Related Research Articles

The Stikine River is a major river in northern British Columbia (BC), Canada and southeastern Alaska in the United States. It drains a large, remote upland area known as the Stikine Country east of the Coast Mountains. Flowing west and south for 610 kilometres (379 mi), it empties into various straits of the Inside Passage near Wrangell, Alaska. About 90 percent of the river's length and 95 percent of its drainage basin are in Canada. Considered one of the last truly wild large rivers in BC, the Stikine flows through a variety of landscapes including boreal forest, steep canyons and wide glacial valleys.

The Tahltan or Nahani are a First Nations people of the Athabaskan-speaking ethnolinguistic group who live in northern British Columbia around Telegraph Creek, Dease Lake, and Iskut. The Tahltan constitute the fourth division of the Nahane.
Telegraph Creek is a small community located off Highway 37 in northern British Columbia at the confluence of the Stikine River and Telegraph Creek. The only permanent settlement on the Stikine River, it is home to approximately 250 members of Tahltan First Nation and non-native residents. The town offers basic services, including Anglican and Catholic churches, a general store, a post office, a clinic with several nurses on-call around the clock, two Royal Canadian Mounted Police officers, and a K-9 school. Steep river banks and rocky gorges form the terraced nature of the geography.
Dease Lake is a small community in the Cassiar Country of the Northern Interior of British Columbia, Canada. It is 230 km south of the Yukon border on Stewart–Cassiar Highway at the south end of the lake of the same name. Dease Lake is the last major centre before the Alaska Highway while driving northbound, and also the junction to Telegraph Creek and the Grand Canyon of the Stikine. Dease Lake Indian Reserve No. 9 is nearby and is under the governance of the Tahltan First Nation band government.
Iskut is a small, mostly Indigenous community in the Stikine Country of northwestern British Columbia. It is located on Highway 37, at the north end of Eddontenajon Lake just south of Dease Lake and the crossing of the Stikine River.

The Stikine Country, also referred to as the Stikine District or simply "the Stikine", is one of the historical geographic regions of the Canadian province of British Columbia, located inland from the central Alaska Panhandle and comprising the basin of the Stikine River and its tributaries. The term Stikine–Iskut is also fairly common to describe the area, and references the Iskut River, the Stikine's largest tributary and describable as its south fork.
Tahltan, or Goon-da-chagga or Goon-tdar-shaga is an unincorporated locality and Indian reserve community of the Tahltan people located east of Telegraph Creek in northern British Columbia, Canada, near the confluence of the Stikine and Tahltan Rivers. The local First Nations government is the Tahltan Band Council. The specific name of the Indian Reserve is Tahltan Indian Reserve No. 1. Other reserves in the immediate vicinity, also governed by this band, are Tahltan Forks Indian Reserve No. 5, Upper Tahltan Indian Reserve No. 4 and Hiusta's Meadow Indian Reserve No. 2.

The Tahltan River is a tributary of the Stikine River in northwest part of the province of British Columbia, Canada. It flows generally east and southeast about 95 km (59 mi) to join the Stikine River at Tahltan, British Columbia. The lower Tahltan River marks the boundary between the Tahltan Highland and the Nahlin Plateau, both of which are part of the larger Stikine Plateau region.
The Dease River First Nation, also known as the Dease River Nation, is a band government of the Kaska Dena people in the Cassiar Country of the Northern Interior of British Columbia. Their offices are located in Good Hope Lake, British Columbia, which is on the Stewart-Cassiar Highway to the east of the abandoned mining town of Cassiar. The registered population of the band is 162.
The Tahltan First Nation, also known as the Tahltan Indian Band, is a band government of the Tahltan people. Their main community and reserves are located at Telegraph Creek, British Columbia. Their language is the Tahltan language, which is an Athabaskan language also known as Nahanni, is closely related to Kaska and Dunneza. Their Indian and Northern Affairs Canada band number is 682. The Tahltan First Nation is joined with the Iskut First Nation in a combined tribal council-type organization known as the Tahltan Nation.
The Tàłtàn Nation is a tribal council-type organization combining the governments of two band governments of the Tahltan people in the Stikine Country of the Northern Interior of British Columbia, Canada. The two member governments are the Iskut First Nation and the Tahltan First Nation, which is also known as the Tahltan Indian Band. The Tahltan Nation is governed by the Tahltan Central Council, which is composed of representatives of 10 families from each band and has its offices at Dease Lake and Telegraph Creek.
The Klappan Coalbed Methane Project is a gas project owned by Shell Canada that looks to develop the coalbed methane from an area in northern British Columbia, near the source of three rivers: the Skeena River, Nass River, and Stikine River, and also the namesake Klappan River. The area is known in environmental politics and native lore as the Sacred Headwaters or Kablona. The project is the source of controversy and is opposed by First Nations groups and non-governmental organizations. If developed, the project will include a network of gas wells connected by roads and pipelines, as well as a pipeline to deliver the gas to market.

