Akure is a city in south-western Nigeria. It is the capital and largest city of Ondo State. The city had a population of 403,000 as of the 2006 population census. It currently hosts a population of 774,000.

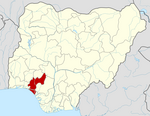
Ondo State is a state in southwestern Nigeria. It was created on 3 February 1976 from the former Western State. It borders Ekiti State to the north, Kogi State to the northeast, Edo State to the east, Delta State to the southeast, Ogun State to the southwest, Osun State to the northwest, and the Atlantic Ocean to the south. The state's capital is Akure, the former capital of the ancient Akure Kingdom. The State includes mangrove-swamp forest near the Bights of Benin.
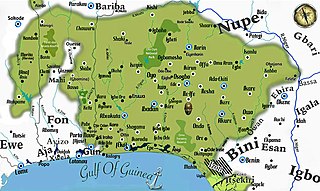
Yorubaland is the homeland and cultural region of the Yoruba people in West Africa. It spans the modern-day countries of Nigeria, Togo and Benin, and covers a total land area of 142,114 km2 or about 60% of the land area of Ghana. Of this land area, 106,016 km2 (74.6%) lies within Nigeria, 18.9% in Benin, and the remaining 6.5% is in Togo. Prior to European colonization, a portion of this area was known as Yoruba country. The geo-cultural space contains an estimated 55 million people, the majority of this population being ethnic Yoruba.
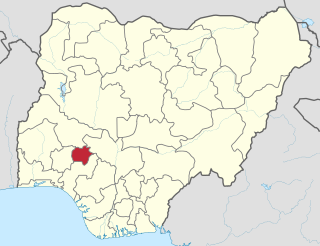
Ekiti State is a state in southwestern Nigeria, bordered to the north by Kwara State, to the northeast by Kogi State, to the south and southeast by Ondo State, and to the west by Osun State. Named for the Ekiti people—the Yoruba subgroup that make up the majority of the state's population—Ekiti State was formed from a part of Ondo State in 1996 and has its capital as the city of Ado-Ekiti.

Owo is a local government area in Ondo state, Nigeria. Between 1400 and 1600 CE, it was the capital of a Yoruba city-state. The local government area has a population of 222,262 based on 2006 population census.

Osun State, occasionally known as the State of Osun by the state government, is a state in southwestern Nigeria; bounded to the east by Ekiti and Ondo states, to the north by Kwara State, to the south by Ogun State and to the west by Oyo State. Named for the River Osun—a vital river which flows through the state—the state was formed from the southeast of Oyo State on 27 August 1991 and has its capital as the city of Osogbo.
Oba-Igbomina, is an ancient Igbomina town in northeastern Isin Local Government Area of Kwara State. It is one of the five related Yoruba towns named "Oba", the others being

Sclerophrys perreti is a species of toad in the family Bufonidae. It is endemic to the Idanre Hills in southwestern Nigeria. Sclerophrys perreti is one of the frogs declared as "Lost" in 2010. However, it was re-discovered at its type locality in 2013. Before that, it had not been seen—possibly—since 1970, and with certainty, since 1963. Common name Perret's toad has been coined for it.

The Roman Catholic Diocese of Ondo is a diocese located in the Ondo State in the Ecclesiastical province of Ibadan in Nigeria. The Cathedral and diocesan secretariat are located in Akure.

The Idanre Hill, or Oke Idanre is located in Idanre town in Ondo State of southwestern Nigeria.

