
The Tasman Sea is a marginal sea of the South Pacific Ocean, situated between Australia and New Zealand. It measures about 2,000 km (1,200 mi) across and about 2,800 km (1,700 mi) from north to south. The sea was named after the Dutch explorer Abel Janszoon Tasman, who in 1642 was the first known person to cross it. British explorer Lieutenant James Cook later extensively navigated the Tasman Sea in the 1770s during his three voyages of exploration.

The Sulu Sea is a body of water in the southwestern area of the Philippines, separated from the South China Sea in the northwest by Palawan and from the Celebes Sea in the southeast by the Sulu Archipelago. Borneo is found to the southwest and Visayas to the northeast.
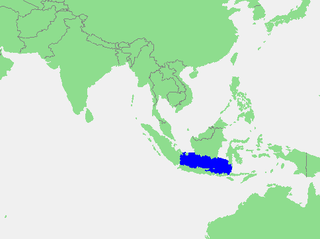
The Java Sea is an extensive shallow sea on the Sunda Shelf, between the Indonesian islands of Borneo to the north, Java to the south, Sumatra to the west, and Sulawesi to the east. Karimata Strait to its northwest links it to the South China Sea. It is a part of the western Pacific Ocean.
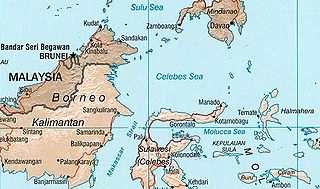
The Celebes Sea of the western Pacific Ocean is bordered on the north by the Sulu Archipelago and Sulu Sea and Mindanao Island of the Philippines, on the east by the Sangihe Islands chain, on the south by Sulawesi's Minahasa Peninsula, and on the west by northern Kalimantan in Indonesia. It extends 420 miles (675 km) north-south by 520 mi (840 km) east-west and has a total surface area of 110,000 square miles (280,000 km2), to a maximum depth of 20,300 feet (6,200 m). South of the Cape Mangkalihat, the sea opens southwest through the Makassar Strait into the Java Sea.

Makassar Strait is a strait between the islands of Borneo and Sulawesi in Indonesia. To the north it joins the Celebes Sea, while to the south it meets the Java Sea. To the northeast, it forms the Sangkulirang Bay south of the Mangkalihat Peninsula. The strait is an important regional shipping route in Southeast Asia.

The Savu Sea is a small sea within Indonesia named for the island of Savu (Sawu) on its southern boundary. It is bounded by Savu and Rai Jua to the south, the islands of Rote and Timor to the east, Flores and the Alor archipelago to the north/northwest, and the island of Sumba to the west/northwest. Between these islands, it flows into the Indian Ocean to the south and west, the Flores Sea to the north, and the Banda Sea to the northeast.

The Banda Sea is one of four seas that surround the Maluku Islands of Indonesia, connected to the Pacific Ocean, but surrounded by hundreds of islands, as well as the Halmahera and Ceram Seas. It is about 1000 km (600 mi) east to west, and about 500 km (300 mi) north to south.

The Halmahera Sea is a regional sea located in the central eastern part of the Australasian Mediterranean Sea. It is centered at about 1°S and 129°E and is bordered by the Pacific Ocean to the north, Halmahera to the west, Waigeo and West Papua to the east, and the Seram Sea to the south. It covers about 95,000 km (59,000 mi) and its topography comprises a number of separate basins and ridges, the chief of which is the Halmahera Basin reaching a depth of 2039 m.

St George's Channel is a sea channel connecting the Irish Sea to the north and the Celtic Sea to the southwest.
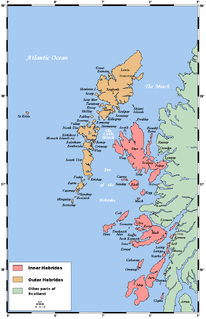
The Minch, also called North Minch, is a strait in north-west Scotland, separating the north-west Highlands and the northern Inner Hebrides from Lewis and Harris in the Outer Hebrides. It was known as Skotlandsfjörð in Old Norse.

