The sphenoid bone is an unpaired bone of the neurocranium. It is situated in the middle of the skull towards the front, in front of the basilar part of the occipital bone. The sphenoid bone is one of the seven bones that articulate to form the orbit. Its shape somewhat resembles that of a butterfly or bat with its wings extended.

The nasal cavity is a large, air-filled space above and behind the nose in the middle of the face. The nasal septum divides the cavity into two cavities, also known as fossae. Each cavity is the continuation of one of the two nostrils. The nasal cavity is the uppermost part of the respiratory system and provides the nasal passage for inhaled air from the nostrils to the nasopharynx and rest of the respiratory tract.

In anatomy, the orbit is the cavity or socket/hole of the skull in which the eye and its appendages are situated. "Orbit" can refer to the bony socket, or it can also be used to imply the contents. In the adult human, the volume of the orbit is 30 millilitres, of which the eye occupies 6.5 ml. The orbital contents comprise the eye, the orbital and retrobulbar fascia, extraocular muscles, cranial nerves II, III, IV, V, and VI, blood vessels, fat, the lacrimal gland with its sac and duct, the eyelids, medial and lateral palpebral ligaments, cheek ligaments, the suspensory ligament, septum, ciliary ganglion and short ciliary nerves.
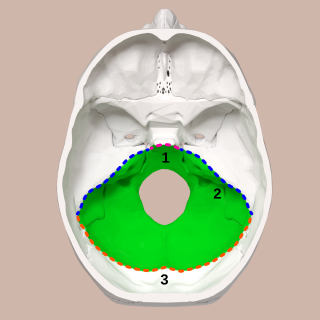
The posterior cranial fossa is the part of the cranial cavity located between the foramen magnum, and tentorium cerebelli. It is formed by the sphenoid bones, temporal bones, and occipital bone. It lodges the cerebellum, and parts of the brainstem.

The superior orbital fissure is a foramen or cleft of the skull between the lesser and greater wings of the sphenoid bone. It gives passage to multiple structures, including the oculomotor nerve, trochlear nerve, ophthalmic nerve, abducens nerve, ophthalmic veins, and sympathetic fibres from the cavernous plexus.

The falx cerebri is a large, crescent-shaped fold of dura mater that descends vertically into the longitudinal fissure between the cerebral hemispheres of the human brain, separating the two hemispheres and supporting dural sinuses that provide venous and CSF drainage to the brain. It is attached to the crista galli anteriorly, and blends with the tentorium cerebelli posteriorly.
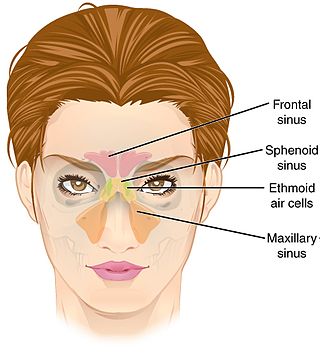
The ethmoid sinuses or ethmoid air cells of the ethmoid bone are one of the four paired paranasal sinuses. Unlike the other three pairs of paranasal sinuses which consist of one or two large cavities, the ethmoidal sinuses entail a number of small air-filled cavities. The cells are located within the lateral mass (labyrinth) of each ethmoid bone and are variable in both size and number. The cells are grouped into anterior, middle, and posterior groups; the groups differ in their drainage modalities, though all ultimately drain into either the superior or the middle nasal meatus of the lateral wall of the nasal cavity.

The foramen spinosum is a small open hole in the greater wing of the sphenoid bone that gives passage to the middle meningeal artery and vein, and the meningeal branch of the mandibular nerve.

