External links
- Histamine+agonist at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- MeSH list of agents 82017442
| Types | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Classes |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| | This pharmacology-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
A histamine agonist is a drug which causes increased activity at one or more of the four histamine receptor subtypes.
H2: Betazole and Impromidine are examples of agonists used in diagnostics to increase histamine.
H3: Betahistine is a weak Histamine1 agonist and a very strong antagonist of the Histamine3 autoreceptor. Antagonizing H3 increases the overall activity of histamine.

A receptor antagonist is a type of receptor ligand or drug that blocks or dampens a biological response by binding to and blocking a receptor rather than activating it like an agonist. Antagonist drugs interfere in the natural operation of receptor proteins. They are sometimes called blockers; examples include alpha blockers, beta blockers, and calcium channel blockers. In pharmacology, antagonists have affinity but no efficacy for their cognate receptors, and binding will disrupt the interaction and inhibit the function of an agonist or inverse agonist at receptors. Antagonists mediate their effects by binding to the active site or to the allosteric site on a receptor, or they may interact at unique binding sites not normally involved in the biological regulation of the receptor's activity. Antagonist activity may be reversible or irreversible depending on the longevity of the antagonist–receptor complex, which, in turn, depends on the nature of antagonist–receptor binding. The majority of drug antagonists achieve their potency by competing with endogenous ligands or substrates at structurally defined binding sites on receptors.

Histamine H3 receptors are expressed in the central nervous system and to a lesser extent the peripheral nervous system, where they act as autoreceptors in presynaptic histaminergic neurons and control histamine turnover by feedback inhibition of histamine synthesis and release. The H3 receptor has also been shown to presynaptically inhibit the release of a number of other neurotransmitters (i.e. it acts as an inhibitory heteroreceptor) including, but probably not limited to dopamine, GABA, acetylcholine, noradrenaline, histamine and serotonin.

The histamine H4 receptor, like the other three histamine receptors, is a member of the G protein-coupled receptor superfamily that in humans is encoded by the HRH4 gene.

The H1 receptor is a histamine receptor belonging to the family of rhodopsin-like G-protein-coupled receptors. This receptor is activated by the biogenic amine histamine. It is expressed in smooth muscles, on vascular endothelial cells, in the heart, and in the central nervous system. The H1 receptor is linked to an intracellular G-protein (Gq) that activates phospholipase C and the inositol triphosphate (IP3) signalling pathway. Antihistamines, which act on this receptor, are used as anti-allergy drugs. The crystal structure of the receptor has been determined (shown on the right/below) and used to discover new histamine H1 receptor ligands in structure-based virtual screening studies.

H2 receptors are positively coupled to adenylate cyclase via Gs alpha subunit. It is a potent stimulant of cAMP production, which leads to activation of protein kinase A. PKA functions to phosphorylate certain proteins, affecting their activity. The drug betazole is an example of a histamine H2 receptor agonist.

ABT-239 is an H3-receptor inverse agonist developed by Abbott. It has stimulant and nootropic effects, and has been investigated as a treatment for ADHD, Alzheimer's disease, and schizophrenia. ABT-239 is more active at the human H3 receptor than comparable agents such as thioperamide, ciproxifan, and cipralisant. It was ultimately dropped from human trials after showing the dangerous cardiac side effect of QT prolongation, but is still widely used in animal research into H3 antagonists / inverse agonists.

Cipralisant (GT-2331, tentative trade name Perceptin) is an extremely potent histamine H3 receptor ligand originally developed by Gliatech. Cipralisant was initially classified as a selective H3 antagonist, but newer research (2005) suggests also agonist properties, i. e. functional selectivity. Cipralisant seemed to be well tolerated during early testing, entering Phase II trials for ADHD in 2000.

