
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention of such infections. They may either kill or inhibit the growth of bacteria. A limited number of antibiotics also possess antiprotozoal activity. Antibiotics are not effective against viruses such as the common cold or influenza; drugs which inhibit growth of viruses are termed antiviral drugs or antivirals rather than antibiotics. They are also not effective against fungi; drugs which inhibit growth of fungi are called antifungal drugs.

Liquorice or licorice is the common name of Glycyrrhiza glabra, a flowering plant of the bean family Fabaceae, from the root of which a sweet, aromatic flavouring can be extracted.

Glycyrrhiza is a genus of about 20 accepted species in the legume family (Fabaceae), with a subcosmopolitan distribution in Asia, Australia, Europe, and the Americas.

Glycyrrhiza uralensis, also known as Chinese liquorice, is a flowering plant native to Asia. It is used as a sweetener and in traditional Chinese medicine.
Shennong Bencaojing is a Chinese book on agriculture and medicinal plants, traditionally attributed to Shennong. Researchers believe the text is a compilation of oral traditions, written between about 206 BC and 220 AD. The original text no longer exists, but is said to have been composed of three volumes containing 365 entries on medicaments and their description.

Ononin is an isoflavone glycoside, the 7-O-β-D-glucopyranoside of formononetin, which in turn is the 4'-O-methoxy derivative of the parent isoflavone daidzein.

Hyperoside is a chemical compound. It is the 3-O-galactoside of quercetin.
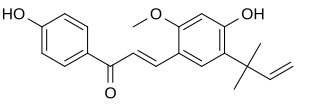
Licochalcone A is a chalconoid, a type of natural phenol. It can be isolated from the root of Glycyrrhiza glabra (liquorice) or Glycyrrhiza inflata. It shows antimalarial, anticancer, antibacterial and antiviral properties in vitro.

Pterocarpans are derivatives of isoflavonoids found in the family Fabaceae. It is a group of compounds which can be described as benzo-pyrano-furano-benzenes which can be formed by coupling of the B ring to the 4-one position.
Glycyrrhiza inflata is a plant species in the genus Glycyrrhiza from China, with common name Chinese licorice. A related species, G. uralensis, however, is more likely the licorice species one finds in traditional Chinese medicine.

Glabridin is a chemical compound that is found in the root extract of licorice. Glabridin is an isoflavane, a type of isoflavonoid. This product is part of a larger family of plant-derived molecules, the natural phenols. Glabridin effectively inhibits platelet activation, so it might become therapeutic agent for thromboembolic disorders.
Lipase inhibitors are substances used to reduce the activity of lipases found in the intestine. Lipases are secreted by the pancreas when fat is present. The primary role of lipase inhibitors is to decrease the gastrointestinal absorption of fats. Fats then tend to be excreted in feces rather than being absorbed to be used as a source of caloric energy, and this can result in weight loss in individuals. These inhibitors could be used for the treatment of obesity, which can subsequently lead to Type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular diseases if not managed. An example of a lipase inhibitor is orlistat.

Liquiritigenin is a flavanone that was isolated from Glycyrrhiza uralensis, and is found in a variety of plants of the Glycyrrhiza genus, including Glycyrrhiza glabra (licorice). It is an estrogenic compound which acts as a selective agonist of the ERβ subtype of the estrogen receptor (ER), though it is also reported to act as an ERα partial agonist at sufficient concentrations. It also has a choleretic effect.

Liquiritin is the 4'-O-glucoside of the flavanone liquiritigenin. Liquiritin is one of flavone compounds derived from licorice.
Liquorice or licorice is the root of Glycyrrhiza glabra from which a somewhat sweet flavor can be extracted.

Mesir Macunu is a traditional Turkish sweet associated with the city of Manisa. Earlier versions of Mesir macunu were not sweet, but rather spicy in flavor.
Novosphingobium endophyticum is a Gram-negative, rod-shaped and aerobic bacterium from the genus Novosphingobium which has been isolated from the roots of the plant Glycyrrhiza uralensis from Yuli County in China.
Brucella endophytica is a Gram-negative, aerobic, rod-shaped and bacteria from the genus of Brucella which has been isolated from the roots of the plant Glycyrrhiza uralensis from Yuli County in China.
A retrochalcone is a chalcone-like compound in which the normally present hydroxy groups at the 2' and 6' positions are missing. The retrochalcone structure has a propenal bridge connected to two benzene rings at each end. The ring closest to the oxygen, is labelled with primed numbers, normally with a hydroxy group at the 4' position. This is the A ring. The ring closest to the double bond is numbered with simple digits starting from 1 at the bridge connection. This is the B ring. There is usually a hydroxy group at the 4 position. The retrochalcones are found naturally where they are derivatives of flavones. Retrochalcones can be classed as minor flavonoids.
Pseudoclavibacter endophyticus is a Gram-positive, aerobic, rod-shaped and non-motile bacterium from the genus Pseudoclavibacter which has been isolated from the roots of the plant Glycyrrhiza uralensis from Yili County in China.












