
Severe storms in Australia refers to the storms, including cyclones, which have caused severe damage in Australia. For comparison, a comprehensive list of all damaging storms can be found on the Australian Bureau of Meteorology website.

The climate of Minneapolis–Saint Paul is the long term weather trends and historical events of the Minneapolis–Saint Paul metropolitan area in east central Minnesota. Minneapolis and St. Paul, together known as the Twin Cities, are the core of the 15th largest metropolitan area in the United States. With a population of 3.6 million people, the region contains approximately 60% of the population of Minnesota. Due to its location in the northern and central portion of the U.S., the Twin Cities has the coldest average temperature of any major metropolitan area in the nation. Winters are very cold, summer is warm and humid, snowfall is common in the winter and thunderstorms with heavy rainfall occur during the spring, summer and autumn. Though winter can be cold, the area receives more sunlight hours in mid-winter than many other warmer parts of the country, including all of the Great Lakes states, the Pacific Northwest, parts of the South, and almost all of the Northeast. Unless otherwise indicated, all normals data presented below are based on data at Minneapolis/St. Paul International Airport, the official Twin Cities climatology station, from the 1981−2010 normals period.

The climate of Sydney, Australia is humid subtropical, shifting from mild and cool in winter to warm and hot in the summer, with no extreme seasonal differences as the weather is moderated by proximity to the ocean, although more contrasting temperatures are recorded in the inland western suburbs. Despite the fact that there is no distinct dry or wet season, rainfall peaks in the first few months of the year and is at its lowest just around the middle of the year, though precipitation can be erratic throughout the year. Precipitation varies across the region, with areas adjacent to the coast being the wettest. According to the Bureau of Meteorology, Sydney falls in the temperate climate zone which has warm to hot summers and no dry season. Sydney's plant hardiness zone ranges from zone 11a to 9b throughout the metropolitan area. Under the Holdridge Life Zones classification, eastern Sydney falls in the Subtropical Moist Forest zone and the western suburbs in the Subtropical Dry Forest zone.
The climate of Houston is classified as a humid subtropical climate, with tropical influences. August normally ranks as the warmest month at an average temperature of 84.6 °F (29.2 °C) and January the coldest month at an average temperature of 53.1 °F (11.7 °C).
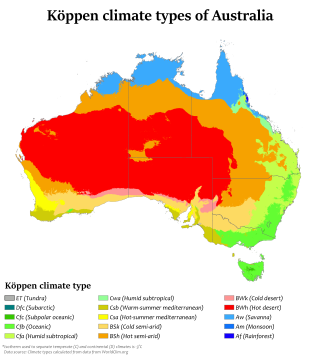
Australia's climate is governed mostly by its size and by the hot, sinking air of the subtropical high pressure belt. This moves north-west and north-east with the seasons. The climate is variable, with frequent droughts lasting several seasons, thought to be caused in part by the El Niño-Southern Oscillation. Australia has a wide variety of climates due to its large geographical size. The largest part of Australia is desert or semi-arid. Only the south-east and south-west corners have a temperate climate and moderately fertile soil. The northern part of the country has a tropical climate, varying between grasslands and desert. Australia holds many heat-related records: the continent has the hottest extended region year-round, the areas with the hottest summer climate, and the highest sunshine duration.

Severe weather is any dangerous meteorological phenomenon with the potential to cause damage, serious social disruption, or loss of human life. Types of severe weather phenomena vary, depending on the latitude, altitude, topography, and atmospheric conditions. High winds, hail, excessive precipitation, and wildfires are forms and effects of severe weather, as are thunderstorms, downbursts, tornadoes, waterspouts, tropical cyclones, and extratropical cyclones. Regional and seasonal severe weather phenomena include blizzards (snowstorms), ice storms, and duststorms.

The climate of the United States varies due to changes in latitude, and a range of geographic features, including mountains and deserts. Generally, on the mainland, the climate of the U.S. becomes warmer the further south one travels, and drier the further west, until one reaches the West Coast.

North Carolina's climate varies from the Atlantic coast in the east to the Appalachian Mountain range in the west. The mountains often act as a "shield", blocking low temperatures and storms from the Midwest from entering the Piedmont of North Carolina.
In Australia, the Federation Drought is the name given to a prolonged period of drought that occurred around the time of Federation in 1901.

The climate of Miami is classified as having a tropical monsoon climate with hot and humid summers; short, warm winters; and a marked drier season in the winter. Its sea-level elevation, coastal location, position just above the Tropic of Cancer, and proximity to the Gulf Stream shape its climate.

The climate of Allentown, Pennsylvania is classified as a humid continental climate. Allentown's warmest month is July with a daily average temperature of 74.7 °F (23.7 °C) and the coldest month being January with a daily average of 29.4 °F (−1.4 °C). The average precipitation of Allentown is 45.35 inches (1,152 mm) per year.

