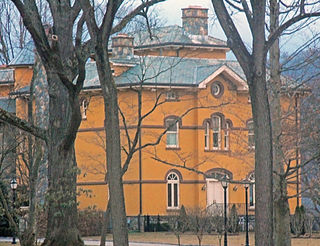The building at 38–48 Richardson Avenue is a historic residential rowhouse in Wakefield, Massachusetts. Built c. 1912, is believed to be one of the oldest rowhouses in the town. They were built by Solon O. Richardson, Jr., on a portion of his family's estate. The building was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1989.

The William King Beck House, also known as River Bluff Plantation, is a historic plantation house on the Alabama River near Camden, Alabama. The main house was built in 1845 for William King Beck and is attributed to architect Alexander J. Bragg. William King Beck was an attorney from North Carolina who migrated to Wilcox County in the 1820s. He was the nephew of William Rufus King, the 13th Vice President of the United States.

The William V. N. Barlow House is on South Clinton Street in Albion, New York, United States. It is a brick building erected in the 1870s in an eclectic mix of contemporary architectural styles, including Second Empire, Italianate, and Queen Anne. Its interior features highly intricate Eastlake style woodwork.

The Richmond Congregational Church is a historic church at 20 Church Street in Richmond, Vermont, United States. Built in 1903-04, it is a significant local example of Colonial Revival architecture, designed by prominent Vermont architect Walter R. B. Willcox. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 2001. The congregation is affiliated with the United Church of Christ; the minister is Rev. Katelyn Macrae.
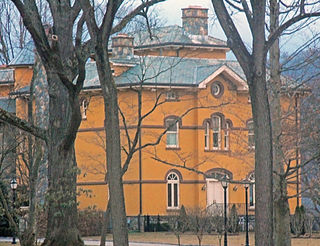
Rock Lawn is a historic house in Garrison, New York, United States. It was built in the mid-19th century from a design by architect Richard Upjohn. In 1982 it was listed on the National Register of Historic Places along with its carriage house, designed by Stanford White and built around 1880.

The James Gamble House is a historic building located in Le Claire, Iowa, United States. It has been listed on the National Register of Historic Places since 1979.

Belle Mina, known as Belmina during the 19th century, is a historic forced-labor farm and plantation house in Belle Mina, Alabama, United States. Completed in 1826, the Late Georgian-style house was built for Alabama's second governor, Thomas Bibb.

The Ingersoll Place Plat Historic District is located in Des Moines, Iowa, United States. It has been listed on the National Register of Historic Places since 2000. The historic significance of the district is based on the concentration of bungalows and square houses as well as a mix of subtypes.

The Bankhead House, also known as Sunset and the John Hollis Bankhead House, is a historic mansion in Jasper, Walker County, Alabama. It was added to the National Register of Historic Places on June 18, 1973.

The Maple Park Historic District is a historic neighborhood that lies northwest of the downtown of Lake Geneva, Wisconsin, United States. Part of the original city plat for Lake Geneva, it was first home to early settlers before the town became known as a retreat for wealthy Chicagoans. The district was added to the National Register of Historic Places in 2005.

The House at 1011 S. Madison Ave. is a historic house located at 1011 South Madison Avenue in Pasadena, California. Architect Sylvanus B. Marston of Marston, Van Pelt & Maybury designed the Prairie School style house, which was built in 1911. The two-story house has a square box plan inspired by a 1907 Frank Lloyd Wright design called "A Fireproof House for $50,000". The house has a horizontal emphasis characteristic of the Prairie School and a low hipped roof. A side porch is located on the north side of the house, which originally also had a front porch that has since been enclosed. Rows of casement windows on the front of each story feature a decorative pattern with three vertical panes and a transom.

The Downtown Chevron Station was a historic service station in Huntsville, Alabama. Built in 1919, it was one of the first buildings in the city tailored to the automobile. The center section of the station was built of brick in a style similar to other commercial and residential buildings in the area. The windows were large panes topped with three vertical panes, and the main entrance had a similar transom. The hipped roof extended from the building towards the corner of Clinton Avenue and Greene Street, providing cover for the pumps. Flat-roofed service bays with multi-pane sash windows were added along the Clinton Avenue side in 1929 and 1938. The building was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1980. It has been demolished since its listing, and a modern office building is on the site.

