An integrated circuit, also known as a microchip, chip or IC, is a small electronic device made up of multiple interconnected electronic components such as transistors, resistors, and capacitors. These components are etched onto a small piece of semiconductor material, usually silicon. Integrated circuits are used in a wide range of electronic devices, including computers, smartphones, and televisions, to perform various functions such as processing and storing information. They have greatly impacted the field of electronics by enabling device miniaturization and enhanced functionality.

Semiconductor device fabrication is the process used to manufacture semiconductor devices, typically integrated circuits (ICs) such as computer processors, microcontrollers, and memory chips that are present in everyday electronic devices. It is a multiple-step photolithographic and physio-chemical process during which electronic circuits are gradually created on a wafer, typically made of pure single-crystal semiconducting material. Silicon is almost always used, but various compound semiconductors are used for specialized applications.

Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company Limited is a Taiwanese multinational semiconductor contract manufacturing and design company. It is the world's second most valuable semiconductor company, the world's largest dedicated independent ("pure-play") semiconductor foundry, and its country's largest company, with headquarters and main operations located in the Hsinchu Science Park in Hsinchu, Taiwan. It is majority owned by foreign investors, and the central government of Taiwan is the largest shareholder. In 2023, the company was ranked 44th in the Forbes Global 2000.
Applied Materials, Inc. is an American corporation that supplies equipment, services and software for the manufacture of semiconductor chips for electronics, flat panel displays for computers, smartphones, televisions, and solar products. The company also supplies equipment to produce coatings for flexible electronics, packaging and other applications. The company is headquartered in Santa Clara, California, and is the second largest supplier of semiconductor equipment in the world based on revenue behind ASML of Netherlands.
The semiconductor industry is the aggregate of companies engaged in the design and fabrication of semiconductors and semiconductor devices, such as transistors and integrated circuits. It formed around 1960, once the fabrication of semiconductor devices became a viable business. The industry's annual semiconductor sales revenue has since grown to over $481 billion, as of 2018.
Fabless manufacturing is the design and sale of hardware devices and semiconductor chips while outsourcing their fabrication to a specialized manufacturer called a semiconductor foundry. These foundries are typically, but not exclusively, located in the United States, China, and Taiwan. Fabless companies can benefit from lower capital costs while concentrating their research and development resources on the end market. Some fabless companies and pure play foundries may offer integrated-circuit design services to third parties.
An integrated device manufacturer (IDM) is a semiconductor company which designs, manufactures, and sells integrated circuit (IC) products.

Semiconductor Manufacturing International Corporation (SMIC) is a partially state-owned publicly listed Chinese pure-play semiconductor foundry company. It is the largest contract chip maker in mainland China.

Amkor Technology, Inc. is a semiconductor product packaging and test services provider. The company has been headquartered in Arizona, since 2005, when it was moved from West Chester, Pennsylvania, also in the United States. The company's Arizona headquarters was originally in Chandler, then later moved to Tempe. The company was founded in 1968 and, as of 2022, has approximately 31,000 employees worldwide and a reported $7.1 billion in sales.
Lam Research Corporation is an American supplier of wafer-fabrication equipment and related services to the semiconductor industry. Its products are used primarily in front-end wafer processing, which involves the steps that create the active components of semiconductor devices and their wiring (interconnects). The company also builds equipment for back-end wafer-level packaging (WLP) and for related manufacturing markets such as for microelectromechanical systems (MEMS).
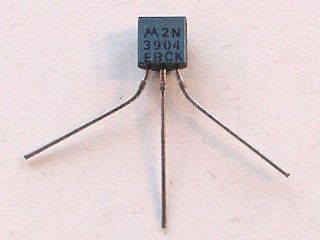
The 2N3904 is a common NPN bipolar junction transistor used for general-purpose low-power amplifying or switching applications. It is designed for low current and power, medium voltage, and can operate at moderately high speeds. It is complementary to the 2N3906 PNP transistor. Both types were registered by Motorola Semiconductor in the mid-1960s.
ASM is a Dutch headquartered multinational corporation that specializes in the design, manufacturing, sales and service of semiconductor wafer processing equipment for the fabrication of semiconductor devices. ASM's products are used by semiconductor manufacturers in front-end wafer processing in their semiconductor fabrication plants. ASM's technologies include atomic layer deposition, epitaxy, chemical vapor deposition and diffusion.

Wafer-level packaging (WLP) is a process where packaging components are attached to an integrated circuit (IC) before the wafer – on which the IC is fabricated – is diced. In WLP, the top and bottom layers of the packaging and the solder bumps are attached to the integrated circuits while they are still in the wafer. This process differs from a conventional process, in which the wafer is sliced into individual circuits (dice) before the packaging components are attached.

Semiconductor consolidation is the trend of semiconductor companies collaborating in order to come to a practical synergy with the goal of being able to operate in a business model that can sustain profitability.

Tokyo Electron Limited, or TEL, is a Japanese electronics and semiconductor company headquartered in Akasaka, Minato-ku, Tokyo, Japan. The company was founded as Tokyo Electron Laboratories, Inc. in 1963. TEL is best known as a supplier of equipment to fabricate integrated circuits (IC), flat panel displays (FPD), and photovoltaic cells (PV). Tokyo Electron Device, or TED, is a subsidiary of TEL specializing in semiconductor devices, electronic components, and networking devices. As of 2011, TEL was the largest manufacturer of IC and FPD production equipment. Listed on the Nikkei 225, in 2024, Tokyo Electron had a market cap of US$114.6 billion, making it the third-most valuable company in Japan in terms of market cap, and the 12th ranked semiconductor-related company worldwide.
Advanced Semiconductor Engineering, Inc., also known as ASE Group, is a provider of independent semiconductor assembling and test manufacturing services, with its headquarters in Kaohsiung, Taiwan.
In the early twenty-first century; foreign investment, government regulations and incentives promoted growth in the Indian electronics industry. The semiconductor industry, which is its most important and resource-intensive sector, profited from the rapid growth in domestic demand. Many industries, including telecommunications, information technology, automotive, engineering, medical electronics, electricity and solar photovoltaic, defense and aerospace, consumer electronics, and appliances, required semiconductors. However, as of 2015, progress was threatened by the talent gap in the Indian sector, since 65 to 70 percent of the market was dependent on imports.
The semiconductor industry, including Integrated Circuit (IC) manufacturing, design, and packaging, forms a major part of Taiwan's IT industry. Due to its strong capabilities in OEM wafer manufacturing and a complete industry supply chain, Taiwan has been able to distinguish itself as a leading microchip manufacturer and dominate the global marketplace. Taiwan’s semiconductor sector accounted for US$115 billion, around 20 percent of the global semiconductor industry. In sectors such as foundry operations, Taiwanese companies account for 50 percent of the world market, with Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (TSMC) the biggest player in the foundry market.
The Chinese semiconductor industry, including integrated circuit design and manufacturing, forms a major part of mainland China's information technology industry.