
A seborrheic keratosis is a non-cancerous (benign) skin tumour that originates from cells in the outer layer of the skin. Like liver spots, seborrheic keratoses are seen more often as people age.

Hyperkeratosis is thickening of the stratum corneum, often associated with the presence of an abnormal quantity of keratin, and also usually accompanied by an increase in the granular layer. As the corneum layer normally varies greatly in thickness in different sites, some experience is needed to assess minor degrees of hyperkeratosis.
Lichen spinulosus is a rare skin disorder characterized by follicular keratotic papules that are grouped into large patches. It is a variant of keratosis pilaris named for its resemblance to a patch of lichen.
Perforating folliculitis is a skin condition in humans characterized by discrete follicular keratotic eruptions involving mainly the hairy parts of the extremities.
Tufted folliculitis presents with doll's hair-like bundling of follicular units, and is seen in a wide range of scarring conditions including chronic staphylococcal infection, chronic lupus erythematosus, lichen planopilaris, Graham-Little syndrome, folliculitis decalvans, acne keloidalis nuchae, immunobullous disorders, and dissecting cellulitis.
Keratosis pilaris atrophicans faciei begins in infancy as follicular papules with perifollicular erythema. Initially, the lesions are restricted to the lateral eyebrows, but with time spread to involve the cheeks and forehead, and may also be associated with keratosis pilaris on the extremities and buttocks.
Atrophodermia vermiculata presents with erythematous follicular papules on the cheeks in childhood and, with time, the lesions develop into pit-like depressions.
Traumatic anserine folliculosis is a curious gooseflesh-like follicular hyperkeratosis that may result from persistent pressure and lateral friction of one skin surface against another.
Alopecia mucinosa is a skin disorder that generally presents, but not exclusively, as erythematous plaques or flat patches without hair primarily on the scalp, neck and face. This can also be present on the body as a follicular mucinosis and may represent a systemic disease.
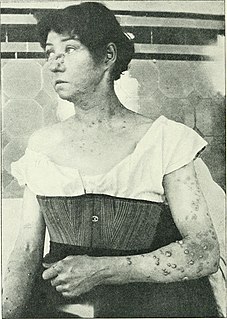
Iododermas are caused by iodides, with the most common sources of exposure being oral and intravenous contrast materials used to treat thyroid disease. The most common type of eruption is an acneiform eruption with numerous acutely inflamed follicular pustules, each surrounded by a ring of hyperemia.

Triangular alopecia is hair loss that may be congenital but usually appears in childhood as a focal patch of loss that may be complete or leaving fine vellus hairs behind. Affected individuals are typically entirely healthy. Hair restoration surgery using follicular unit transplantation has been a successful treatment modality for TTA
Follicular atrophoderma is a skin condition consisting of follicular indentations without hairs, notably occurring on extensor surfaces of the hands, legs and arms.
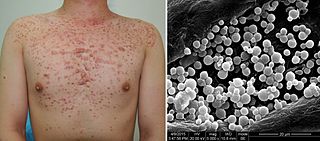
Pityrosporum folliculitis is a skin condition caused by infection by Pityrosporum yeast.
Superficial pustular folliculitis is a superficial folliculitis with thin-walled pustules at the follicular openings.
Post-vaccination follicular eruption is a cutaneous condition that occurs 9 to 11 days following vaccination, and is characterized in multiple follicular, erythematous papules.
Cutaneous B-cell lymphomas constitute a group of diseases that occur less commonly than cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, and are characterized histologically by B-cells that appear similar to those normally found in germinal centers of lymph nodes. Conditions included in this group are:

Pilomatricoma, is a benign skin tumor derived from the hair matrix. These neoplasms are relatively uncommon and typically occur on the scalp, face, and upper extremities. Clinically, pilomatricomas present as a subcutaneous nodule or cyst with unremarkable overlying epidermis that can range in size from 0.5-3.0 cm, but the largest reported case was 24 cm.

Trichoblastomas are a cutaneous condition characterized by benign neoplasms of follicular germinative cells. Trichoblastic fibroma is a designation used to characterize small nodular trichoblastomas with conspicuous fibrocytic stroma, sometimes constituting over 50% of the lesion.
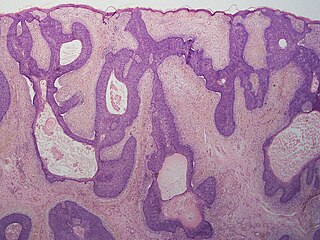
A basaloid follicular hamartoma is a cutaneous condition characterized as distinctive benign adnexal tumor that has several described variants.

Proliferating trichilemmal cysts are a cutaneous condition characterized by proliferations of squamous cells forming scroll-like structures.