Olusegun Rahman Mimiko ; born 3 October 1954), is a Nigerian doctor and politician, he was the senatorial candidate of the Zenith Labour Party for Ondo Central District in the 2019 Senate elections. He served as the 16th, and fifth civilian, Governor of Ondo State, Nigeria, from February 2009 to February 2017. The first two-term governor of Ondo state and the first Labour Party governor in Nigeria. Mimiko was previously a federal minister for housing and urban development, a secretary to the Ondo State Government, and a two-time Ondo State Commissioner for Health.
Idanre Forest Reserve is in Idanre local government area of the Nigerian state of Ondo, in the south-west part of the country. This International Union for Conservation of Nature designated nature reserve covers 561 square kilometres (217 sq mi).It is a lowland rainforest with an altitude of 10 to 400 meters.
Akure Forest Reserve is a protected area in southwest Nigeria, covering 66 km2 (25 sq mi).
Ipetu-Ijesa also called Ipetu-Aro Odo among its inhabitants is a town in Oriade local government area, in Osun State, Nigeria. It is located in the western part of Nigeria, about 40 km from Ile-Ife and 37 km from Akure. The people are of the Yoruba ethnic group. The title of the traditional king of Ipetu-Ijesa is Ajalaye of Ipetu-Ijesa. The present Oba(King) is His Royal Highness Oba Samson Adeleke Agunbiade Oke, Agunbiade III.
Oyin Akoko is a settlement in Akoko North-West Local government area of Ondo State, Nigeria. It lies 251 km southeast of Abuja, the Nigerian capital. The closest airport to Oyin Akoko is located at Akure 68 km to the north-west. The Yoruba language is spoken in the town.

Igbara-Oke, popularly referred to as Nodal Town, is an Ekiti town in Ondo State, Nigeria. It is the headquarters of Ifedore Local Government Council. The total population for the local government area was 176,372 as at 2006. Igbara-Oke is a Yoruba town and the inhabitants are largely engaged in agriculture. Igbara-Oke is a town that shares border with three states in Nigeria, Ondo, Osun and Ekiti states. Igbara-Oke is a tripatite town. An entry point into Ondo State when coming from either Osun or Ekiti State. A land of peace, unity, love and harmony. A land that is viable for industrial and infrastructural development. Igbara-Oke has Thirteen (13) Satellites towns and villages.
Cocoa production is important to the economy of Nigeria. Cocoa is the leading agricultural export of the country and Nigeria is currently the world's fourth largest producer of cocoa, after Ivory Coast, Indonesia and Ghana, and the third largest exporter, after Ivory Coast and Ghana. The crop was a major foreign exchange earner for Nigeria in the 1950s and 1960s and in 1970 the country was the second largest producer in the world but following investments in the oil sector in the 1970s and 1980s, Nigeria's share of world output declined. In 2010, cocoa production accounted for only 0.3% of agricultural GDP. Average cocoa beans production in Nigeria between 2000 and 2010 was 389,272 tonnes per year rising from 170,000 tonnes produced in 1999.

The Ekiti people are one of the largest historical subgroups of the larger Yoruba people of West Africa, located in Nigeria. They are classified as a Central Yoruba group, alongside the Ijesha, Igbomina, Yagba and Ifes. Ekiti State is populated exclusively by Ekiti people; however, it is but a segment of the historic territorial domain of Ekiti-speaking groups, which historically included towns in Ondo State such as Akure, Ilara-Mokin, Ijare, and Igbara-oke. Ogbagi, Irun, Ese, Oyin, Igasi, Afin and Eriti in the Akoko region, as well as some towns in Kwara State, are also culturally Ekiti, although belong in other states today.
Ilara-Mokin is located in a central part of Ifedore local government of Ondo State. Ilara-Mokin is about 12 km from Ondo state capital, and has Ipogun, Ipinsa, Ikota, Ibule-Soro and Ero as neighbouring towns.
Ode Usen, also known as Ufe kekere and Ode Awure is the name of a small town in Edo state, Nigeria. It also doubles as the name of a Yoruba subgroup consisting of culturally related villages situated between Ofosu in the west and Ogbese in the east. Usen is surrounded on all sides by smaller villages and farmsteads known in the local Yoruba dialect as Egunre. some of the villages under the authority of Usen include; Arere, Oladaro, Arekpa, Ogunweyin, Ogidigbo, Ilorin (Ulorin), Ukankan, Ajegunle, Obomen, Aghakpo, Leleji, Ofaran, Okeodo, Adeyanba. These villages were all founded by people from Usen and speak the same dialect of the Yoruba language. There are also other communities that speak the same dialect of the Yoruba language as Usen, but are not within its political auspices such as Igue Ogho between Ekiadolo and Usen.