Ciproxifan is an extremely potent histamine H3 inverse agonist/antagonist.
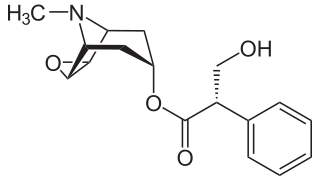
A muscarinic receptor antagonist (MRA) is a type of anticholinergic agent that blocks the activity of the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor. The muscarinic receptor is a protein involved in the transmission of signals through certain parts of the nervous system, and muscarinic receptor antagonists work to prevent this transmission from occurring. Notably, muscarinic antagonists reduce the activation of the parasympathetic nervous system. The normal function of the parasympathetic system is often summarised as "rest-and-digest", and includes slowing of the heart, an increased rate of digestion, narrowing of the airways, promotion of urination, and sexual arousal. Muscarinic antagonists counter this parasympathetic "rest-and-digest" response, and also work elsewhere in both the central and peripheral nervous systems.

Alpha-adrenergic agonists are a class of sympathomimetic agents that selectively stimulates alpha adrenergic receptors. The alpha-adrenergic receptor has two subclasses α1 and α2. Alpha 2 receptors are associated with sympatholytic properties. Alpha-adrenergic agonists have the opposite function of alpha blockers. Alpha adrenoreceptor ligands mimic the action of epinephrine and norepinephrine signaling in the heart, smooth muscle and central nervous system, with norepinephrine being the highest affinity. The activation of α1 stimulates the membrane bound enzyme phospholipase C, and activation of α2 inhibits the enzyme adenylate cyclase. Inactivation of adenylate cyclase in turn leads to the inactivation of the secondary messenger cyclic adenosine monophosphate and induces smooth muscle and blood vessel constriction.

Antihistamines are drugs which treat allergic rhinitis, common cold, influenza, and other allergies. Typically, people take antihistamines as an inexpensive, generic drug that can be bought without a prescription and provides relief from nasal congestion, sneezing, or hives caused by pollen, dust mites, or animal allergy with few side effects. Antihistamines are usually for short-term treatment. Chronic allergies increase the risk of health problems which antihistamines might not treat, including asthma, sinusitis, and lower respiratory tract infection. Consultation of a medical professional is recommended for those who intend to take antihistamines for longer-term use.
A serotonin antagonist, or serotonin receptor antagonist, is a drug used to inhibit the action of serotonin and serotonergic drugs at serotonin (5-HT) receptors.

Dimaprit is a histamine analog working as a selective H2 histamine receptor agonist.
An H3 receptor antagonist is a classification of drugs used to block the action of histamine at the H3 receptor.

A-349,821 is a potent and selective histamine H3 receptor antagonist (or possibly an inverse agonist). It has nootropic effects in animal studies, although there do not appear to be any plans for clinical development at present and it is currently only used in laboratory research.

VUF-5681 is a potent and selective histamine antagonist which binds selectively to the H3 subtype. However while VUF-5681 blocks the activity of more potent H3 agonists, recent studies suggest that it may have some weak partial agonist activity when administered by itself.

Proxyfan is a histamine H3 receptor ligand which is a "protean agonist", producing different effects ranging from full agonist, to antagonist, to inverse agonist in different tissues, depending on the level of constitutive activity of the histamine H3 receptor. This gives it a complex activity profile in vivo which has proven useful for scientific research.
Pitolisant, sold under the brand name Wakix among others, is a medication for the treatment of excessive daytime sleepiness in adults with narcolepsy. It is a histamine 3 (H3) receptor antagonist/inverse agonist. It represents the first commercially available medication in its class. Pitolisant enhances the activity of histaminergic neurons in the brain that function to improve a person's wakefulness.
UR-AK49 is a drug used in scientific research which acts as a potent antagonist for the Neuropeptide Y / Pancreatic polypeptide receptor Y4, and also as a partial agonist at the histamine receptors H1 and H2. UR-AK49 is a pure antagonist at Y4 with no partial agonist effects, and although it is only slightly selective for Y4 over the related Y1 and Y5 receptors, as the first non-peptide Y4 antagonist developed UR-AK49 is expected to be useful in the study of this receptor and its role in the body.