
HMAS Melbourne (R21) was a Majestic-class light aircraft carrier operated by the Royal Australian Navy (RAN) from 1955 until 1982, and was the third and final conventional aircraft carrier to serve in the RAN. Melbourne was the only Commonwealth naval vessel to sink two friendly warships in peacetime collisions.

Empress of Australia was a ferry operated by the Australian National Line. Ordered in 1962 by the Australian National Line and launched by Cockatoo Docks & Engineering Company on 18 January 1964, Empress of Australia was the largest passenger ferry built in the world.

HMAS Jervis Bay was a wave piercing catamaran that operated in the Royal Australian Navy (RAN).

HSC Incat 045 is a fast ferry operated by Trasmapi. Launched in 1997, she was initially chartered out as a civilian ferry, then became the first large catamaran to enter military service when she was commissioned into the Royal Australian Navy as HMAS Jervis Bay (AKR 45) from 1999 to 2001.

MS Princess Seaways is a cruiseferry operated and owned by the Danish shipping company DFDS Seaways on a route connecting North Shields, England, to IJmuiden in the Netherlands. She was built in 1986 as Peter Pan by Seebeckwerft, Bremerhaven, Germany for TT-Line. Between 1993 and 2002, the ship was operated by TT-Line Company of Tasmania under the name Spirit of Tasmania a service across the Bass Strait. In 2002, the ship was sold to Fjord Line and renamed Fjord Norway for service from Denmark. In 2006, she was sold to DFDS Seaways and sailed as Princess of Norway before being given her current name in 2011.

Australian National Line (ANL) was a coastal shipping line established in by the Government of Australia in 1956. It was sold in 1998 to CMA CGM.

HMAS Banks was an Explorer class general-purpose vessel of the Royal Australian Navy (RAN), serving in a range of capacities from 1960 until 1995. She was named in honour of Sir Joseph Banks, the botanist aboard HM Bark Endeavour during the discovery of the eastern coast of Australia in 1770.

MS Princess of Tasmania was an Australian-built roll-on/roll-off passenger ship. She was built by the State Dockyard in Newcastle, New South Wales for the Australian National Line. Laid down on 15 November 1957, she was launched on 15 December 1958. As built, the ship had a tonnage value of 3,964 gross register tons (GRT), was 113.32 metres (371.8 ft) long, had a beam of 17.73 metres (58.2 ft), and a draught of 4.74 metres (15.6 ft). Two 9-cylinder Nydquist & Holm Polar M69TS diesels supplied 8,600 horsepower (6,400 kW) to the propellers, allowing a maximum speed of 17.75 knots. Up to 334 passengers and 142 vehicles could be carried. Princess of Tasmania was given the IMO number: 5284986. The ship was the first RO/RO passenger ship in the southern hemisphere, and at the time of launch, the largest vessel built in Australia.

The State Dockyard was a ship building and maintenance facility operated by the Government of New South Wales in Carrington, Newcastle, New South Wales, Australia between 1942 and 1987.

HMS Nairana was a passenger ferry that was requisitioned by the Royal Navy (RN) as a seaplane carrier in 1917. She was laid down in Scotland in 1914 as TSS Nairana for the Australian shipping line Huddart Parker, but construction was suspended after the outbreak of the First World War. Following resumption of work, the ship was launched in 1915, and converted to operate wheeled aircraft from her forward flying-off deck, as well as floatplanes that were lowered into the water. She saw service during the war with the Grand Fleet, and in 1918–19 supported the British intervention in the Russian Civil War.
HMAS Air Sprite was an air-sea rescue vessel operated by the Royal Australian Navy (RAN). She was an Australian-built version of the 63-foot (19 m) air-sea rescue vessels which the RAN operated during World War II, with the only difference being that she was fitted with a lattice mast instead of the tripod masts in the older ships. Air Sprite was ordered in 1958 and was built by Lars Halvorsen and Sons in Sydney. She was commissioned into the RAN on 15 June 1960 and was based at HMAS Creswell at Jervis Bay near the RAN Fleet Air Arm's base, HMAS Albatross.

