
The Marshall Islands, officially the Republic of the Marshall Islands, is an island country west of the International Date Line and north of the equator in the Micronesia region in the Northwestern Pacific Ocean. The territory consists of 29 coral atolls and five islands, divided across two island chains: Ratak in the east and Ralik in the west. 97.87% of its territory is water, the largest proportion of water to land of any sovereign state. The country shares maritime boundaries with Wake Island to the north, Kiribati to the southeast, Nauru to the south, and the Federated States of Micronesia to the west. The capital and largest city is Majuro, home to approximately half of the country's population.

A tuna is a saltwater fish that belongs to the tribe Thunnini, a subgrouping of the Scombridae (mackerel) family. The Thunnini comprise 15 species across five genera, the sizes of which vary greatly, ranging from the bullet tuna up to the Atlantic bluefin tuna, which averages 2 m (6.6 ft) and is believed to live up to 50 years.

The albacore, known also as the longfin tuna, is a species of tuna of the order Scombriformes. It is found in temperate and tropical waters across the globe in the epipelagic and mesopelagic zones. There are six distinct stocks known globally in the Atlantic, Pacific, and Indian oceans, as well as the Mediterranean Sea. The albacore has an elongate, fusiform body with a conical snout, large eyes, and remarkably long pectoral fins. Its body is a deep blue dorsally and shades of silvery white ventrally. Individuals can reach up to 1.4 m in length.

Longline fishing, or longlining, is a commercial fishing angling technique that uses a long main line with baited hooks attached at intervals via short branch lines called snoods or gangions. A snood is attached to the main line using a clip or swivel, with the hook at the other end. Longlines are classified mainly by where they are placed in the water column. This can be at the surface or at the bottom. Lines can also be set by means of an anchor, or left to drift. Hundreds or even thousands of baited hooks can hang from a single line. This can lead to many deaths of different marine species. Longliners – fishing vessels rigged for longlining – commonly target swordfish, tuna, halibut, sablefish and many other species.

Bycatch, in the fishing industry, is a fish or other marine species that is caught unintentionally while fishing for specific species or sizes of wildlife. Bycatch is either the wrong species, the wrong sex, or is undersized or juveniles of the target species. The term "bycatch" is also sometimes used for untargeted catch in other forms of animal harvesting or collecting. Non-marine species that are caught but regarded as generally "undesirable" are referred to as rough fish or coarse fish.
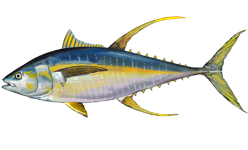
The yellowfin tuna is a species of tuna found in pelagic waters of tropical and subtropical oceans worldwide.

Pelagic fish live in the pelagic zone of ocean or lake waters—being neither close to the bottom nor near the shore—in contrast with demersal fish that live on or near the bottom, and reef fish that are associated with coral reefs.

A fish aggregatingdevice (FAD) is a man-made object used to attract pelagic fish such as marlin, tuna and mahi-mahi. They usually consist of buoys or floats tethered to the ocean floor. FADs attract fish for reasons that vary by species.

The bigeye tuna is a species of true tuna of the genus Thunnus, belonging to the wider mackerel family Scombridae. In Hawaiian, it is one of two species known as ʻahi, the other being the yellowfin tuna. Bigeye tuna are found in the open waters of all tropical and temperate oceans, but not in the Mediterranean Sea.

The Western and Central Pacific Fisheries Commission (WCPFC) is a regional fisheries management organisation established to conserve and manage tuna and other highly migratory fish stocks across the western and central areas of the Pacific Ocean. Its full name is Commission for the Conservation and Management of Highly Migratory Fish Stocks in the Western and Central Pacific Ocean. It commenced operations in late 2005, and its secretariat is based in Pohnpei, in the northern Pacific state of the Federated States of Micronesia.

Cross Seamount is a seamount far southwest of the Hawaii archipelago, about equidistant from the cities of Honolulu and Kona. It is one of the numerous seamounts surrounding Hawaii, although unrelated to the Hawaiian hotspot. It is notable for being one of the best studied of the numerous seamounts surrounding Hawaii, as it has been included in numerous biological surveys, most recently in 2007. It is also a site of offshore fishing, for its abundant tuna. The fishery management problems at Cross Seamount are typical of management problems in many fisheries, and its small size makes it a scientifically useful model for the analysis of fishery management.