The Kildare–McCormick House is a historic residence in Huntsville, Alabama. The highly ornate, Queen Anne-style mansion was built in 1886–87. Its early owners contributed to the development of Huntsville, both through industrial projects and philanthropic efforts. The house was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1982.

The Phelps–Jones House is a historic residence in Huntsville, Alabama. One of the oldest buildings in Alabama, it was built in 1818, shortly after the initial federal land sale in Madison County in 1809. Despite having many owners, the original character of the house has remained. The two-story house is built of brick laid in Flemish bond, and has Federal and Georgian details. The original block has a bedroom and parlor separated by a central hall, with a dining room in an ell to the northeast. Staircases in the hall and dining room led to three bedrooms on the second floor. In 1956, a porch in the crook of the ell was enclosed, adding a bathroom and small bedroom. Another porch off the rear of the dining room was enclosed and converted into a kitchen. Interior woodwork, including six mantels, is in provincial Federal style. The façade is five bays wide, with twelve-over-twelve sash windows on the ground floor and twelve-over-eight on the second. A narrow hipped roof porch covers the double front door; originally a wider porch covered a single door flanked by narrow sidelights and topped with a transom. The house was listed on the Alabama Register of Landmarks and Heritage in 1979 and the National Register of Historic Places in 1982.

The Lincoln Mill and Mill Village Historic District is a historic district in Huntsville, Alabama. Opened in 1900, it quickly grew to be Huntsville's largest cotton mill in the first quarter of the 20th century. After closing in 1955, the mills were converted to office space that was used by the U.S. space program. Two of the older production buildings burned in 1980, but one main building and numerous houses built for workers remain. The district was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 2010.

The Ford–Countess House is a historic residence near Huntsville in Madison County, Alabama. Hezekiah Ford came to Madison County from Cumberland County, Virginia, in 1813, and began purchasing land on which to build a cotton plantation. He acquired the land on which the house stands in 1820, and built the two-story, brick I-house soon after. Ford died in 1839, and the land was owned by his wife, Nancy, until her death in 1844. Hezekiah's brother, John, then assumed ownership, and the plantation stayed in his family until 1904. It reached a peak of 280 acres, and the family owned 69 slaves in 1860. James W. Burcum owned the property from 1904 until 1911, when it was sold to Stephen H. Countess of Tuscaloosa. The Countess family still owns and farms the land, although the house has not been occupied since 1995.

The Ernest Edward Greene House is a historic residence in Cullman, Alabama. The house was built in 1913 by Ernest Edward Greene, the superintendent of Southern Cotton Oil Company. After Greene's death in 1922, the house was passed on to several more owners, including John George Luyben, Sr., who lived in the house for 34 years.

Nappanee Eastside Historic District is a national historic district located at Nappanee, Elkhart County, Indiana. The district encompasses 138 contributing buildings in a predominantly residential section of Nappanee. It was developed between about 1880 and 1940, and includes notable examples of Italianate, Queen Anne, Colonial Revival, and Prairie School style architecture. Located in the district are the separately listed Frank and Katharine Coppes House and Arthur Miller House.

The Goodwillie–Allen House is a small American Craftsman-style bungalow located in Bend, Oregon. The house was constructed in 1904 by Arthur Goodwillie, the first mayor of Bend. Today, the building is owned by the City of Bend. It is the oldest structure inside the city limits of Bend, the oldest American craftsman style house in Deschutes County, Oregon, and the second oldest craftsman-style bungalow in Oregon. The Goodwillie–Allen House was added to the National Register of Historic Places in 2007.

The East Side Historic District is a historic neighborhood of Stoughton, Wisconsin of stylish homes built mostly from 1890 to 1915. It was added to the State Register of Historic Places in 1996 and added to the National Register of Historic Places in the following year.