Related Research Articles
In chemistry, amines are compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are formally derivatives of ammonia, wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituent such as an alkyl or aryl group. Important amines include amino acids, biogenic amines, trimethylamine, and aniline. Inorganic derivatives of ammonia are also called amines, such as monochloramine.

In organic chemistry, a carboxylic acid is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group attached to an R-group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is R−COOH or R−CO2H, with R referring to the alkyl, alkenyl, aryl, or other group. Carboxylic acids occur widely. Important examples include the amino acids and fatty acids. Deprotonation of a carboxylic acid gives a carboxylate anion.

In organic chemistry, ethers are a class of compounds that contain an ether group—an oxygen atom connected to two alkyl or aryl groups. They have the general formula R−O−R′, where R and R′ represent the alkyl or aryl groups. Ethers can again be classified into two varieties: if the alkyl or aryl groups are the same on both sides of the oxygen atom, then it is a simple or symmetrical ether, whereas if they are different, the ethers are called mixed or unsymmetrical ethers. A typical example of the first group is the solvent and anaesthetic diethyl ether, commonly referred to simply as "ether". Ethers are common in organic chemistry and even more prevalent in biochemistry, as they are common linkages in carbohydrates and lignin.

In organic chemistry, an aldehyde is an organic compound containing a functional group with the structure R−CH=O. The functional group itself can be referred to as an aldehyde but can also be classified as a formyl group. Aldehydes are a common motif in many chemicals important in technology and biology.
Hydroboration–oxidation reaction is a two-step hydration reaction that converts an alkene into an alcohol. The process results in the syn addition of a hydrogen and a hydroxyl group where the double bond had been. Hydroboration–oxidation is an anti-Markovnikov reaction, with the hydroxyl group attaching to the less-substituted carbon. The reaction thus provides a more stereospecific and complementary regiochemical alternative to other hydration reactions such as acid-catalyzed addition and the oxymercuration–reduction process. The reaction was first reported by Herbert C. Brown in the late 1950s and it was recognized in his receiving the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1979.
An ylide or ylid is a neutral dipolar molecule containing a formally negatively charged atom (usually a carbanion) directly attached to a heteroatom with a formal positive charge (usually nitrogen, phosphorus or sulfur), and in which both atoms have full octets of electrons. The result can be viewed as a structure in which two adjacent atoms are connected by both a covalent and an ionic bond; normally written X+–Y−. Ylides are thus 1,2-dipolar compounds, and a subclass of zwitterions. They appear in organic chemistry as reagents or reactive intermediates.
In organic chemistry, the diazo group is an organic moiety consisting of two linked nitrogen atoms at the terminal position. Overall charge-neutral organic compounds containing the diazo group bound to a carbon atom are called diazo compounds or diazoalkanes and are described by the general structural formula R2C=N+=N−. The simplest example of a diazo compound is diazomethane, CH2N2. Diazo compounds should not be confused with azo compounds or with diazonium compounds.
The Kornblum oxidation, named after Nathan Kornblum, is an organic oxidation reaction that converts alkyl halides and tosylates into carbonyl compounds.

Organoboron chemistry or organoborane chemistry is the chemistry of organoboron compounds or organoboranes, which are chemical compounds of boron and carbon that are organic derivatives of borane (BH3), for example trialkyl boranes..

