
A liquid-crystal display (LCD) is a flat-panel display or other electronically modulated optical device that uses the light-modulating properties of liquid crystals combined with polarizers. Liquid crystals do not emit light directly but instead use a backlight or reflector to produce images in color or monochrome.
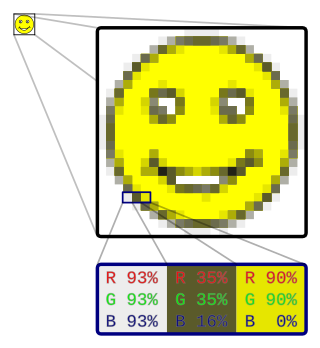
In computer graphics and digital photography, a raster graphic represents a two-dimensional picture as a rectangular matrix or grid of pixels, viewable via a computer display, paper, or other display medium. A raster is technically characterized by the width and height of the image in pixels and by the number of bits per pixel. Raster images are stored in image files with varying dissemination, production, generation, and acquisition formats.

Interlaced video is a technique for doubling the perceived frame rate of a video display without consuming extra bandwidth. The interlaced signal contains two fields of a video frame captured consecutively. This enhances motion perception to the viewer, and reduces flicker by taking advantage of the phi phenomenon.

Dots per inch is a measure of spatial printing, video or image scanner dot density, in particular the number of individual dots that can be placed in a line within the span of 1 inch (2.54 cm). Similarly, dots per centimetre refers to the number of individual dots that can be placed within a line of 1 centimetre (0.394 in).

An LCD projector is a type of video projector for displaying video, images or computer data on a screen or other flat surface. It is a modern equivalent of the slide projector or overhead projector. To display images, LCD projectors typically send light from a metal-halide lamp through a prism or series of dichroic filters that separates light to three polysilicon panels – one each for the red, green and blue components of the video signal. As polarized light passes through the panels, individual pixels can be opened to allow light to pass or closed to block the light. The combination of open and closed pixels can produce a wide range of colors and shades in the projected image.
The refresh rate, also known as vertical refresh rate or vertical scan rate in reference to terminology originating with the cathode-ray tubes (CRTs), is the number of times per second that a raster-based display device displays a new image. This is independent from frame rate, which describes how many images are stored or generated every second by the device driving the display. On CRT displays, higher refresh rates produce less flickering, thereby reducing eye strain. In other technologies such as liquid-crystal displays, the refresh rate affects only how often the image can potentially be updated.

The display resolution or display modes of a digital television, computer monitor, or other display device is the number of distinct pixels in each dimension that can be displayed. It can be an ambiguous term especially as the displayed resolution is controlled by different factors in cathode ray tube (CRT) displays, flat-panel displays and projection displays using fixed picture-element (pixel) arrays.
Pixels per inch (ppi) and pixels per centimetre are measurements of the pixel density of an electronic image device, such as a computer monitor or television display, or image digitizing device such as a camera or image scanner. Horizontal and vertical density are usually the same, as most devices have square pixels, but differ on devices that have non-square pixels. Pixel density is not the same as resolution — where the former describes the amount of detail on a physical surface or device, the latter describes the amount of pixel information regardless of its scale. Considered in another way, a pixel has no inherent size or unit, but when it is printed, displayed, or scanned, then the pixel has both a physical size (dimension) and a pixel density (ppi).
A thin-film-transistor liquid-crystal display is a type of liquid-crystal display that uses thin-film-transistor technology to improve image qualities such as addressability and contrast. A TFT LCD is an active matrix LCD, in contrast to passive matrix LCDs or simple, direct-driven LCDs with a few segments.
Dither is an intentionally applied form of noise used to randomize quantization error, preventing large-scale patterns such as color banding in images. Dither is routinely used in processing of both digital audio and video data, and is often one of the last stages of mastering audio to a CD.
Overscan is a behaviour in certain television sets in which part of the input picture is cut off by the visible bounds of the screen. It exists because cathode-ray tube (CRT) television sets from the 1930s to the early 2000s were highly variable in how the video image was positioned within the borders of the screen. It then became common practice to have video signals with black edges around the picture, which the television was meant to discard in this way.

A closed-circuit television camera is a type of surveillance camera that transmits video signals to a specific set of monitors or video recording devices, rather than broadcasting the video over public airwaves. The term "closed-circuit" indicates that the video feed is only accessible to a limited number of people or devices with authorized access. Cameras can be either analog or digital. Walter Bruch was the inventor of the CCTV camera.

The original ZX Spectrum computer produces a one bit per pixel, bitmapped colour graphics video output. A composite video signal is generated through an RF modulator, and was designed for use with contemporary 1980s television sets.

A parallax barrier is a device placed in front of an image source, such as a liquid crystal display, to allow it to show a stereoscopic or multiscopic image without the need for the viewer to wear 3D glasses. Placed in front of the normal LCD, it consists of an opaque layer with a series of precisely spaced slits, allowing each eye to see a different set of pixels, so creating a sense of depth through parallax in an effect similar to what lenticular printing produces for printed products and lenticular lenses for other displays. A disadvantage of the method in its simplest form is that the viewer must be positioned in a well-defined spot to experience the 3D effect. However, recent versions of this technology have addressed this issue by using face-tracking to adjust the relative positions of the pixels and barrier slits according to the location of the user's eyes, allowing the user to experience the 3D from a wide range of positions. Another disadvantage is that the horizontal pixel count viewable by each eye is halved, reducing the overall horizontal resolution of the image.

Microsoft PixelSense was an interactive surface computing platform that allowed one or more people to use and touch real-world objects, and share digital content at the same time. The PixelSense platform consists of software and hardware products that combine vision based multitouch PC hardware, 360-degree multiuser application design, and Windows software to create a natural user interface (NUI).

Optimum HDTV viewing distance is the distance that provides the viewer with the optimum immersive visual HDTV experience.
"21:9" is a consumer electronics (CE) marketing term to describe the ultrawide aspect ratio of 64:27, designed to show films recorded in CinemaScope and equivalent modern anamorphic formats. The main benefit of this screen aspect ratio is a constant display height when displaying other content with a lesser aspect ratio.
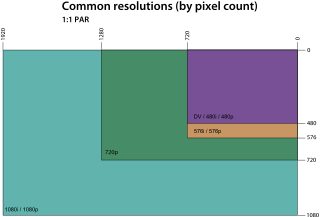
A display resolution standard is a commonly used width and height dimension of an electronic visual display device, measured in pixels. This information is used for electronic devices such as a computer monitor. Certain combinations of width and height are standardized and typically given a name and an initialism which is descriptive of its dimensions.
This glossary defines terms that are used in the document "Defining Video Quality Requirements: A Guide for Public Safety", developed by the Video Quality in Public Safety (VQIPS) Working Group. It contains terminology and explanations of concepts relevant to the video industry. The purpose of the glossary is to inform the reader of commonly used vocabulary terms in the video domain. This glossary was compiled from various industry sources.











