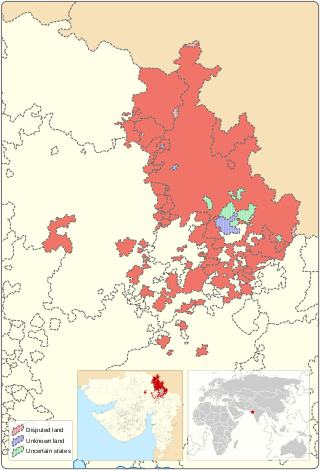
Mahi Kantha was a political agency or collection of princely states in British India, within the Gujarat Division of Bombay Presidency. In 1933, the states of the Mahi Kantha Agency, except for Danta, were included in the Western India States Agency. The total area of the agency was 8,094 km2 (3,125 sq mi); the population in 1901 was 361,545.

Rewa Kantha was a political agency of British India, managing the relations of the British government's Bombay Presidency with a collection of princely states. It stretched for about 150 miles between the plain of Gujarat and the hills of Malwa, from the Tapti River to the Mahi River crossing the Rewa River, from which it takes its name.
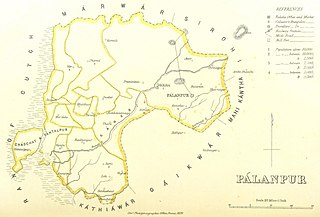
Palanpur Agency, also spelled Pahlunpore Agency, was a political agency or collection of princely states in British India, within the Gujarat Division of Bombay Presidency. In 1933, the native states of the Mahi Kantha Agency, except for Danta, were included in the Western India States Agency. The agency, headquartered at Palanpur, oversaw some 17 princely states and estates in the area, encompassing an area of 6393 square miles (16,558 km2) and a population, in 1901, of 467,271.

An agency of British India was an internally autonomous or semi-autonomous unit of British India whose external affairs were governed by an agent designated by the Viceroy of India.

Bhavnagar State was a princely state with 13 Gun Salutes during the British Raj. It was part of Kathiawar Agency in Saurashtra. The hereditary Kotwals of the royal palace of Bhavnagar were Talpada Kolis of Radhavanaj village of Kheda district.

Rajkot State was one of the princely states of India during the period of British rule. It was a 9-gun salute state belonging to the Kathiawar Agency of the Bombay Presidency. Its capital was in Rajkot, located in the historical Halar region of Kathiawar on the banks of the Aji River. Nowadays, Rajkot is the fourth largest city of Gujarat state.

Baroda State was a kingdom within the Maratha Confederacy and later a princely state in present-day Gujarat. It was ruled by the Gaekwad dynasty from its formation in 1721 until its accession to the newly formed Dominion of India in 1949. With the city of Baroda (Vadodara) as its capital, its relations with the British Raj authorities were managed by the Baroda Residency. The revenue of the state in 1901 was Rs. 13,661,000. Baroda formally acceded to the Dominion of India on 1 May 1949, before which an interim government was formed in the state.

Vav is a town and the headquarters of Vav Taluka in banaskantha district in Gujarat state of India. Vav is the largest taluka of the district.

Jambughoda is a Wildlife Sanctuary situated in Jambughoda Tehsil, in the South-Central part of Gujarat, and the Khathiar-Gir dry deciduous forests' ecoregion in India. It is located 70 km from Vadodara and 20 km from prominent tourist places such as Pawagadh and Champaner.

Palanpur State was a princely state of India during the British Raj. It was a Salute state with the Nawab of Palanpur having a hereditary salute of 13-guns. It was the main state of the Palanpur Agency. Palanpur State became a British protectorate in 1809/17; its capital was the city of Palanpur.

Jafarabad, or Jafrabad State, was a tributary princely state in India during the British Raj. It was located in the Kathiawar Peninsula on the Gujarat coast. The state had formerly been part of the Baroda Agency and later of the Kathiawar Agency of the Bombay Presidency.

The Kingdom of Santrampur or later Sant State was a kingdom and later a princely state in subsidiary alliance with British India. It was ruled by Mahipavat branch of the Paramara dynasty.

Morvi State, also spelled as Morvee State or Morbi State, was a princely salute state in the historical Halar prant (district) of Kathiawar during the British Raj.

Surgana State was a princely state of the Bombay Presidency during the era of the British Raj. It was the only state belonging to the Nasik Agency. Its capital was Surgana in Nashik District of present-day Maharashtra. It was ruled by Kolis of Pawar dynasty.

Baroda and Gujarat States Agency was a political agency of British India, managing the relations of the British government of the Bombay Presidency with a collection of princely states.

Lunavada State, also known as Lunawada State, was a princely state in India during the time of the British Raj. Its last ruler acceded to the Union of India on 10 June 1948.
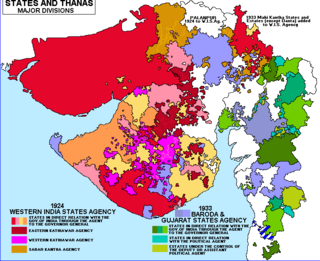
The Baroda, Western India and Gujarat States Agency was an agency of the Indian Empire, managing the relations of the Provincial Government of the Bombay Presidency with a collection of princely states.

Jhabua State was one of the princely states of India during the period of the British Raj. It had its capital in Jhabua town. Most of the territory of the princely state was inhabited by the Bhil people, who constituted a majority of the population. The revenue of the state in 1901 was Rs.1,10,000.

Radhanpur State was a kingdom and later princely state in India during the British Raj. Its rulers belonged to a family of Babi House, the state was once a polity within the Mughal Empire. The last ruling Nawab of Radhanpur, Nawab Murtaza Khan, signed the instrument of accession to the Indian Union on 10 June 1948.

Sanjeli, cotila or sometimes known as Sanjeda Mehvassi, is a Hindu former petty princely state, located in the present Gujarat state in western India.





















