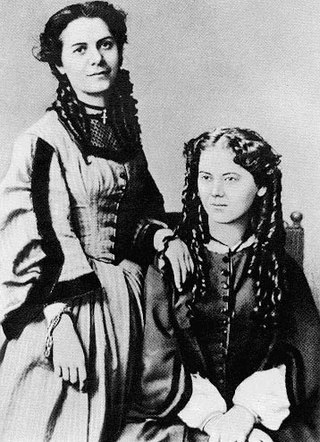Karl Marx was a German-born philosopher, economist, historian, sociologist, political theorist, journalist, critic of political economy, and revolutionary socialist. His best-known works are the 1848 pamphlet The Communist Manifesto and the three-volume Das Kapital (1867–1894); the latter employs his theory of historical materialism in an analysis of capitalism, representing his greatest intellectual achievement. His theories and ideas, and their subsequent development, are collectively known as Marxism, and have exerted enormous influence on intellectual, economic, and political history.

Friedrich Engels was a German philosopher, historian, political theorist, critic of political economy, and revolutionary socialist. He was also a businessman, journalist, and Karl Marx's closest friend and collaborator.

Johann Kaspar Schmidt, known professionally as Max Stirner, was a German post-Hegelian philosopher, dealing mainly with the Hegelian notion of social alienation and self-consciousness. Stirner is often seen as one of the forerunners of nihilism, existentialism, psychoanalytic theory, postmodernism and individualist anarchism.
The opium of the people or opium of the masses is a dictum used in reference to religion, derived from a frequently paraphrased partial statement of German sociologist and critic of political economy Karl Marx: "Religion is the opium of the people." In context, the statement is part of Marx's structural-functionalist argument that religion was constructed by people to calm uncertainty over their role in the universe and in society.

The Rheinische Zeitung was a 19th-century German newspaper, edited most famously by Karl Marx. The paper was launched in January 1842 and terminated by Prussian state censorship in March 1843. The paper was eventually succeeded by a daily newspaper launched by Karl Marx on behalf of the Communist League in June 1848, called the Neue Rheinische Zeitung.

The Neue Rheinische Zeitung: Organ der Demokratie was a German daily newspaper, published by Karl Marx in Cologne between 1 June 1848 and 19 May 1849. It is recognised by historians as one of the most important dailies of the Revolutions of 1848 in Germany. The paper was regarded by its editors and readers as the successor of an earlier Cologne newspaper, the Rheinische Zeitung, also edited for a time by Karl Marx, which had been suppressed by state censorship over five years earlier.

Revolution and Counter-Revolution in Germany is a book by Friedrich Engels, with contributions by Karl Marx. Originally a series of articles in the New York Daily Tribune published from 1851 to 1852 under Marx's byline, the material was first published in book form under the editorship of Eleanor Marx Aveling in 1896. It was not until 1913 that Engels' authorship was publicly known although some new editions continued to appear incorrectly listing Marx as the author as late as 1971.
Jenny Caroline Marx Longuet was the eldest daughter of Jenny von Westphalen Marx and Karl Marx. Briefly a political journalist writing under the pen name J. Williams, Longuet taught language classes and had a family of five sons and a daughter before her death to cancer at the age of 38.

Charles Félix César Longuet was a journalist and prominent figure in the French working-class movement, including the 1871 Paris Commune, as well as a Proudhonist member of the General Council of the First International or International Working Men's Association. He served as Corresponding Secretary for Belgium (1866), delegate to the Lausanne (1867), Brussels (1868), the London Conference (1871) and the (1872). He was also the editor of the publication Journal Officiel.

Influences on Karl Marx are generally thought to have been derived from three main sources, namely German idealist philosophy, French socialism and English and Scottish political economy.

Georg Friedrich Daumer was a German poet and philosopher. He was educated at the gymnasium of his native city, at that time directed by the famous philosopher Hegel.

Helene Demuth was a German housekeeper who worked for Jenny and Karl Marx, and later served as the household manager and political confidante of Friedrich Engels.

Marx/Engels Collected Works is the largest existing collection of English translations of works by Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels. Its 50 volumes contain publications by Marx and Engels released during their lifetimes, many unpublished manuscripts of Marx's economic writings, and extensive personal correspondence. The Collected Works, for the most part compiled by the Institute of Marxism-Leninism of the CC CPSU, was issued from 1975 to 2004 by Progress Publishers in collaboration with Lawrence and Wishart and International Publishers.
The Mountain, with its members collectively called Democratic Socialists, was a political group of the French Second Republic.
August Hermann Ewerbeck, known by his middle name of Hermann, was a pioneer socialist political activist, writer, and translator. A physician by vocation and a German by birth, Ewerbeck is best remembered as an early political associate of Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels, as a leader of the Parisian communities of the utopian socialist organization, League of the Just, and as the translator of the French writings of Étienne Cabet and Ludwig Feuerbach into German.

Manchester has historically influenced political and social thinking in Britain and been a hotbed for new, radical thinking, particularly during the Industrial Revolution.

The Poverty of Philosophy is a book by Karl Marx published in Paris and Brussels in 1847, where he lived in exile from 1843 until 1849. It was originally written in French as a critique of the economic and philosophical arguments of French anarchist Pierre-Joseph Proudhon set forth in his 1846 book The System of Economic Contradictions, or The Philosophy of Poverty.

Moses (Moritz) Hess was a German-Jewish philosopher, early communist and Zionist thinker. His socialist theories led to disagreements with Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels. He is considered a pioneer of Labor Zionism.
Edgar Marcel Longuet, was a French physician and socialist activist, and a grandson of Karl Marx.
Saul Kussiel Padover was a historian and political scientist at the New School for Social Research in New York City who wrote biographies of philosophers and politicians such as Karl Marx and Thomas Jefferson.