Project Mercury was the first human spaceflight program of the United States, running from 1958 through 1963. An early highlight of the Space Race, its goal was to put a man into Earth orbit and return him safely, ideally before the Soviet Union. Taken over from the US Air Force by the newly created civilian space agency NASA, it conducted 20 uncrewed developmental flights, and six successful flights by astronauts. The program, which took its name from Roman mythology, cost $2.68 billion. The astronauts were collectively known as the "Mercury Seven", and each spacecraft was given a name ending with a "7" by its pilot.

Skylab was the United States' first space station, launched by NASA, occupied for about 24 weeks between May 1973 and February 1974. It was operated by three trios of astronaut crews: Skylab 2, Skylab 3, and Skylab 4. Operations included an orbital workshop, a solar observatory, Earth observation and hundreds of experiments. Skylab's orbit eventually decayed and it disintegrated in the atmosphere on July 11, 1979, scattering debris across the Indian Ocean and Western Australia.

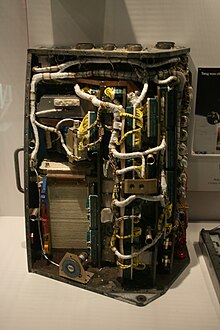
The Apollo Guidance Computer (AGC) was a digital computer produced for the Apollo program that was installed on board each Apollo command module (CM) and Apollo Lunar Module (LM). The AGC provided computation and electronic interfaces for guidance, navigation, and control of the spacecraft. The AGC was the first computer based on silicon integrated circuits. The computer's performance was comparable to the first generation of home computers from the late 1970s, such as the Apple II, TRS-80, and Commodore PET.

Gemini 3 was the first crewed mission in NASA's Project Gemini and was the first time two American astronauts flew together into space. On March 23, 1965, astronauts Gus Grissom and John Young flew three low Earth orbits in their spacecraft, which they nicknamed Molly Brown. It was the first U.S. mission in which the crew fired thrusters to change the size and shape of their orbit, a key test of spacecraft maneuverability vital for planned flights to the Moon. It was also the final crewed flight controlled from Cape Kennedy Air Force Station in Florida, before mission control functions were moved to a new control center at the newly opened Manned Spacecraft Center in Houston, Texas.

Mercury-Atlas 6 (MA-6) was the first crewed American orbital spaceflight, which took place on February 20, 1962. Piloted by astronaut John Glenn and operated by NASA as part of Project Mercury, it was the fifth human spaceflight, preceded by Soviet orbital flights Vostok 1 and 2 and American sub-orbital flights Mercury-Redstone 3 and 4.
MIL-STD-1750A or 1750A is the formal definition of a 16-bit computer instruction set architecture (ISA), including both required and optional components, as described by the military standard document MIL-STD-1750A (1980). Since August 1996, it has been inactive for new designs.

Gemini 4 was the second crewed spaceflight in NASA's Project Gemini, occurring in June 1965. It was the tenth crewed American spaceflight. Astronauts James McDivitt and Ed White circled the Earth 66 times in four days, making it the first US flight to approach the five-day flight of the Soviet Vostok 5. The highlight of the mission was the first space walk by an American, during which White floated free outside the spacecraft, tethered to it, for approximately 23 minutes.

Gemini 5 was a 1965 crewed spaceflight in NASA's Project Gemini. It was the third crewed Gemini flight, the eleventh crewed American spaceflight, and the nineteenth human spaceflight of all time. It was also the first time an American crewed space mission held the world record for duration, set on August 26, 1965, by breaking the Soviet Union's previous record set by Vostok 5 in 1963. This record might have been one day longer; however, Gemini V was cut short, due to the approach of Hurricane Betsy.

Gemini 7 was a 1965 crewed spaceflight in NASA's Gemini program. It was the fourth crewed Gemini flight, the twelfth crewed American spaceflight, and the twenty-first crewed spaceflight including Soviet flights and X-15 flights above the Kármán line. The crew of Frank Borman and Jim Lovell spent nearly 14 days in space, making a total of 206 orbits. Their spacecraft was the passive target for the first crewed space rendezvous performed by the crew of Gemini 6A.
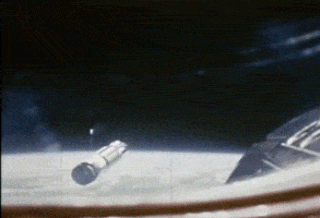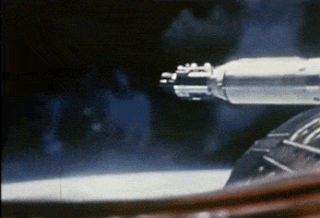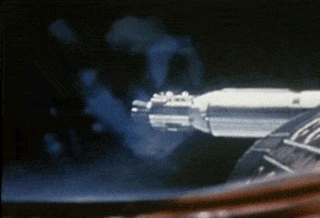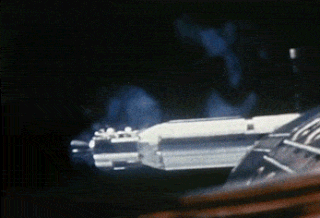
Gemini 8 was the sixth crewed spaceflight in NASA's Gemini program. It was launched on March 16, 1966, and was the 14th crewed American flight and the 22nd crewed spaceflight overall. The mission conducted the first docking of two spacecraft in orbit, but also suffered the first critical in-space system failure of a U.S. spacecraft which threatened the lives of the astronauts and required an immediate abort of the mission. The crew returned to Earth safely.

