The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a method widely used to make millions to billions of copies of a specific DNA sample rapidly, allowing scientists to amplify a very small sample of DNA sufficiently to enable detailed study. PCR was invented in 1983 by American biochemist Kary Mullis at Cetus Corporation. Mullis and biochemist Michael Smith, who had developed other essential ways of manipulating DNA, were jointly awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1993.

The human genome is a complete set of nucleic acid sequences for humans, encoded as the DNA within each of the 24 distinct chromosomes in the cell nucleus. A small DNA molecule is found within individual mitochondria. These are usually treated separately as the nuclear genome and the mitochondrial genome. Human genomes include both protein-coding DNA sequences and various types of DNA that does not encode proteins. The latter is a diverse category that includes DNA coding for non-translated RNA, such as that for ribosomal RNA, transfer RNA, ribozymes, small nuclear RNAs, and several types of regulatory RNAs. It also includes promoters and their associated gene-regulatory elements, DNA playing structural and replicatory roles, such as scaffolding regions, telomeres, centromeres, and origins of replication, plus large numbers of transposable elements, inserted viral DNA, non-functional pseudogenes and simple, highly repetitive sequences. Introns make up a large percentage of non-coding DNA. Some of this non-coding DNA is non-functional junk DNA, such as pseudogenes, but there is no firm consensus on the total amount of junk DNA.
A microsatellite is a tract of repetitive DNA in which certain DNA motifs are repeated, typically 5–50 times. Microsatellites occur at thousands of locations within an organism's genome. They have a higher mutation rate than other areas of DNA leading to high genetic diversity. Microsatellites are often referred to as short tandem repeats (STRs) by forensic geneticists and in genetic genealogy, or as simple sequence repeats (SSRs) by plant geneticists.
An inverted repeat is a single stranded sequence of nucleotides followed downstream by its reverse complement. The intervening sequence of nucleotides between the initial sequence and the reverse complement can be any length including zero. For example, 5'---TTACGnnnnnnCGTAA---3' is an inverted repeat sequence. When the intervening length is zero, the composite sequence is a palindromic sequence.

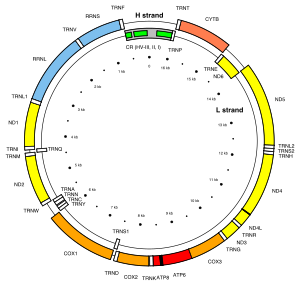
Mitochondrial DNA is the DNA located in the mitochondria organelles in a eukaryotic cell that converts chemical energy from food into adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Mitochondrial DNA is a small portion of the DNA contained in a eukaryotic cell; most of the DNA is in the cell nucleus, and, in plants and algae, the DNA also is found in plastids, such as chloroplasts.
The coding region of a gene, also known as the coding DNA sequence (CDS), is the portion of a gene's DNA or RNA that codes for a protein. Studying the length, composition, regulation, splicing, structures, and functions of coding regions compared to non-coding regions over different species and time periods can provide a significant amount of important information regarding gene organization and evolution of prokaryotes and eukaryotes. This can further assist in mapping the human genome and developing gene therapy.
The ribosomal DNA consists of a group of ribosomal RNA encoding genes and related regulatory elements, and is widespread in similar configuration in all domains of life. The ribosomal DNA encodes the non-coding ribosomal RNA, integral structural elements in the assembly of ribosomes, its importance making it the most abundant section of RNA found in cells of eukaryotes. Additionally, these segments includes regulatory sections, such as a promotor specific to the RNA polymerase I, as well as both transcribed and non-transcribed spacer segments.
In genetics, a minisatellite is a tract of repetitive DNA in which certain DNA motifs are typically repeated two to several hundred times. Minisatellites occur at more than 1,000 locations in the human genome and they are notable for their high mutation rate and high diversity in the population. Minisatellites are prominent in the centromeres and telomeres of chromosomes, the latter protecting the chromosomes from damage. The name "satellite" refers to the early observation that centrifugation of genomic DNA in a test tube separates a prominent layer of bulk DNA from accompanying "satellite" layers of repetitive DNA. Minisatellites are small sequences of DNA that do not encode proteins but appear throughout the genome hundreds of times, with many repeated copies lying next to each other.
In molecular biology, an amplicon is a piece of DNA or RNA that is the source and/or product of amplification or replication events. It can be formed artificially, using various methods including polymerase chain reactions (PCR) or ligase chain reactions (LCR), or naturally through gene duplication. In this context, amplification refers to the production of one or more copies of a genetic fragment or target sequence, specifically the amplicon. As it refers to the product of an amplification reaction, amplicon is used interchangeably with common laboratory terms, such as "PCR product."
Genetics, a discipline of biology, is the science of heredity and variation in living organisms.
Slipped strand mispairing is a mutation process which occurs during DNA replication. It involves denaturation and displacement of the DNA strands, resulting in mispairing of the complementary bases. Slipped strand mispairing is one explanation for the origin and evolution of repetitive DNA sequences.
A trinucleotide repeat expansion, also known as a triplet repeat expansion, is the DNA mutation responsible for causing any type of disorder categorized as a trinucleotide repeat disorder. These are labelled in dynamical genetics as dynamic mutations. Triplet expansion is caused by slippage during DNA replication, also known as "copy choice" DNA replication. Due to the repetitive nature of the DNA sequence in these regions, 'loop out' structures may form during DNA replication while maintaining complementary base pairing between the parent strand and daughter strand being synthesized. If the loop out structure is formed from the sequence on the daughter strand this will result in an increase in the number of repeats. However, if the loop out structure is formed on the parent strand, a decrease in the number of repeats occurs. It appears that expansion of these repeats is more common than reduction. Generally, the larger the expansion the more likely they are to cause disease or increase the severity of disease. Other proposed mechanisms for expansion and reduction involve the interaction of RNA and DNA molecules.