International Seafood Sustainability Foundation (ISSF) was formed in 2009 as a global, non-profit partnership among the tuna industry, scientists and World Wide Fund for Nature. The multistakeholder group states its mission is "to undertake science-based initiatives for the long-term conservation and sustainable use of tuna stocks, reducing bycatch and promoting ecosystem health". Regional Fisheries Management Organizations (RFMOs) are primarily responsible for managing the world's tuna stocks—skipjack, yellowfin and albacore tuna, the species most commonly processed for canned and shelf-stable tuna products, but their parliamentary procedures too often allow the short-term economic and political interests of nations to prevent sustainable measures from being adopted. ISSF works to ensure that effective international management practices are in place to maintain the health of all the tuna stocks.
The Nauru Agreement Concerning Cooperation in the Management of Fisheries of Common Interest, or The Nauru Agreement is an Oceania subregional agreement between the Federated States of Micronesia, Kiribati, the Marshall Islands, Nauru, Palau, Papua New Guinea, Solomon Islands and Tuvalu. The eight signatories collectively control 25–30% of the world's tuna supply and approximately 60% of the western and central Pacific tuna supply.

The Pacific Islands Forum Fisheries Agency (FFA) is an intergovernmental agency established in 1979 to facilitate regional co-operation and co-ordination on fisheries policies between its member states in order to achieve conservation and optimum utilisation of living marine resources, in particular highly migratory fish stocks, for the benefit of the peoples of the region, in particular the developing countries. The office campus is located in Honiara, Solomon Islands

Fishing is important to the national economy of Vanuatu. It is the main source of income for many in the islands and Vanuatu's biggest export. According to 2009 figures, approximately 77% of households in Vanuatu are involved in fishing activity. According to 2005 figures, Vanuatu caught 151,080 fish in that year, with frozen fish accounted for half of Vanuatu's commodity exports.

The Western Pacific Regional Fishery Management Council (WPRFMC) is one of eight regional councils established under the Magnuson-Stevens Fishery Conservation and Management Act (MSA) in 1976 to manage offshore fisheries. The WPRFMC's jurisdiction includes the US exclusive economic zone (EEZ) waters around the State of Hawaii; US Territories of American Samoa and Guam; the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands (CNMI); and the US Pacific remote island areas of Johnston, Midway, Palmyra and Wake Atolls; Baker, Howland and Jarvis Islands; and Kingman Reef. This area of nearly 1.5 million square miles is the size of the continental United States and constitutes about half of the entire US EEZ. It spans both sides of the equator and both sides of the dateline. The WPRFMC also manages domestic fisheries based in the US Pacific Islands that operate on the high seas.
The Hawaii longline fishery is managed under Western Pacific Regional Fishery Management Council’s (WPRFMC's) Pelagics Fisheries Ecosystem Plan. Through this plan, the WPRFMC has introduced logbooks, observers, vessel monitoring systems, fishing gear modifications and spatial management for the Hawaii longline fishery. Until relatively recently, the main driver for management of the Hawaii longline fishery has been bycatch and not fishery resources.

Rhea Medine Moss-Christian is the executive director and former chair of the Western and Central Pacific Fisheries Commission (WCPFC), the governing body for the world's largest tuna fishery, which conserves and manages fish stocks across the western and central Pacific Ocean. She was the first woman to hold either of these roles. She previously chaired the Marshall Islands National Nuclear Commission and advised the Marshall Islands Government on oceans and trade.

US FWS Hugh M. Smith was an American fisheries science research vessel in commission from 1949 to 1959 in the fleet of the United States Department of the Interior's Fish and Wildlife Service. She was among the first U.S. fisheries science vessels to explore the central Pacific Ocean in search of commercially valuable populations of fish.

US FWS Charles H. Gilbert was an American fisheries science research vessel in commission from 1952 to 1970 in the fleet of the United States Department of the Interior's Fish and Wildlife Service and from 1970 to 1973 in the fleet of the National Oceanic Atmospheric Administration as NOAAS Charles H. Gilbert. She was among the first U.S. fisheries science vessels to explore the central Pacific Ocean in search of commercially valuable populations of fish.




















