
George Gideon Oliver Osborne is a former British politician and newspaper editor who served as Chancellor of the Exchequer from 2010 to 2016 and as First Secretary of State from 2015 to 2016 in the Cameron government. A member of the Conservative Party, he was Member of Parliament (MP) for Tatton from 2001 to 2017. He was editor of the Evening Standard from 2017 to 2020.

Taxation in the United Kingdom may involve payments to at least three different levels of government: central government, devolved governments and local government. Central government revenues come primarily from income tax, National Insurance contributions, value added tax, corporation tax and fuel duty. Local government revenues come primarily from grants from central government funds, business rates in England, Council Tax and increasingly from fees and charges such as those for on-street parking. In the fiscal year 2014–15, total government revenue was forecast to be £648 billion, or 37.7 per cent of GDP, with net taxes and National Insurance contributions standing at £606 billion.
The 2005 Canadian federal budget was the budget of the Government of Canada for the 2005–2006 fiscal year. It was presented on February 23, 2005, by Finance Minister Ralph Goodale. It was the first Canadian federal budget presented by a minority government since the budget of the Joe Clark Progressive Conservative government in 1979, which was defeated by the opposition parties.
In the UK tax system, personal allowance is the threshold above which income tax is levied on an individual's income. A person who receives less than their own personal allowance in taxable income in a given tax year does not pay income tax; otherwise, tax must be paid according to how much is earned above this level. Certain residents are entitled to a larger personal allowance than others. Such groups include: the over-65s, blind people, and married couples where at least one person in the marriage was born before 6 April 1935. People earning over £100,000 a year have a smaller personal allowance. For every £2 earned above £100,000, £1 of the personal allowance is lost; meaning that incomes high enough will not have a personal allowance.

Gordon Brown's term as the prime minister of the United Kingdom began on 27 June 2007 when he accepted Queen Elizabeth II's invitation to form a new administration, replacing Tony Blair, and ended on 11 May 2010 upon his resignation. While serving as prime minister, Brown also served as the first lord of the treasury, the minister for the civil service, the leader of the Labour Party, and the Member of Parliament (MP) for Dunfermline East and later for Kirkcaldy and Cowdenbeath from 1983 to 2015.
The Canadian federal budget for the 2009-2010 fiscal year was presented to the House of Commons of Canada by Finance Minister Jim Flaherty on January 27, 2009. The federal budget included $40 billion in stimulus and $20 billion in personal income tax cuts.

David Cameron's term as the prime minister of the United Kingdom began on 11 May 2010, when he accepted Queen Elizabeth II's invitation to form a new administration, succeeding Gordon Brown of the Labour Party, and ended on 13 July 2016 upon his resignation. While serving as prime minister, Cameron also served as the first lord of the treasury, minister for the civil service and leader of the Conservative Party. He resigned following the 2016 referendum that favoured Brexit, which he had opposed.

The Conservative–Liberal Democrat coalition agreement was a policy document drawn up following the 2010 general election in the United Kingdom. It formed the terms of reference governing the Cameron–Clegg coalition, the coalition government comprising MPs from the Conservative Party and the Liberal Democrats.

The June 2010 United Kingdom Budget, officially also known as Responsibility, freedom, fairness: a five-year plan to re-build the economy, was delivered by George Osborne, Chancellor of the Exchequer, to the House of Commons in his budget speech that commenced at 12.33pm on Tuesday, 22 June 2010. It was the first budget of the Conservative-Liberal Democrat coalition formed after the general election of May 2010. The government dubbed it an "emergency budget", and stated that its purpose was to reduce the national debt accumulated under the Labour government.
Universal Credit is a United Kingdom social security payment. It is means-tested and is replacing and combining six benefits for working-age households with a low income: income-related Employment and Support Allowance, income-based Jobseeker's Allowance, and Income Support; Child Tax Credit and Working Tax Credit; and Housing Benefit. An award of UC is made up of different elements, which become payable to the claimant if relevant criteria apply: a standard allowance for singles or couples, child elements and disabled child elements for children in the household, housing cost element, childcare costs element, as well as elements for being a carer or having an illness or disability and therefore having limited capability to work.

The 2011 United Kingdom budget, officially called 2011 Budget – A strong and stable economy, growth and fairness, was delivered by George Osborne, the Chancellor of the Exchequer, to the House of Commons on 23 March 2011.
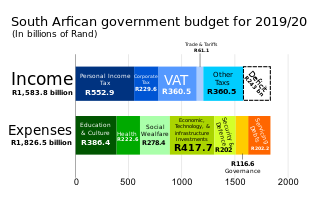
Taxation may involve payments to a minimum of two different levels of government: central government through SARS or to local government. Prior to 2001 the South African tax system was "source-based", where in income is taxed in the country where it originates. Since January 2001, the tax system was changed to "residence-based" wherein taxpayers residing in South Africa are taxed on their income irrespective of its source. Non residents are only subject to domestic taxes.

The United Kingdom government austerity programme is a fiscal policy that was adopted for a period in the early 21st century following the Great Recession. The term was used by the Coalition and Conservative governments in office from 2010 to 2019, and again during the 2021–present United Kingdom cost of living crisis.

The 2012 United Kingdom budget was delivered by George Osborne, the Chancellor of the Exchequer, to the House of Commons on Wednesday 21 March 2012.

The 2013 United Kingdom budget was delivered by George Osborne, the Chancellor of the Exchequer, to the House of Commons on Wednesday 20 March 2013.
This article details the fourteen austerity packages passed by the Government of Greece between 2010 and 2017. These austerity measures were a result of the Greek government-debt crisis and other economic factors. All of the legislation listed remains in force.
The 2013 Ontario budget, known as the Prosperous and Fair Ontario Act, is the budget for the province of Ontario for fiscal year 2013. It was presented to the Legislative Assembly of Ontario for its first reading on 2 May 2013 by Charles Sousa, the Minister of Finance of the Government of Ontario, and received Royal Assent on 13 June 2013.
Tuition fees in the United Kingdom were reintroduced for full-time resident students in 1998, as a means of funding tuition to undergraduate and postgraduate certificate students at universities. Since their introduction, the fees have been reformed multiple times by several bills, with the cap on fees notably rising to £9,000 a year for the 2012–13 academic year.

The March 2021 United Kingdom budget, officially known as Protecting the Jobs and Livelihoods of the British People was a budget delivered by Rishi Sunak, the Chancellor of the Exchequer in March 2021. It was expected to be delivered in Autumn 2020, but was postponed because of the COVID-19 pandemic. It succeeds the budget held in March 2020, and the summer statement and Winter Economy Plan held in summer and autumn 2020, respectively. The budget is the second under Boris Johnson's government, also the second to be delivered by Sunak and the second since Britain's withdrawal from the European Union. The budget was the first for government expenditure in the United Kingdom to exceed £1 trillion.

George Osborne served as Chancellor of the Exchequer from 2010 to 2016 in the Cameron–Clegg coalition and Cameron majority government. His tenure pursued austerity policies aimed at reducing the budget deficit and launched the Northern Powerhouse initiative. He had previously served as Shadow Chancellor of the Exchequer from 2005 to 2010. He was succeeded by Philip Hammond.








