Related Research Articles
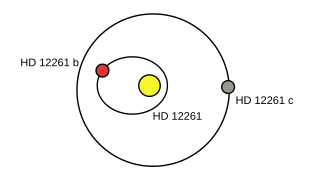
HD 12661 is a G-type main sequence star in the northern constellation of Aries. The star is slightly larger and more massive than the Sun, with an estimated age of seven billion years. It has two known extrasolar planets.
HD 217107 is a yellow subgiant star approximately 65 light-years away from Earth in the constellation of Pisces. Its mass is very similar to the Sun's, although it is considerably older. Two planets have been discovered orbiting the star: one is extremely close and completes an orbit every seven days, while the other is much more distant, taking fourteen years to complete an orbit.
HD 38529 is a binary star approximately 138 light-years away in the constellation of Orion.
HD 217107 b is an extrasolar planet approximately 65 light-years away from Earth in the constellation of Pisces. The planet was discovered orbiting the star HD 217107 approximately every seven days, classifying the planet as a hot Jupiter. Because of the planet's somewhat eccentric orbit, scientists were able to confirm another planet within the system.

HD 217107 c is an extrasolar planet approximately 64 light-years away from Earth in the constellation of Pisces. The planet was the second planet to be discovered orbiting the star HD 217107. HD 217107 c's existence was hypothesized in 1998 due to the eccentricity of the inner planet's orbit and confirmed in 2005 when radial velocity studies of the star indicated another, more distant and massive companion orbiting the star. The planet has an eccentric orbit lasting on order of a decade.

HD 12661 b is a giant exoplanet two and a half times the mass of Jupiter orbiting around the star HD 12661.
HD 11964 c is an extrasolar planet approximately 110 light-years away in the constellation of Cetus. The planet was discovered in a close-orbit around the yellow subgiant star HD 11964. The planet has a minimum mass 35 times the mass of Earth and is located in a mildly eccentric orbit which takes almost 38 days to complete. HD 11964 c was a possible planet discovered on the same day as HD 11964 b in 2005. HD 11964 c was first proposed in a paper published in 2007, and finally confirmed with new data presented in a review of multi-planet systems which appeared on the arXiv preprint website in 2008.
HD 11964 b is an extrasolar planet, a gas giant like Jupiter approximately 110 light-years away in the constellation of Cetus. The planet orbits the yellow subgiant star HD 11964 in a nearly-circular orbit, taking over 5 years to complete a revolution around the star at a distance of 3.34 astronomical units.
HD 92788 is a star in the equatorial constellation of Sextans. It has a yellow hue but is too dim to be visible to the naked eye, having an apparent visual magnitude of 7.31. The star is located at a distance of 113 light years from the Sun based on parallax, but is drifting closer with a radial velocity of −4.5 km/s. Two planets have been found in orbit around the star.
HD 142 b is a jovian exoplanet approximately 85.5 light years away in the constellation of Phoenix. This planet was discovered in 2001 by the Anglo-Australian Planet Search team.
HD 4113 b is a jovian planet located approximately 137 light-years away in the constellation of Sculptor, orbiting the star HD 4113. This planet has a very eccentric orbit with a 527-day period at 1.28 AU from the parent star. At periastron, the distance is 0.124 AU and at apastron, the distance is 2.44 AU.
HD 52265 b is a gas giant exoplanet located approximately 98 light-years away in the constellation of Monoceros, orbiting the star HD 52265. The planet has a minimum mass slightly more than that of Jupiter. Mean distance between the planet and the star is half that of Earth from the Sun. It was discovered by both the California and Carnegie Planet Search team and the Geneva Extrasolar Planet Search team independently of each other. By studying the fluctuations of the brightness of a host star, the inclination of the stars equator was determined. This allowed to calculate its true mass, assuming that the planet orbits in the plane of the star's equator.
HD 167042 b is a gas giant extrasolar planet located approximately 163 light-years away in the constellation of Draco, orbiting the star HD 167042. The mass 1.7 MJ is only minimum since the inclination of the orbital plane is unknown. As it is typical for most known extrasolar planets, it orbits less than 3 AU from the parent star, hence taking less than 2,000 days to revolve. For this planet, it orbits at 1.30 AU and taking 413 days to revolve around the star. Unlike most exoplanets, the eccentricity of the orbit is low, only 3%.
HD 222582 b is an extrasolar planet that is 8.37 times the mass of Jupiter orbiting the star HD 222582. The orbital period is 572 days and orbits at a semimajor axis of 1.35 AU in one of the most eccentric orbits of any known planets.
HD 38529 b is an extrasolar planet approximately 138 light years away in the constellation of Orion. This planet was discovered in 2000. Because of its mass it is likely a gas giant.
HD 89307 b is an exoplanet orbiting the star HD 89307 located approximately 104 light-years away in the constellation of Leo. The planet takes roughly 2164 days or 5.9 years to orbit its star. The planet's minimum mass is 1.92 MJ; initially, the true mass could not be determined since the inclination was unknown. As is common for many long-period exoplanets, the eccentricity is greater than any planets in the Solar System, orbiting at an average distance of 3.28 AU. The speed of the wobble caused by the planet's gravity is 31 meters per second. The average orbital velocity is 16.6 m/s. In 2023, the inclination and true mass of HD 89307 b were determined via astrometry.
HD 213240 b is an extrasolar planet located approximately 133 light-years from the Solar System in the constellation of Grus. It is a gas giant orbiting the G-type star HD 213240.
HD 40307 b is an extrasolar planet orbiting the star HD 40307, located 42 light-years away in the direction of the southern constellation Pictor. The planet was discovered by the radial velocity method, using the European Southern Observatory's HARPS apparatus, in June 2008. It is the second smallest of the planets orbiting the star, after HD 40307 e. The planet is of interest as this star has relatively low metallicity, supporting a hypothesis that different metallicities in protostars determine what kind of planets they will form.

HAT-P-8b is an extrasolar planet located approximately 720 light years away in the constellation of Pegasus, orbiting the 10th magnitude star GSC 02757-01152. This planet was discovered by transit on December 5, 2008. Despite the designation as HAT-P-8b, it is the 11th planet discovered by the HATNet Project. The mass of the planet is 50% more than Jupiter while the radius is also 50% more than Jupiter. The mass of this planet is exact since the inclination of the orbit is known, typical for transiting planets. This is a so-called “hot Jupiter” because this Jupiter-like gas giant planet orbits in a really close torch orbit around the star, making this planet extremely hot. The distance from the star is roughly 20 times smaller than that of Earth from the Sun, which places the planet roughly 8 times closer to its star than Mercury is from the Sun. The “year” on this planet lasts only 3 days, 1 hour, 49 minutes, and 54 seconds, compared with Earth's 365 days, 6 hours, 9 minutes, and 10 seconds in a sidereal year.
HD 30562 b is an extrasolar planet which orbits the F-type main sequence star HD 30562, located approximately 85.4 light years away in the constellation Eridanus.
References
- ↑ Fischer, Debra A.; et al. (2001). "Planetary Companions to HD 12661, HD 92788, and HD 38529 and Variations in Keplerian Residuals of Extrasolar Planets". The Astrophysical Journal. 551 (2): 1107–1118. Bibcode:2001ApJ...551.1107F. doi: 10.1086/320224 .