Related Research Articles

Ascites is the abnormal build-up of fluid in the abdomen. Technically, it is more than 25 ml of fluid in the peritoneal cavity, although volumes greater than one liter may occur. Symptoms may include increased abdominal size, increased weight, abdominal discomfort, and shortness of breath. Complications can include spontaneous bacterial peritonitis.
In medicine, a shunt is a hole or a small passage that moves, or allows movement of, fluid from one part of the body to another. The term may describe either congenital or acquired shunts; acquired shunts may be either biological or mechanical.

Esophageal varices are extremely dilated sub-mucosal veins in the lower third of the esophagus. They are most often a consequence of portal hypertension, commonly due to cirrhosis. People with esophageal varices have a strong tendency to develop severe bleeding which left untreated can be fatal. Esophageal varices are typically diagnosed through an esophagogastroduodenoscopy.

Portal hypertension is abnormally increased portal venous pressure – blood pressure in the portal vein and its branches, that drain from most of the intestine to the liver. Portal hypertension is defined as a hepatic venous pressure gradient greater than 5 mmHg. Cirrhosis is the most common cause of portal hypertension; other, less frequent causes are therefore grouped as non-cirrhotic portal hypertension. When it becomes severe enough to cause symptoms or complications, treatment may be given to decrease portal hypertension itself or to manage its complications.
Gastrointestinal bleeding, also called gastrointestinal hemorrhage (GIB), is all forms of bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract, from the mouth to the rectum. When there is significant blood loss over a short time, symptoms may include vomiting red blood, vomiting black blood, bloody stool, or black stool. Small amounts of bleeding over a long time may cause iron-deficiency anemia resulting in feeling tired or heart-related chest pain. Other symptoms may include abdominal pain, shortness of breath, pale skin, or passing out. Sometimes in those with small amounts of bleeding no symptoms may be present.

Gastric varices are dilated submucosal veins in the lining of the stomach, which can be a life-threatening cause of bleeding in the upper gastrointestinal tract. They are most commonly found in patients with portal hypertension, or elevated pressure in the portal vein system, which may be a complication of cirrhosis. Gastric varices may also be found in patients with thrombosis of the splenic vein, into which the short gastric veins that drain the fundus of the stomach flow. The latter may be a complication of acute pancreatitis, pancreatic cancer, or other abdominal tumours, as well as hepatitis C. Gastric varices and associated bleeding are a potential complication of schistosomiasis resulting from portal hypertension.

Hepatic encephalopathy (HE) is an altered level of consciousness as a result of liver failure. Its onset may be gradual or sudden. Other symptoms may include movement problems, changes in mood, or changes in personality. In the advanced stages it can result in a coma.
Shunt may refer to:

Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt is an artificial channel within the liver that establishes communication between the inflow portal vein and the outflow hepatic vein. It is used to treat portal hypertension which frequently leads to intestinal bleeding, life-threatening esophageal bleeding and the buildup of fluid within the abdomen (ascites).
The Model for End-Stage Liver Disease, or MELD, is a scoring system for assessing the severity of chronic liver disease. It was initially developed to predict mortality within three months of surgery in patients who had undergone a transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) procedure, and was subsequently found to be useful in determining prognosis and prioritizing for receipt of a liver transplant. This score is now used by the United Network for Organ Sharing (UNOS) and Eurotransplant for prioritizing allocation of liver transplants instead of the older Child-Pugh score.
A porto-systemic shunt or porta-systemic shunt (PSS), also known as a liver shunt, is a bypass of the liver by the body's circulatory system. It can be either a congenital or acquired condition and occurs in humans as well as in other species of animals. Congenital PSS are extremely rare in humans but are relatively common in dogs. Thus, a large part of medical and scientific literature on the subject is grounded in veterinary medicine.

In medicine, a distal splenorenal shunt procedure (DSRS), also splenorenal shunt procedure and Warren shunt, is a surgical procedure in which the distal splenic vein is attached to the left renal vein. It is used to treat portal hypertension and its main complication. It was developed by W. Dean Warren.
Tips may refer to:

Portal hypertensive gastropathy refers to changes in the mucosa of the stomach in patients with portal hypertension; by far the most common cause of this is cirrhosis of the liver. These changes in the mucosa include friability of the mucosa and the presence of ectatic blood vessels at the surface. Patients with portal hypertensive gastropathy may experience bleeding from the stomach, which may uncommonly manifest itself in vomiting blood or melena; however, portal hypertension may cause several other more common sources of upper gastrointestinal bleeding, such as esophageal varices and gastric varices. On endoscopic evaluation of the stomach, this condition shows a characteristic mosaic or "snake-skin" appearance to the mucosa of the stomach.
Anorectal varices are the dilation of collateral submucosal vessels due to backflow in the veins of the rectum. Typically this occurs due to portal hypertension which shunts venous blood from the portal system through the portosystemic anastomosis present at this site into the systemic venous system. This can also occur in the esophagus, causing esophageal varices, and at the level of the umbilicus, causing caput medusae. Between 44% and 78% of patients with portal hypertension get anorectal varices.
The Sugiura procedure is a surgical technique that involves the removal and transection of the blood vessels that supply the upper portion of the stomach and the esophagus. The procedure also involves a splenectomy. The operation was originally developed to treat bleeding esophageal varices that were untreatable by other conventional methods. It was originally developed as a two-step operation, but has been modified numerous times by many surgeons since its original creation.
Jeanne LaBerge is American interventional radiologist known for her work establishing the field of interventional radiology as a primary specialty in medicine. She was named a fellow of the Society of Cardiovascular and Interventional Radiology in 1992.
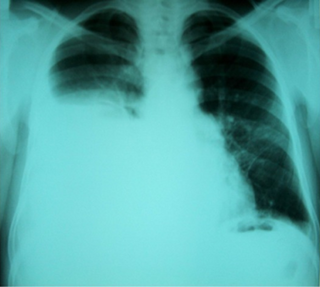
Hepatic hydrothorax is a rare form of pleural effusion that occurs in people with liver cirrhosis. It is defined as an effusion of over 500 mL in people with liver cirrhosis that is not caused by heart, lung, or pleural disease. It is found in 5-10% of people with liver cirrhosis and 2-3% of people with pleural effusions. It is much more common on the right side, with 85% of cases occurring on the right, 13% on the left, and 2% in both. Although it is most common in people with severe ascites, cases have been reported where people only had mild or no ascites. Symptoms are not specific, and mostly involve the respiratory system.
Congenital portosystemic shunts (PSS) is a hereditary condition in dogs and cats, its frequency varying depending on the breed. The shunts found mainly in small dog breeds such as Shih Tzus, Tibetan Spaniels, Miniature Schnauzers and Yorkshire Terriers, and in cats such as Persians, British Shorthairs, Himalayans, and mixed breeds are usually extrahepatic, while the shunts found in large dog breeds such as Irish Wolfhounds and Labrador Retrievers tend to be intrahepatic.
Balloon-occluded retrograde transvenous obliteration (BRTO) is an endovascular procedure used for the treatment of gastric varices. When performing the procedure, an interventional radiologist accesses blood vessels using a catheter, inflates a balloon and injects a substance into the variceal blood vessels that causes blockage of those vessels. To prevent the flow of the agent out of the intended site, a balloon is inflated during the procedure, which occludes.
References
- ↑ Haskal ZJ, Scott M, Rubin RA, Cope C (April 1994). "Intestinal varices: treatment with the transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt". Radiology. 191 (1): 183–7. doi:10.1148/radiology.191.1.8134568. PMID 8134568.