The Iskut River, located in the northwest part of the province of British Columbia is the largest tributary of the Stikine River, entering it about 11 km (6.8 mi) above its entry into Alaska.
The Twin River is a tributary of the Iskut River in the northwest part of the province of British Columbia, Canada. From its source in Twin Glacier the Twin River flows south for about 11 km (6.8 mi), east of Hoodoo Mountain to the Iskut River north of the Craig River watershed. The Twin River's watershed covers 203 km2 (78 sq mi), and its mean annual discharge is an estimated 16.7 m3/s (590 cu ft/s). The river's watershed's land cover is classified as 77.2% snow/glacier, 9.8% barren, 4.5% conifer forest, and small amounts of other cover.
Tahltan Indian Reserve No. 10, referred to by Statistics Canada for census purposes as Tahtlan 10, is an Indian reserve of the Tahltan First Nation located one mile north of the confluence of the Klastline River with the Stikine in the Stikine Country of the northwestern British Columbia Interior of Canada.
The Tuya River is a major tributary of the Stikine River in northwest part of the province of British Columbia, Canada. From its source at High Tuya Lake in Tuya Mountains Provincial Park just south of Ash Mountain, the highest peak of the Tuya Range, the Tuya River flows south about 200 km (120 mi) to meet the Stikine River in the Grand Canyon of the Stikine. The Tuya River's main tributary is the Little Tuya River. The Tuya River divides the Tanzilla Plateau on the east from the Kawdy Plateau, to the northwest, and the Nahlin Plateau, to the southwest. All three are considered sub-plateaus of the Stikine Plateau. The Tuya River's watershed covers 3,575 km2 (1,380 sq mi), and its mean annual discharge is estimated at 36.9 m3/s (1,300 cu ft/s). The mouth of the Tuya River is located about 24 km (15 mi) northeast of Telegraph Creek, British Columbia, about 67 km (42 mi) southwest of Dease Lake, British Columbia, and about 210 km (130 mi) east of Juneau, Alaska. The Tuya River's watershed's land cover is classified as 35.7% shrubland, 31.4% conifer forest, 14.0% mixed forest, 7.2% herbaceous, and small amounts of other cover.
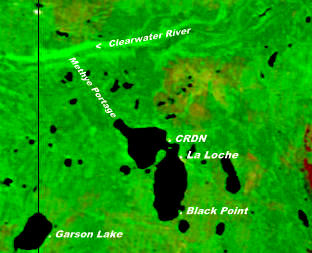
The Clearwater River Dene Nation is a Dene First Nations band government in the boreal forest area of northern Saskatchewan, Canada. It maintains offices in the village of Clearwater River situated on the eastern shore of Lac La Loche. The Clearwater River Dene Nation reserve of Clearwater River shares its southern border with the village of La Loche.
Hartz Creek is a tributary of the Tahltan River, part of the Stikine River watershed in northwest part of the province of British Columbia, Canada. It flows generally south and southwest for roughly 14 km (8.7 mi) to join the Tahltan River about 4.5 km (2.8 mi) north of Tahltan, British Columbia at the Tahltan River's confluence with the Stikine River. Hartz Creek's watershed covers 39.1 km2 (15.1 sq mi), and its mean annual discharge is estimated at 0.315 m3/s (11.1 cu ft/s). The mouth of Hartz Creek is located about 18 km (11 mi) northeast of Telegraph Creek, British Columbia, about 73 km (45 mi) southwest of Dease Lake, British Columbia, and about 200 km (120 mi) east of Juneau, Alaska. Hartz Creek's watershed's land cover is classified as 44.2% shrubland, 30.7% mixed forest, 20.8% conifer forest, and small amounts of other cover.
The Inhini River is a tributary of the Iskut River in the northwest part of the province of British Columbia, Canada, in Cassiar Land District. From its source in the glaciers of Simma Mountain and Mount Rastus, the Inhini River flows north for about 25 km (16 mi) to the Iskut River just east of the Iskut's confluence with the Stikine River.
The Little Iskut River is a tributary of the Iskut River in the northwest part of the province of British Columbia, Canada, in Cassiar Land District. From its source at Little Ball Lake in Mount Edziza Provincial Park, the Little Iskut River flows about 45 km (28 mi), generally north to the vicinity of Mowdale Lake, then southeast and south to the Iskut River just below Cascade Falls. The Little Iskut River is part of the Stikine River drainage basin, as the Iskut River is a major tributary of the Stikine.
References
- ↑ "First Nation Detail, inac.gc.ca". Crown–Indigenous Relations and Northern Affairs Canada . Government of Canada. Retrieved 2009-01-31.
- ↑ BCGNIS entry "Stikine River Indian Reserve 7" [ permanent dead link ]
- ↑ BC Govt Aboriginal Relations and Reconciliation webpage
- ↑ "page at Aboriginal Canada Portal". Archived from the original on 2008-03-29. Retrieved 2009-01-31.