
Corvinus University of Budapest is a private research university in Budapest, Hungary. The university currently has an enrolment of approximately 9,600 students, with a primary focus on business administration, economics, and social sciences, operating in Budapest and Székesfehérvár since 1948. Corvinus University accepts students at six faculties and offer courses leading to degrees at the bachelor, master and doctoral level in specialisations taught in Hungarian, English, French or German.

Kőbánya is the 10th district of Budapest and one of the largest by territory. It is located in southeast Pest, easily accessible from the downtown by Metro 3, whose terminus is named Kőbánya-Kispest.

Gyöngyös is a town in Heves county in Hungary, 80 km (50 mi) east of Budapest. Situated at the foot of the Sár-hegy and Mátra mountains, it is the home of numerous food production plants, including milk production and sausage factories. It is also the home of many vineyards on the slopes of the Sárhegy.
A biopharmaceutical, also known as a biological medical product, or biologic, is any pharmaceutical drug product manufactured in, extracted from, or semisynthesized from biological sources. Different from totally synthesized pharmaceuticals, they include vaccines, whole blood, blood components, allergenics, somatic cells, gene therapies, tissues, recombinant therapeutic protein, and living medicines used in cell therapy. Biologics can be composed of sugars, proteins, nucleic acids, or complex combinations of these substances, or may be living cells or tissues. They are isolated from living sources—human, animal, plant, fungal, or microbial. They can be used in both human and animal medicine.

Dorog is a small town in Komárom-Esztergom County, Hungary. It lies 38 km (24 mi) north-west from the center of Budapest.

Aceclofenac is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) analog of diclofenac. It is used for the relief of pain and inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis and ankylosing spondylitis.

Stada Arzneimittel AG is a pharmaceutical company based in Bad Vilbel, Germany which specializes on a three-pillar strategy consisting of consumer healthcare products, generics and specialty pharma. Worldwide, STADA Arzneimittel AG sells its products in approximately 120 countries. In 2022, revenue totaled €3.79 billion.
Christopher William Long was a British diplomat. Following his retirement in 1998, Long served as director of the Oxford University Foreign Service Programme from 1999 to 2003.
Repros Therapeutics Inc. (Nasdaq: RPRX), was a US-based development stage biopharmaceutical company headquartered in The Woodlands, Texas. Founded in 1987 as Zonagen, it focused on the development of oral small molecule drugs to address major unmet medical needs in male and female health. Joseph S. Podolski was the CEO of this company.
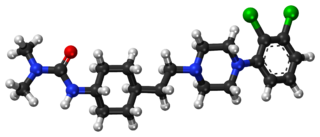
Cariprazine, sold under the brand name Vraylar among others, is an atypical antipsychotic developed by Gedeon Richter, which is used in the treatment of schizophrenia, bipolar mania, bipolar depression, and major depressive disorder. It acts primarily as a D3 and D2 receptor partial agonist, with a preference for the D3 receptor. Cariprazine is also a partial agonist at the serotonin 5-HT1A receptor and acts as an antagonist at 5-HT2B and 5-HT2A receptors, with high selectivity for the D3 receptor. It is taken by mouth.
AbbVie Inc. is an American pharmaceutical company headquartered in North Chicago, Illinois. It is ranked sixth on the list of largest biomedical companies by revenue. In 2023, the company's seat in Forbes Global 2000 was 74. The company's primary product is Humira (adalimumab), administered via injection. It is approved to treat autoimmune diseases including rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn's disease, plaque psoriasis, and ulcerative colitis.

Amneal Pharmaceuticals, Inc. is an American publicly traded generics and specialty pharmaceutical company. The company is headquartered in Bridgewater, New Jersey.
CIG Pannonia Life Insurance Plc. is a Hungarian multinational financial services company headquartered in Budapest. Its core business and focus is life and non-life insurance. At present, CIG Pannonia is engaged in the life insurance business in Hungary, Romania and Slovakia.
Allergan plc is an American, Irish-domiciled pharmaceutical company that acquires, develops, manufactures and markets brand name drugs and medical devices in the areas of medical aesthetics, eye care, central nervous system, and gastroenterology. The company is the maker of Botox.

Gedeon Richter was a Hungarian pharmacist, founder of Gedeon Richter plc and a pioneer of the modern Hungarian pharmaceutical industry.
Ernest Loumaye is a Belgian entrepreneur known for his works in the women's health care industry. He is the co-founder and CEO of ObsEva, a clinical-stage biopharmaceutical company focused on the clinical development and commercialization of novel therapeutics for severe medical conditions relating to women’s reproductive and pregnancy health.

János Csák is a Hungarian corporate leader, honorary professor of management, who has been the Minister of Culture and Innovation since 24 May 2022. Formerly, he served as Ambassador of Hungary to the United Kingdom between 2011 and 2014.
Peter Grootenhuis was a Dutch-American Medicinal Chemist. Grootenhuis was the Project Leader and Co-Inventor of Ivacaftor (VX-770), the first CFTR potentiator FDA approved drug to treat the underlying cause of Cystic Fibrosis (CF) in patients with certain mutations in the Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator (CFTR) gene, who account for 4-5% of CF cases. Grootenhuis also led the Vertex team to subsequent discovery of Orkambi, the combination of Ivacaftor and Lumacaftor(VX-809), approved to treat CF in people with two copies of the F508del mutation. Most recently, Grootenhuis's team discovered Tezacaftor (VX-661) and Elexacaftor (VX-445), which in combination with Ivacaftor are the components of Trikafta, a drug approved by the FDA in 2019 to treat CF in more than 90% of CF patients. For Grootenhuis’ contributions to the discovery of these compounds, he was awarded the 2018 IUPAC Richter Prize, the American Chemical Society’s 2013 Heroes of Chemistry Award, and inducted into the American Chemical Society Division of Medicinal Chemistry Hall of Fame. Grootenhuis has contributed to the discovery of over 11 clinical candidates, co-authored more than 100 peer reviewed papers and is inventor of 65 + U.S Patents, and more than 50 EU Patents.

Baron William de Gelsey of Gelse and Beliscse, internationally known as William de Gelsey, was a British banker and economist of Hungarian origin. He was chief adviser of the Board of Directors of UniCredit CAIB Securities and chairman of the board of directors at the pharmaceutical company Richter Gedeon Nyrt.

The Faculty of Science of Eötvös Loránd University was founded in 1949 and it is located in Lágymányos Campus, Újbuda, Budapest, Hungary.