Microsatellite instability (MSI) is the condition of genetic hypermutability that results from impaired DNA mismatch repair (MMR). The presence of MSI represents phenotypic evidence that MMR is not functioning normally.

16S ribosomal RNA is the RNA component of the 30S subunit of a prokaryotic ribosome. It binds to the Shine-Dalgarno sequence and provides most of the SSU structure.

Mitochondrially encoded 12S ribosomal RNA is the SSU rRNA of the mitochondrial ribosome. In humans, 12S is encoded by the MT-RNR1 gene and is 959 nucleotides long. MT-RNR1 is one of the 37 genes contained in animal mitochondria genomes. Their 2 rRNA, 22 tRNA and 13 mRNA genes are very useful in phylogenetic studies, in particular the 12S and 16S rRNAs. The 12S rRNA is the mitochondrial homologue of the prokaryotic 16S and eukaryotic nuclear 18S ribosomal RNAs. Mutations in the MT-RNR1 gene may be associated with hearing loss. The rRNA gene also encodes a peptide MOTS-c, also known as Mitochondrial-derived peptide MOTS-c or Mitochondrial open reading frame of the 12S rRNA-c.

In molecular biology, a framework region is a subdivision of the variable region (Fab) of the antibody. The variable region is composed of seven amino acid regions, four of which are framework regions and three of which are hypervariable regions. The framework region makes up about 85% of the variable region. Located on the tips of the Y-shaped molecule, the framework regions are responsible for acting as a scaffold for the complementarity determining regions (CDR), also referred to as hypervariable regions, of the Fab. These CDRs are in direct contact with the antigen and are involved in binding antigen, while the framework regions support the binding of the CDR to the antigen and aid in maintaining the overall structure of the four variable domains on the antibody. To increase its stability, the framework region has less variability in its amino acid sequences compared to the CDR.
The human mitochondrial molecular clock is the rate at which mutations have been accumulating in the mitochondrial genome of hominids during the course of human evolution. The archeological record of human activity from early periods in human prehistory is relatively limited and its interpretation has been controversial. Because of the uncertainties from the archeological record, scientists have turned to molecular dating techniques in order to refine the timeline of human evolution. A major goal of scientists in the field is to develop an accurate hominid mitochondrial molecular clock which could then be used to confidently date events that occurred during the course of human evolution.

The mtDNA control region is an area of the mitochondrial genome which is non-coding DNA. This region controls RNA and DNA synthesis. It is the most polymorphic region of the human mtDNA genome, with polymorphism concentrated in hypervariable regions. The average nucleotide diversity in these regions is 1.7%. Despite this variability, an RNA transcript from this region has a conserved secondary structure (pictured) which has been found to be under selective pressure. There are 12 other secondary structures in the human mtDNA control region with differing amounts of conservation.

An amplicon sequence variant (ASV) is any one of the inferred single DNA sequences recovered from a high-throughput analysis of marker genes. Because these analyses, also called "amplicon reads," are created following the removal of erroneous sequences generated during PCR and sequencing, using ASVs makes it possible to distinguish sequence variation by a single nucleotide change. The uses of ASVs include classifying groups of species based on DNA sequences, finding biological and environmental variation, and determining ecological patterns.
Reverse complement polymerase chain reaction (RC-PCR) is a modification of the polymerase chain reaction (PCR). It is primarily used to generate amplicon libraries for DNA sequencing by next generation sequencing (NGS). The technique permits both the amplification and the ability to append sequences or functional domains of choice independently to either end of the generated amplicons in a single closed tube reaction. RC-PCR was invented in 2013 by Daniel Ward and Christopher Mattocks at Salisbury NHS Foundation Trust, UK.