Gemini 11 was the ninth crewed spaceflight mission of NASA's Project Gemini, which flew from September 12 to 15, 1966. It was the 17th crewed American flight and the 25th spaceflight to that time. Astronauts Charles "Pete" Conrad Jr. and Richard F. Gordon Jr. performed the first direct-ascent rendezvous with an Agena Target Vehicle, docking with it 1 hour 34 minutes after launch; used the Agena rocket engine to achieve a record high-apogee Earth orbit; and created a small amount of artificial gravity by spinning the two spacecraft connected by a tether. Gordon also performed two extra-vehicular activities for a total of 2 hours 41 minutes.

Gemini 12 was a 1966 crewed spaceflight in NASA's Project Gemini. It was the 10th and final crewed Gemini flight, the 18th crewed American spaceflight, and the 26th spaceflight of all time, including X-15 flights over 100 kilometers (54 nmi). Commanded by Gemini VII veteran James A. Lovell, the flight featured three periods of extravehicular activity (EVA) by rookie Edwin "Buzz" Aldrin, lasting a total of 5 hours and 30 minutes. It also achieved the fifth rendezvous and fourth docking with an Agena target vehicle.
A service module is a component of a crewed space capsule containing a variety of support systems used for spacecraft operations. Usually located in the uninhabited area of the spacecraft, the service module serves a storehouse of critical subsystems and supplies for the mission such as electrical systems, environmental control, and propellant tanks. The service module is jettisoned upon the completion of the mission, and usually burns up during atmospheric reentry.

The IBM System/4 Pi is a family of avionics computers used, in various versions, on the F-15 Eagle fighter, E-3 Sentry AWACS, Harpoon Missile, NASA's Skylab, MOL, and the Space Shuttle, as well as other aircraft. Development began in 1965, deliveries in 1967.

Project Gemini was the second United States human spaceflight program to fly. Conducted after the first American crewed space program, Project Mercury, while the Apollo program was still in early development, Gemini was conceived in 1961 and concluded in 1966. The Gemini spacecraft carried a two-astronaut crew. Ten Gemini crews and 16 individual astronauts flew low Earth orbit (LEO) missions during 1965 and 1966.

A space capsule is a spacecraft designed to transport cargo, scientific experiments, and/or astronauts to and from space. Capsules are distinguished from other spacecraft by the ability to survive reentry and return a payload to the Earth's surface from orbit or sub-orbit, and are distinguished from other types of recoverable spacecraft by their blunt shape, not having wings and often containing little fuel other than what is necessary for a safe return. Capsule-based crewed spacecraft such as Soyuz or Orion are often supported by a service or adapter module, and sometimes augmented with an extra module for extended space operations. Capsules make up the majority of crewed spacecraft designs, although one crewed spaceplane, the Space Shuttle, has flown in orbit.

Flight controllers are personnel who aid space flight by working in such Mission Control Centers as NASA's Mission Control Center or ESA's European Space Operations Centre. Flight controllers work at computer consoles and use telemetry to monitor various technical aspects of a space mission in real-time. Each controller is an expert in a specific area and constantly communicates with additional experts in the "back room". The flight director, who leads the flight controllers, monitors the activities of a team of flight controllers, and has overall responsibility for success and safety.

The Launch Vehicle Digital Computer (LVDC) was a computer that provided the autopilot for the Saturn V rocket from launch, through Earth orbit insertion, and the trans-lunar injection burn that would send the Apollo spacecraft to the Moon. Designed and manufactured by IBM's Electronics Systems Center in Owego, New York, it was one of the major components of the Instrument Unit, fitted to the S-IVB stage of the Saturn V and Saturn IB rockets. The LVDC also supported pre- and post-launch checkout of the Saturn hardware. It was used in conjunction with the Launch Vehicle Data Adaptor (LVDA) which performed signal conditioning from the sensor inputs to the computer from the launch vehicle.

The Apollo Abort Guidance System was a backup computer system providing an abort capability in the event of failure of the Lunar Module's primary guidance system during descent, ascent or rendezvous. As an abort system, it did not support guidance for a lunar landing.

Globus IMP instruments were spacecraft navigation instruments used in Soviet and Russian crewed spacecraft. The IMP acronym stems from the Russian expression Indicator of position in flight, but the instrument is informally referred to as the Globus. It displays the nadir of the spacecraft on a rotating terrestrial globe. It functions as an onboard, autonomous indicator of the spacecraft's location relative to Earth coordinates. An electro-mechanical device in the tradition of complex post-World War II clocks such as master clocks, the Globus IMP instrument incorporates hundreds of mechanical components common to horology. This instrument is a mechanical computer for navigation akin to the Norden bombsight. It mechanically computes complex functions and displays its output through mechanical displacements of the globe and other indicator components. It also modulates electric signals from other instruments.