Related Research Articles
Most languages of Europe belong to the Indo-European language family. Out of a total European population of 744 million as of 2018, some 94% are native speakers of an Indo-European language; within Indo-European, the three largest phyla are Romance, Germanic, and Slavic with more than 200 million speakers each, between them accounting for close to 90% of Europeans. Smaller phyla of Indo-European found in Europe include Hellenic, Baltic, Albanian, Celtic and Indo-Aryan.
Ethnologue: Languages of the World is an annual reference publication in print and online that provides statistics and other information on the living languages of the world. It was first issued in 1951, and is now published annually by SIL International, a U.S.-based, worldwide, Christian non-profit organization. SIL's main purpose is to study, develop and document languages for religious purposes and to promote literacy.
Luhya is a Bantu language of western Kenya.

Ifugao or Batad is a Malayo-Polynesian language spoken in the northern valleys of Ifugao, Philippines. It is a member of the Northern Luzon subfamily and is closely related to the Bontoc and Kankanaey languages. It is a dialect continuum, and its four main varieties—such as Tuwali—are sometimes considered separate languages.
Wetarese is an Austronesian language of Wetar, an island in the south Maluku, Indonesia, and of the nearby islands Liran and Atauro, the latter island located in East Timor north of Dili.
Aer is an Indo-Aryan language spoken by 300 people in Sindh, Pakistan.
The Tharu or Tharuhat languages are any of the Indo-Aryan languages spoken by the Tharu people of the Terai region in Nepal, and neighboring regions of Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh and Bihar in India.
Central Tibetan, also known as Dbus, Ü or Ü-Tsang, is the most widely spoken Tibetic language and the basis of Standard Tibetan.
Yaka, also spelled Iaca and Iyaka, is a Bantu language spoken in the Democratic Republic of the Congo and Angola. There are two dialects, Yaka proper, which comprises 99% of speakers, and Ngoongo. The alleged varieties Pelende and Lonzo are political rather than ethnolinguistic entities.
The Ki language, Tuki, is a Southern Bantoid language of Cameroon.
Buyu, or Buyi, is a Bantu language of Lake Tanganyika that is closely related to Nyanga.
Bala (Lobala) is a Bantu language of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. According to Maho (2009), it includes Boko (Iboko).
Kayan is a dialect cluster spoken by the Kayan people of Borneo. It is a cluster of closely related dialects with limited mutual intelligibility, and is itself part of the Kayan-Murik group of Austronesian languages.
Kinabatangan is a language of Sabah.
Kulisusu is an Austronesian language of Southeast Sulawesi, Indonesia. It is part of a dialect chain with two minor languages, Koroni and Taloki.
Lamaholot, also known as Solor or Solorese, is a Central Malayo-Polynesian dialect cluster of Flores, Indonesia. The varieties may not be all mutually intelligible; Keraf (1978) reports that there are 18 languages under the name.
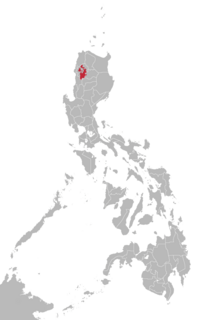
Itneg is a South-Central Cordilleran dialect continuum found in the island of Luzon, Philippines. This language and Ilocano are spoken by the Itneg people in Abra.
Kimaragang (Marigang), Tobilung, and Rungus are varieties of a single Austronesian language of Sabah, Malaysia. The three varieties share moderate mutual intelligibility. Children are not learning it well in some areas.
Masela (Marsela) is the language of Marsela Island in southern Maluku, Indonesia. Regional varieties are distinct; Ethnologue counts it as three languages.
References
- ↑ Labir language at Ethnologue (16th ed., 2009)
- ↑ Labir at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015)