north aspect rises 1,500 feet (457 meters) above Cooney Lake in one-half mile, and the south aspect rises 3,600 feet (1,097 meters) above Lundy Canyon in 1.5 mile. The first ascent of the summit was made in 1905 by George R. Davis, Albert Hale Sylvester, and Pearson Chapman, all with the United States Geological Survey.