The 2010 Western Australian storms were a series of storms that travelled over southwestern Western Australia on 21 and 22 March 2010. One of the more intense storm cells passed directly over the capital city of Perth between 3:30pm and 5:00pm on Monday 22 March 2010. It is the costliest natural disaster in Western Australian history, with the damage bill estimated at $1.08 billion.

The 2010 Northern Hemisphere summer heat waves included severe heat waves that impacted most of the United States, Kazakhstan, Mongolia, China, Hong Kong, North Africa and the European continent as a whole, along with parts of Canada, Russia, Indochina, South Korea and Japan during July 29 2010. The first phase of the global heatwaves was caused by a moderate El Niño event, which lasted from June 2009 to May 2010. The first phase lasted only from April 2010 to June 2010, and caused only moderate above average temperatures in the areas affected. But it also set new record high temperatures for most of the area affected, in the Northern Hemisphere. The second phase was caused by a very strong La Niña event, which lasted from June 2010 to June 2011. According to meteorologists, the 2010–11 La Niña event was one of the strongest La Niña events ever observed. That same La Niña event also had devastating effects in the Eastern states of Australia. The second phase lasted from June 2010 to October 2010, caused severe heat waves, and multiple record-breaking temperatures. The heatwaves began in April 2010, when strong anticyclones began to develop, over most of the affected regions, in the Northern Hemisphere. The heatwaves ended in October 2010, when the powerful anticyclones over most of the affected areas dissipated.

The Geography of Atlanta encompasses 132.4 square miles (342.9 km2), of which 131.7 square miles (341.1 km2) is land and 0.7 square miles (1.8 km2) is water. The city is situated among the foothills of the Appalachian Mountains, and at 1,050 feet (320 m) above mean sea level, Atlanta has the highest elevation among major cities east of the Mississippi River. Atlanta straddles the Eastern Continental Divide, such that rainwater that falls on the south and east side of the divide flows into the Atlantic Ocean, while rainwater on the north and west side of the divide flows into the Gulf of Mexico. Atlanta sits atop a ridge south of the Chattahoochee River, which is part of the ACF River Basin. Located at the far northwestern edge of the city, much of the river's natural habitat is preserved, in part by the Chattahoochee River National Recreation Area.
The Australian summer of 2012–2013, known as the Angry Summer or Extreme Summer, resulted in 123 weather records being broken over a 90-day period, including the hottest day ever recorded for January on record, the hottest summer average on record, and a record seven days in a row when the whole country averaged above 39 °C (102 °F). Single-day temperature records were broken in dozens of towns and cities, as well as single-day rainfall records, and several rivers flooded to new record highs.
Perth, the capital city of the state of Western Australia, has a Mediterranean climate, with hot, dry summers and mild, wet winters. February is the hottest month of the year, with an average high of 31.6 °C (88.9 °F), and July is the coldest month of the year, with an average low of 7.9 °C (46.2 °F). 77% of rain in Perth falls between May and September. Perth has an average of 8.8 hours of sunshine per day, which equates to around 3,200 hours of annual sunshine, and 138.7 clear days annually, making it the sunniest capital city in Australia.

Melbourne, the state capital of Victoria and the second most populous city in Australia, has a temperate oceanic climate and is well known for its changeable weather conditions. This is mainly due to Melbourne's geographical location. This temperature differential is most pronounced in the spring and summer months and can cause strong cold fronts to form. These cold fronts can be responsible for all sorts of severe weather from gales to severe thunderstorms and hail, minor temperature drops, and heavy rain. The city experiences little humidity in summer, except at the end of hot spells following thunderstorms and rain.

Brisbane has a humid subtropical climate with year-round period with warm to hot temperatures. Brisbane generally experiences 3 months of mild cool winter from June to August.

Severe weather events or extreme weather events in Sydney, Australia, include hailstorms, thunderstorms, gale, bushfires, heatwaves, drought, and flash flooding from heavy rain. Sydney is rarely affected by cyclones, although remnants of cyclones do affect the city.
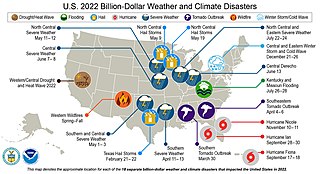
The following is a list of weather events that occurred on Earth in the year 2022. The year began with a La Niña. There were several natural disasters around the world from various types of weather, including blizzards, cold waves, droughts, heat waves, wildfires, floods, tornadoes, and tropical cyclones. The deadliest weather event of the year were the European heat waves, which killed over 26,000 people, 11,000 of which were in France. The costliest weather event of the year was Hurricane Ian, which caused at least $112.9 billion in damages in Florida and Cuba. Another significant weather event was the Pakistan floods, which killed 1,739 people and a total of $14.9 billion in damages.


















