In the human skull, the zygomatic bone, also called cheekbone or malar bone, is a paired irregular bone which articulates with the maxilla, the temporal bone, the sphenoid bone and the frontal bone. It is situated at the upper and lateral part of the face and forms the prominence of the cheek, part of the lateral wall and floor of the orbit, and parts of the temporal fossa and the infratemporal fossa. It presents a malar and a temporal surface; four processes, and four borders.

The external carotid artery is a major artery of the head and neck. It arises from the common carotid artery when it splits into the external and internal carotid artery. The external carotid artery supplies blood to the face, brain and neck.

In anatomy, the orbit is the cavity or socket/hole of the skull in which the eye and its appendages are situated. "Orbit" can refer to the bony socket, or it can also be used to imply the contents. In the adult human, the volume of the orbit is 30 millilitres, of which the eye occupies 6.5 ml. The orbital contents comprise the eye, the orbital and retrobulbar fascia, extraocular muscles, cranial nerves II, III, IV, V, and VI, blood vessels, fat, the lacrimal gland with its sac and duct, the eyelids, medial and lateral palpebral ligaments, cheek ligaments, the suspensory ligament, septum, ciliary ganglion and short ciliary nerves.
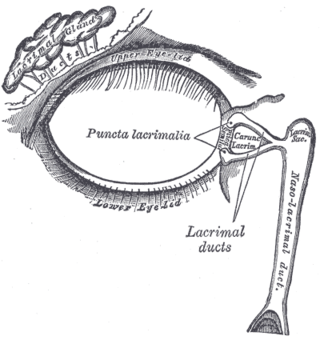
The lacrimal glands are paired exocrine glands, one for each eye, found in most terrestrial vertebrates and some marine mammals, that secrete the aqueous layer of the tear film. In humans, they are situated in the upper lateral region of each orbit, in the lacrimal fossa of the orbit formed by the frontal bone. Inflammation of the lacrimal glands is called dacryoadenitis. The lacrimal gland produces tears which are secreted by the lacrimal ducts, and flow over the ocular surface, and then into canals that connect to the lacrimal sac. From that sac, the tears drain through the lacrimal duct into the nose.

The canthus is either corner of the eye where the upper and lower eyelids meet. More specifically, the inner and outer canthi are, respectively, the medial and lateral ends/angles of the palpebral fissure.

The ophthalmic artery (OA) is an artery of the head. It is the first branch of the internal carotid artery distal to the cavernous sinus. Branches of the ophthalmic artery supply all the structures in the orbit around the eye, as well as some structures in the nose, face, and meninges. Occlusion of the ophthalmic artery or its branches can produce sight-threatening conditions.

The orbicularis oculi is a muscle in the face that closes the eyelids. It arises from the nasal part of the frontal bone, from the frontal process of the maxilla in front of the lacrimal groove, and from the anterior surface and borders of a short fibrous band, the medial palpebral ligament.

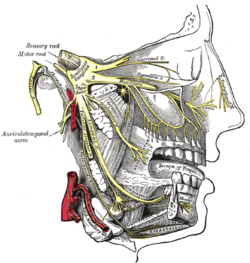
In neuroanatomy, the maxillary nerve (V2) is one of the three branches or divisions of the trigeminal nerve, the fifth (CN V) cranial nerve. It comprises the principal functions of sensation from the maxilla, nasal cavity, sinuses, the palate and subsequently that of the mid-face, and is intermediate, both in position and size, between the ophthalmic nerve and the mandibular nerve.

The tarsi or tarsal plates are two comparatively thick, elongated plates of dense connective tissue, about 10 mm (0.39 in) in length for the upper eyelid and 5 mm for the lower eyelid; one is found in each eyelid, and contributes to its form and support. They are located directly above the lid margins. The tarsus has a lower and upper part making up the palpebrae.
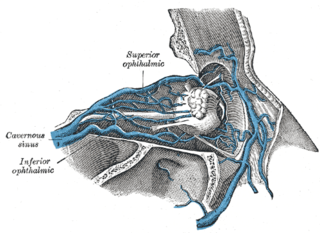
The superior ophthalmic vein is a vein of the orbit that drains venous blood from structures of the upper orbit. It is formed by the union of the angular vein, and supraorbital vein. It passes backwards within the orbit alongside the ophthalmic artery, then exits the orbit through the superior orbital fissure to drain into the cavernous sinus.

The zygomaticofacial nerve (or zygomaticofacial branch of zygomatic nerve or malar branch of zygomatic nerve) is a cutaneous (sensory) branch of the maxillary nerve (CN V2) that arises within the orbit. The zygomaticofacial nerve penetrates the inferolateral angle of the orbit, emerging into the face through the zygomaticofacial foramen, then penetrates the orbicularis oculi muscle to reach and innervate the skin of the prominence of the cheek.

The angular vein is a vein of the face. It is the upper part of the facial vein, above its junction with the superior labial vein. It is formed by the junction of the supratrochlear vein and supraorbital vein, and joins with the superior labial vein. It drains the medial canthus, and parts of the nose and the upper lip. It can be a route of spread of infection from the danger triangle of the face to the cavernous sinus.

The infraorbital nerve is a branch of the maxillary nerve. It arises in the pterygopalatine fossa. It passes through the inferior orbital fissure to enter the orbit. It travels through the orbit, then enters and traverses the infraorbital canal, exiting the canal at the infraorbital foramen to reach the face. It provides sensory innervation to the skin and mucous membranes around the middle of the face.

The medial palpebral ligament is a ligament of the face. It attaches to the frontal process of the maxilla, the lacrimal groove, and the tarsus of each eyelid. It has a superficial (anterior) and a deep (posterior) layer, with many surrounding attachments. It connects the medial canthus of each eyelid to the medial part of the orbit. It is a useful point of fixation during eyelid reconstructive surgery.

The superior tarsal muscle is a smooth muscle adjoining the levator palpebrae superioris muscle that helps to raise the upper eyelid.

The dorsal nasal artery is an artery of the face. It is one of the two terminal branches of the ophthalmic artery. It contributes arterial supply to the lacrimal sac, and outer surface of the nose.

The medial palpebral arteries are arteries of the head that contribute arterial blood supply to the eyelids. They are derived from the ophthalmic artery; a single medial palpebral artery issues from the ophthalmic artery before splitting into a superior and an inferior medial palpebral artery, each supplying one eyelid.
In anatomy, arterial tree is used to refer to all arteries and/or the branching pattern of the arteries. This article regards the human arterial tree. Starting from the aorta:

The zygomatic branches of the facial nerve (malar branches) are nerves of the face. They run across the zygomatic bone to the lateral angle of the orbit. Here, they supply the orbicularis oculi muscle, and join with filaments from the lacrimal nerve and the zygomaticofacial branch of the maxillary nerve (CN V2).

The lateral palpebral arteries are the two large branches of those terminal branches of the lacrimal gland that supply the eyelid, with one lateral palpebral artery supplying one eyelid or the other. They pass medial-ward within the eyelid. They anastomose with medial palpebral arteries to form an arterial cricle.