The Arafura Sea lies west of the Pacific Ocean, overlying the continental shelf between Australia and Western New Guinea, which is the Indonesian part of the Island of New Guinea.

The Flores Sea covers 240,000 square kilometres (93,000 sq mi) of water in Indonesia. The sea is bounded on the north by the island of Celebes and on the south by Sunda Islands of Flores and Sumbawa.

The Balearic Sea is a body of water in the Mediterranean Sea near the Balearic Islands. The Ebro River flows into this small sea.

The Molucca Sea is located in the western Pacific Ocean, around the vicinity of Indonesia, specifically bordered by the Indonesian Islands of Celebes (Sulawesi) to the west, Halmahera to the east, and the Sula Islands to the south. The Molucca Sea has a total surface area of 77,000 square miles. The Molucca Sea is rich in coral and has many diving sites due to the deepness of its waters. The deepness of the water explains the reasoning behind dividing the sea into three zones, which functions to transport water from the Pacific Ocean to the shallower seas surrounding it. The deepest hollow in the Molucca Sea is the 15,780-foot (4,810-meter) Batjan basin. This region is known for its periodic experiences of earthquakes, which stems from the sea itself being a micro plate, in which the Molucca Sea is being subducted in two opposite directions: one in the direction of the Eurasian Plate to the west and the other in the direction of the Philippines Sea Plate to the east.

The Seram Sea or Ceram Sea is one of several small seas between the scattered islands of Indonesia. It is a section of the Pacific Ocean with an area of approximately one hundred twenty thousand square kilometres (46,000 sq mi) located between Buru and Seram, which are two of the islands once called the South Moluccas. These islands are the native habitat of plants long coveted for their use as spices, such as nutmeg, cloves, and black peppercorns, and the seas surrounding them were busy shipping routes. The Seram Sea is also the habitat of several species of tropical goby and many other fish. Like many other small Indonesian seas, the Seram Sea is rocky and very tectonically active.

The Sea of the Hebrides is a small, partly sheltered section of the North Atlantic Ocean, indirectly off the southern part of the north-west coast of Scotland. To the east are the mainland of Scotland and the northern Inner Hebrides ; to the west are the southern Outer Hebrides islands, principally South Uist, Eriskay, and Barra. To the north is the Little Minch, a channel connecting it with the Minch.
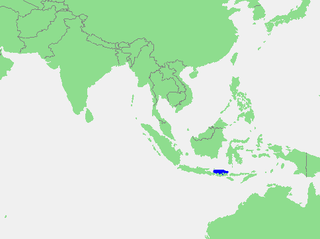
The Bali Sea is the body of water north of the island of Bali and south of Kangean Island in Indonesia. The sea forms the south-west part of the Flores Sea, and the Madura Strait opens into it from the west.
The Coastal Waters of Southeast Alaska and British Columbia is a marine area designated by the International Hydrographic Organization (IHO).

The borders of the oceans are the limits of Earth's oceanic waters. The definition and number of oceans can vary depending on the adopted criteria. The principal divisions of the five oceans are the Pacific Ocean, Atlantic Ocean, Indian Ocean, Southern (Antarctic) Ocean, and Arctic Ocean. Smaller regions of the oceans are called seas, gulfs, bays, straits, and other terms. Geologically, an ocean is an area of oceanic crust covered by water.

The Malin Sea is a marginal sea of the North-East Atlantic over the Malin Shelf, the continental shelf north of Ireland and southwest of Scotland. It is connected to the Irish Sea by the North Channel, and overlaps the Inner Seas off the West Coast of Scotland. Of the UK Shipping Forecast areas, the Malin Sea covers most of Malin, and by some definitions extends into Rockall. The area is within the exclusive economic zones of Ireland and the United Kingdom.



