The Bamford–Stevens reaction is a chemical reaction whereby treatment of tosylhydrazones with strong base gives alkenes. It is named for the British chemist William Randall Bamford and the Scottish chemist Thomas Stevens Stevens (1900–2000). The usage of aprotic solvents gives predominantly Z-alkenes, while protic solvent gives a mixture of E- and Z-alkenes. As an alkene-generating transformation, the Bamford–Stevens reaction has broad utility in synthetic methodology and complex molecule synthesis.
In organic chemistry, Madelung synthesis is a chemical reaction that produces indoles by the intramolecular cyclization of N-phenylamides using strong base at high temperature. The Madelung synthesis was reported in 1912 by Walter Madelung, when he observed that 2-phenylindole was synthesized using N-benzoyl-o-toluidine and two equivalents of sodium ethoxide in a heated, airless reaction. Common reaction conditions include use of sodium or potassium alkoxide as base in hexane or tetrahydrofuran solvents, at temperatures ranging between 200–400 °C. A hydrolysis step is also required in the synthesis. The Madelung synthesis is important because it is one of few known reactions that produce indoles from a base-catalyzed thermal cyclization of N-acyl-o-toluidines.
In organic chemistry, umpolung or polarity inversion is the chemical modification of a functional group with the aim of the reversal of polarity of that group. This modification allows secondary reactions of this functional group that would otherwise not be possible. The concept was introduced by D. Seebach and E.J. Corey. Polarity analysis during retrosynthetic analysis tells a chemist when umpolung tactics are required to synthesize a target molecule.

The Dakin oxidation is an organic redox reaction in which an ortho- or para-hydroxylated phenyl aldehyde or ketone reacts with hydrogen peroxide in base to form a benzenediol and a carboxylate. Overall, the carbonyl group is oxidised, whereas the H2O2 is reduced.

A Grignard reagent or Grignard compound is a chemical compound with the general formula R−Mg−X, where X is a halogen and R is an organic group, normally an alkyl or aryl. Two typical examples are methylmagnesium chloride Cl−Mg−CH3 and phenylmagnesium bromide (C6H5)−Mg−Br. They are a subclass of the organomagnesium compounds.
Silyl enol ethers in organic chemistry are a class of organic compounds that share a common functional group composed of an enolate bonded through its oxygen end to an organosilicon group. They are important intermediates in organic synthesis.

Organozinc chemistry is the study of the physical properties, synthesis, and reactions of organozinc compounds, which are organometallic compounds that contain carbon (C) to zinc (Zn) chemical bonds.
A carbon–oxygen bond is a polar covalent bond between atoms of carbon and oxygen. Carbon–oxygen bonds are found in many inorganic compounds such as carbon oxides and oxohalides, carbonates and metal carbonyls, and in organic compounds such as alcohols, ethers, carbonyl compounds and oxalates. Oxygen has 6 valence electrons of its own and tends to fill its outer shell with 8 electrons by sharing electrons with other atoms to form covalent bonds, accepting electrons to form an anion, or a combination of the two. In neutral compounds, an oxygen atom can form up to two single bonds or one double bond with carbon, while a carbon atom can form up to four single bonds or two double bonds with oxygen.
The Abramov reaction is the related conversions of trialkyl to α-hydroxy phosphonates by the addition to carbonyl compounds. In terms of mechanism, the reaction involves attack of the nucleophilic phosphorus atom on the carbonyl carbon. It was named after the Russian chemist Vasilii Semenovich Abramov (1904–1968) in 1957.
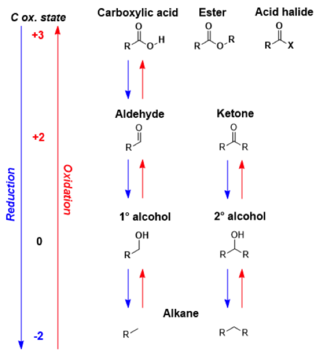
In organic chemistry, carbonyl reduction is the organic reduction of any carbonyl group by a reducing agent.

Reductions with samarium(II) iodide involve the conversion of various classes of organic compounds into reduced products through the action of samarium(II) iodide, a mild one-electron reducing agent.
References
- ↑ Godfrey, Alexander G.; Ganem, Bruce (1990-05-30). "Ready oxidation of halides to aldehydes using trimethylamine N-oxide in dimethylsulfoxide". Tetrahedron Letters . 31 (34): 4825–4826. doi: 10.1016/S0040-4039(00)97742-6 .
- ↑ Smith, Amos B.; Basu, Kallol; Bosanac, Todd (2007-11-13). "Total Synthesis of (−)-Okilactomycin". Journal of the American Chemical Society . 129 (48): 14872–14874. doi:10.1021/ja077569l. PMID 17997560.