The ophthalmic nerve (CN V1) is a sensory nerve of the head. It is one of three divisions of the trigeminal nerve (CN V), a cranial nerve. It has three major branches which provide sensory innervation to the eye, and the skin of the upper face and anterior scalp, as well as other structures of the head.
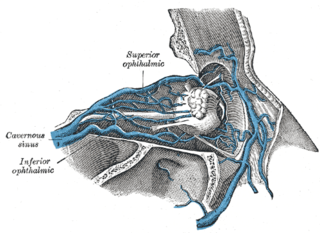
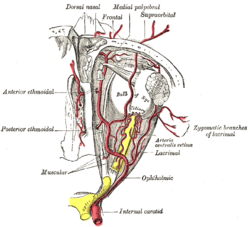
The superior ophthalmic vein is a vein of the orbit that drains venous blood from structures of the upper orbit. It is formed by the union of the angular vein, and supraorbital vein. It passes backwards within the orbit alongside the ophthalmic artery, then exits the orbit through the superior orbital fissure to drain into the cavernous sinus.
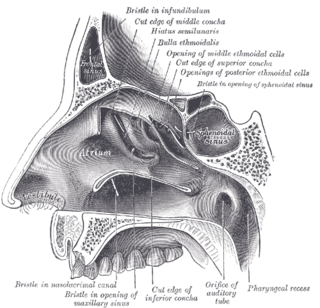
The sphenoid sinus is a paired paranasal sinus occurring within the body of the sphenoid bone. It represents one pair of the four paired paranasal sinuses. The pair of sphenoid sinuses are separated in the middle by a septum of sphenoid sinuses. Each sphenoid sinus communicates with the nasal cavity via the opening of sphenoidal sinus. The two sphenoid sinuses vary in size and shape, and are usually asymmetrical.

The zygomatic nerve is a branch of the maxillary nerve. It arises in the pterygopalatine fossa and enters the orbit through the inferior orbital fissure before dividing into its two terminal branches: the zygomaticotemporal nerve and zygomaticofacial nerve.

The anterior ethmoidal artery is a branch of the ophthalmic artery in the orbit. It exits the orbit through the anterior ethmoidal foramen alongside the anterior ethmoidal nerve. It contributes blood supply to the ethmoid sinuses, frontal sinuses, the dura mater, lateral nasal wall, and nasal septum. It issues a meningeal branch, and nasal branches.

The anterior ethmoidal nerve is a nerve of the head. It is a branch of the nasociliary nerve (itself a branch of the ophthalmic nerve (V1)). It arises in the orbit, and enters first the cranial cavity and then the nasal cavity. It provides sensory innervation to part of the meninges, parts of the nasal cavity, and part of the skin of the nose.

The anterior cranial fossa is a depression in the floor of the cranial base which houses the projecting frontal lobes of the brain. It is formed by the orbital plates of the frontal, the cribriform plate of the ethmoid, and the small wings and front part of the body of the sphenoid; it is limited behind by the posterior borders of the small wings of the sphenoid and by the anterior margin of the chiasmatic groove. The lesser wings of the sphenoid separate the anterior and middle fossae.

The infratemporal fossa is an irregularly shaped cavity that is a part of the skull. It is situated below and medial to the zygomatic arch. It is not fully enclosed by bone in all directions. It contains superficial muscles, including the lower part of the temporalis muscle, the lateral pterygoid muscle, and the medial pterygoid muscle. It also contains important blood vessels such as the middle meningeal artery, the pterygoid plexus, and the retromandibular vein, and nerves such as the mandibular nerve (CN V3) and its branches.

The posterior auricular nerve is a nerve of the head. It is a branch of the facial nerve. It communicates with branches from the vagus nerve, the great auricular nerve, and the lesser occipital nerve. Its auricular branch supplies the posterior auricular muscle, the intrinsic muscles of the auricle, and gives sensation to the auricle. Its occipital branch supplies the occipitalis muscle.

The sphenoparietal sinus is a paired dural venous sinus situated along the posterior edge of the lesser wing of either sphenoid bone. It drains into the cavernous sinus.

The human nose is the first organ of the respiratory system. It is also the principal organ in the olfactory system. The shape of the nose is determined by the nasal bones and the nasal cartilages, including the nasal septum, which separates the nostrils and divides the nasal cavity into two.

The base of skull, also known as the cranial base or the cranial floor, is the most inferior area of the skull. It is composed of the endocranium and the lower parts of the calvaria.