
The Laird LC-DW300 and LC-DW500 Super Solution aka "Sky Buzzard" was a racing biplane built in the early 1930s by Matty Laird for the Cleveland Speed Foundation, Laird was already famous in the air racing circuit. It had a large radial engine and an extremely faired windshield. Other than being a biplane, it was similar in appearance to the Gee Bee, a more famous racer from the period. It was an advanced design for the time because of the relatively clean aerodynamic construction and tight engine cowling.

The Velocity Model 173 SE is an entry level canard pusher aircraft from Velocity Aircraft. The four seat, rear engine aircraft may be powered by a 160 hp (120 kW) Lycoming IO-320 or a 200 hp (150 kW) Lycoming IO-360 engine.

The Sharp Nemesis NXT is a sport-class kit-built aircraft. It is designed for air racing. It was designed by Nemesis Air Racing's president Jon Sharp, as a follow-on to the Sharp Nemesis. It is a single seat, single engine, low wing, retractable gear kit aircraft. As designed, the aircraft is powered by a Lycoming TIO-540-NXT Thunderbolt six-cylinder engine.

The Chester Jeep aka the Chester Special #1 was an air racer built by Art Chester for the 1932 National Air Races. The aircraft once held the world's speed record for aircraft at 237 mph (381 km/h).
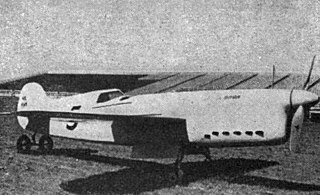
The Chester Goon aka The Chester Special #2 was a single-engine taildragger-configuration monoplane racer built for the 1938 National Air Races.

The Folkerts SK-1,Speed King One, Mono Special, Matilda, Fordon-Neumann Special, Hardwick-Whittenbeck Special was a racer built for the 1930 American Cirrus Aircraft Engine Company sponsored American Cirrus Derby.

The Folkerts SK-2, also known as Speed King Two, "Toots" and "Miss Detroit" was a racer built for the 1936 National Air Races

Chief Oshkosha.k.a.Buster is a homebuilt racing plane designed to compete in the 1931 American Cirrus Races.

The Howard DGA-4 a.k.a. Mike, and DGA-5 a.k.a. Ike and "Miss Chevrolet" was the next in a series of racers from Ben Howard. He built two examples, "Mike" and "Ike", each with a different landing gear design.

The Wittman DFA aka Little Bonzo is a homebuilt racing aircraft designed to compete in midget racing.

The Wedell-Williams Model 22 was a racing aircraft, two examples of which were built in the United States in the early 1930s by the Wedell-Williams Air Service Corporation. It was one of three early projects by aircraft designer Jimmy Wedell to create a racer and was built specifically to compete in the 1930 All-American Flying Derby from Buffalo to Detroit. It was a braced, low-wing monoplane originally powered by an inline Cirrus engine and equipped with fixed landing gear in large spats.

The Rider-Elmendorf R-5 Jackrabbit is an aircraft designed and built to compete in the National Air Races.

The Microleve Corsario is a Brazilian amphibious ultralight flying boat that was designed and produced by Microleve of Rio de Janeiro. The aircraft was supplied as a kit for amateur construction.

The Polen Special, is a homebuilt racing aircraft built to become the fastest four cylinder aircraft in the world.

The Sport Performance Aviation Panther is a single seat, all-metal, homebuilt aircraft under development by Sport Performance Aviation of Green Cove Springs, Florida. The aircraft is intended to be supplied as plans and as a kit for amateur construction.

The Hawks Miller HM-1, named Time Flies was an American racing aircraft that was the joint project of pilot-owner, Frank Hawks and Howell W. "Pete" Miller, chief engineer for the Granville Brothers. Although very advanced for its time with an enclosed cockpit that highlighted its streamlined lines, development ended after a crash during testing. A completely new design emerged when the aircraft was re-configured as a two-seat military aircraft.
The Miller JM-2 was an American Formula One Air Racing homebuilt aircraft that was designed by Jim W Miller and produced by JW Miller Aviation of Marble Falls, Texas. When it was available the aircraft was supplied in the form of plans for amateur construction.

The Williams W-17 Stinger is an American homebuilt racing aircraft that was designed for Formula One Air Racing by Art Williams and produced by his company, Williams Aircraft Design of Northridge, California, introduced in 1971. The aircraft was at one time available in the form of plans for amateur construction, but only one was ever constructed.
The CEI Free Spirit Mk II, also called the Cabrinha Free Spirit Mark II and the Cabrinha Model 423, is a three-seat American homebuilt aircraft that was designed by Richard Cabrinha and produced by CEI of Auburn, California, introduced at AirVenture in 1995. The aircraft was intended to be supplied as a kit for amateur construction, but only prototypes seem to have been completed.

The Miles & Atwood Special is a racing aircraft developed during the interwar period



















