
Venice is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto region. It is built on a group of 118 small islands that are separated by canals and linked by over 400 bridges. The islands are in the shallow Venetian Lagoon, an enclosed bay lying between the mouths of the Po and the Piave rivers. In 2020, 258,685 people resided in the Comune di Venezia, of whom around 55,000 live in the historical city of Venice. Together with Padua and Treviso, the city is included in the Padua-Treviso-Venice Metropolitan Area (PATREVE), which is considered a statistical metropolitan area, with a total population of 2.6 million.

Burano is an island in the Venetian Lagoon, northern Italy, near Torcello at the northern end of the lagoon, known for its lace work and brightly coloured homes. The primary economy is tourism.

Murano is a series of islands linked by bridges in the Venetian Lagoon, northern Italy. It lies about 1.5 kilometres north of Venice and measures about 1.5 km (0.9 mi) across with a population of just over 5,000. It is famous for its glass making. It was once an independent comune, but is now a frazione of the comune of Venice.

The Lido, or Venice Lido, is an 11-kilometre-long (7-mile) barrier island in the Venetian Lagoon, northern Italy; it is home to about 20,400 residents. The Venice Film Festival takes place at the Lido late August/early September.

Trogir is a historic town and harbour on the Adriatic coast in Split-Dalmatia County, Croatia, with a population of 10,818 (2011) and a total municipal population of 13,260 (2011). The historic city of Trogir is situated on a small island between the Croatian mainland and the island of Čiovo. It lies 27 kilometres west of the city of Split.
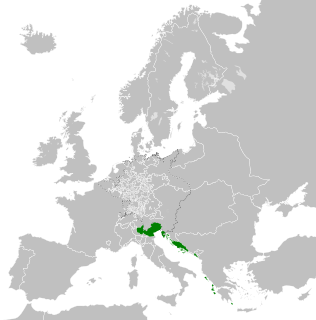
The Republic of Venice or Venetian Republic, traditionally known as La Serenissima, was a sovereign state and maritime republic in parts of present-day Italy which existed from 697 AD until 1797 AD. Centered on the lagoon communities of the prosperous city of Venice, it incorporated numerous overseas possessions in modern Croatia, Slovenia, Montenegro, Greece, Albania and Cyprus. The republic grew into a trading power during the Middle Ages and strengthened this position in the Renaissance. Citizens spoke the still-surviving Venetian language, although publishing in (Florentine) Italian became the norm during the Renaissance.

San Giorgio Maggiore is one of the islands of Venice, northern Italy, lying east of the Giudecca and south of the main island group. The island, or more specifically its Palladian church, is an important landmark. It has been much painted, featuring for example in a series by Monet.

Mazzorbo is one of various islands in the northern part of the Lagoon of Venice. Like the other islands in this part of the lagoon, it was the site one of the earliest settlements in the lagoon which predated the development of Venice. However, these islands then declined and were eventually abandoned. In the 1980s the architect Giancarlo De Carlo built a brightly coloured residential neighbourhood to help to repopulate Mazzorbo. In 2019 its population was 256. It is linked to Burano by a wooden bridge. It was once an important trading centre but is now known for its vineyards and orchards. Its main attraction is the fourteenth century church of Santa Caterina.

San Lazzaro degli Armeni is a small island in the Venetian Lagoon which has been home to the monastery of the Mekhitarists, an Armenian Catholic congregation, since 1717. It is the primary center of the Mekhitarists, while the Mekhitarist Monastery of Vienna is their primary abbey.

San Servolo is an Italian island in the Venetian Lagoon, to the southeast of San Giorgio Maggiore. Earlier housing a monastery of Benedictine monks, later an asylum for the insane, the island is now home to a museum, Venice International University, and the prestigious International College of Ca' Foscari University.

The San Giorgio Monastery was a Benedictine monastery in Venice, Italy, located on the island of San Giorgio Maggiore. It stands next to the Church of San Giorgio Maggiore, which serves the monastic community. The old monastic buildings currently serves as the headquarters of the Cini Foundation.

San Giorgio Maggiore is a 16th-century Benedictine church on the island of the same name in Venice, northern Italy, designed by Andrea Palladio, and built between 1566 and 1610. The church is a basilica in the classical Renaissance style and its brilliant white marble gleams above the blue water of the lagoon opposite the Piazzetta di San Marco and forms the focal point of the view from every part of the Riva degli Schiavoni.

San Nicolò al Lido refers to both the San Nicolò Church and most importantly to its annexed Monastery of San Nicolò located in Venice, northern Italy. It is located in the northern part of the Lido di Venezia and houses the relics of Saint Nicholas, patron of sailors. From this church, the traditional thanksgiving Mass of the Sposalizio del Mare is celebrated. The complex houses monks of the Franciscan order.

San Giorgio in Alga is an island of the Venetian lagoon, northern Italy, lying between the Giudecca and Fusina.

San Francesco del Deserto is an island in the Venetian Lagoon in Véneto, Italy, with a surface of some 4 ha. It is located between Sant'Erasmo and Burano. It houses a minorites convent.

Vignole is an island in the Venetian Lagoon, northern Italy, with a surface of some 69.20 ha. It is located north-east of Venice, between the islands of Sant'Erasmo and La Certosa.

San Marco in Boccalama was an island, now submerged, in the Venetian Lagoon, northern Italy. It was located between Campana, Sant'Angelo della Polvere and the motte di Volpego. The name derived from the presence of a church dedicated to St. Mark, and to its location at the mouth the Lama, an old branch of the river Brenta's mouth.

Sant'Angelo della Polvere (originally called Sant'Angelo di Concordia, later Sant'Angelo di Contorta and Sant'Angelo di Caotorta) is an island in the Venetian Lagoon, in the Contorta channel, not far from the Giudecca and the island of San Giorgio in Alga. An Italian state property, it has a surface of 0.53 ha and is home to four buildings.

Isola di San Clemente is a small island in the Venetian Lagoon in Italy. For centuries it housed a monastic settlement, and more recently an asylum. It is now the site of a luxury hotel.

Venetian Dalmatia refers to parts of Dalmatia under the rule of the Republic of Venice, mainly from the 16th to the 18th centuries. The first possessions were acquired around 1000, having taken the coastal parts of the Kingdom of Croatia, but Venetian Dalmatia was fully consolidated from 1420 and lasted until 1797 when the republic disappeared with Napoleon's conquests.



