HMAS Jeparit was an Australian National Line (ANL) bulk carrier which was operated by the Royal Australian Navy (RAN) between 1969 and 1972. She was launched in 1964 and transported supplies to Australian military forces in South Vietnam between 1966 and 1972 under both civil and military ownership. She returned to service with ANL in 1972, being sold in 1979 to a Greek shipping company and renamed Pleias. She continued in civilian service under several names before being broken up in 1993.

HMAS Doomba was a Royal Australian Navy (RAN) warship of World War II. Built for the Royal Navy around the end of World War I as the Hunt-class minesweeper HMS Wexford, the ship only saw two years of service before she was decommissioned in 1921 and sold to the Doomba Shipping Company. The vessel was renamed SS Doomba, converted into a passenger ship, and operated in the waters around Brisbane until 1939, when she was requisitioned by the RAN for wartime service. Serving first as an auxiliary minehunter, then an auxiliary anti-submarine vessel, HMAS Doomba was purchased outright by the RAN in 1940, and served until early 1946, when she was sold and converted into a linseed oil lighter. Doomba was scuttled off Dee Why, New South Wales in 1976.

MV Duntroon was a passenger motor ship built for the Melbourne Steamship Company, that saw military service as a troopship between 1942 and 1949. She was built by Swan, Hunter & Wigham Richardson, Walker, Newcastle upon Tyne, and entered service in 1939.

HMAS Goorangai was a 223-ton auxiliary minesweeper of the Royal Australian Navy (RAN). She was built in 1919 for the Government of New South Wales, then sold in 1926 to the fishing company Cam & Sons. The trawler was requisitioned for military service following the outbreak of World War II, converted into a minesweeper, and assigned to Melbourne. She was sunk in an accidental collision with MV Duntroon in 1940, becoming the RAN's first loss of World War II, and the first RAN surface ship to be lost in wartime.

Bass Strait Ferries have been the ships that have been used for regular transport across Bass Strait between Tasmania and Victoria in mainland Australia, as well as the various attempts to link Tasmania with Sydney. Historically, some regular shipping services in the twentieth century linked Sydney, Melbourne and Hobart with the Bass Strait ports: Launceston's various port locations, Devonport and Burnie. The distinction between coastal shipping and Bass Strait ferry has been blurred at times.
TRV Tuna (801) was one of three Torpedo Recovery Vessels operated by the Royal Australian Navy (RAN) and Defence Maritime Services (DMS). Ordered in 1969, the vessel, originally identified as TRV 253, was completed in 1970 and assigned to the torpedo firing range at Jervis Bay. The ship received a name and the pennant number "TRV 801" in 1983. In 1988, the three vessels were sold to DMS. Tuna was assigned to the naval base at HMAS Creswell in Jervis Bay. Tuna was active in DMS service as of 2007.
The Cockatoo Docks & Engineering Company was a ship building and maintenance company which operated the Cockatoo Island Dockyard on Cockatoo Island in Sydney, Australia between 1933 and 1992.

The Steam Yacht Ena is a steam yacht that was built in 1900 for Thomas Dibbs, the commodore of the Royal Sydney Yacht Squadron. It was used as his private vessel for entertaining guests on Sydney Harbour and Pittwater until the beginning of World War I. In 1917 the yacht was purchased by the Royal Australian Navy (RAN) and used as the auxiliary patrol vessel HMAS Sleuth in the waters around the Torres Strait and Thursday Island, before later being used as a training ship tender based in Sydney.
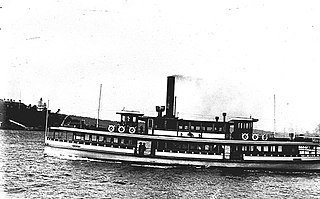
Lady Denman is a former Sydney Harbour ferry built in 1912 for the Balmain New Ferry Company. She was later run by Sydney Ferries Limited and its government successors. She is now preserved at the Jervis Bay Maritime Museum near her original build site in Huskisson, New South Wales, Australia.


















