
The TGV is France's intercity high-speed rail service, operated mainly by SNCF. SNCF worked on a high-speed rail network from 1966 to 1974 and presented the project to President Georges Pompidou who approved it. Originally designed as turbotrains to be powered by gas turbines, TGV prototypes evolved into electric trains with the 1973 oil crisis. In 1976 the SNCF ordered 87 high-speed trains from Alstom. Following the inaugural service between Paris and Lyon in 1981 on the LGV Sud-Est, the network, centered on Paris, has expanded to connect major cities across France and in neighbouring countries on a combination of high-speed and conventional lines. The TGV network in France carries about 110 million passengers a year.

The Société nationale des chemins de fer français is France's national state-owned railway company. Founded in 1938, it operates the country's national rail traffic along with Monaco, including the TGV, on France's high-speed rail network. Its functions include operation of railway services for passengers and freight, as well as maintenance and signalling of rail infrastructure. The railway network consists of about 35,000 km (22,000 mi) of route, of which 2,600 km (1,600 mi) are high-speed lines and 14,500 km (9,000 mi) electrified. About 14,000 trains are operated daily.

Gare Montparnasse, officially Paris Montparnasse, one of the seven large Paris railway termini, is located in the 14th and 15th arrondissements.

The Ligne à Grande Vitesse Nord, typically shortened to LGV Nord, is a French 333-kilometre (207 mi)-long high-speed rail line, opened in 1993, that connects Paris to the Belgian border and the Channel Tunnel via Lille.

The TGV Atlantique (TGV-A) is a class of high-speed trains used in France by SNCF; they were built by Alstom between 1988 and 1992, and were the second generation of TGV trains, following on from the TGV Sud-Est trainsets. The trains were named after the Ligne à Grande Vitesse Atlantique that they were originally built for.

The SNCF TGV Réseau (TGV-R) is a TGV train built by Alstom between 1992 and 1996 for SNCF, the French national railway for use on high-speed TGV services. The Réseau trainsets are based on the earlier TGV Atlantique. The first Réseau sets entered service in 1993.

The Ligne à Grande Vitesse Est européenne, typically shortened to LGV Est, is a French high-speed rail line that connects Vaires-sur-Marne and Vendenheim. The line halved the travel time between Paris and Strasbourg and provides fast services between Paris and the principal cities of Eastern France as well as Luxembourg and Germany. The LGV Est is a segment of the Main Line for Europe project to connect Paris with Budapest with high-speed rail service.

The SNCF TGV Sud-Est was a French high speed TGV train built by Alstom and Francorail-MTE and operated by SNCF, the French national railway company. A total of 111 trainsets were built between 1978 and 1988 for the first TGV service in France between Paris and Lyon which opened in 1981. The trainsets were semi-permanently coupled, consisting of two power cars (locomotives) and eight articulated passenger carriages, ten in the case of the tri-voltage sets. The trains were named after the Ligne à Grande Vitesse Sud-Est that they first operated on. They were also referred to as TGV-PSE, an abbreviation of Paris Sud-Est.

The LGV Atlantique is a high-speed rail line running from Gare Montparnasse in Paris towards the Atlantic coast of France. It opened in 1989–1990 and has two intermediate stations: Massy TGV station and Vendôme-Villiers-sur-Loir TGV station. It divides into two parts at Courtalain, one going westward to Le Mans, the second one going southwestward to Tours. Both branches have been extended, by the LGV Bretagne-Pays de la Loire and the LGV Sud Europe Atlantique.

The LGV Sud Europe Atlantique, also known as the LGV Sud-Ouest or LGV L'Océane, is a high-speed railway line between Tours and Bordeaux, in France. It is used by TGV trains operated by SNCF. It is an extension of the southern arm of the LGV Atlantique, with the western extension being LGV Bretagne-Pays de la Loire. Both extensions to the high-speed line were inaugurated on 28 February 2017, with services beginning on 2 July 2017. The line, which was at the time the biggest European railway construction project, was built by the LISEA consortium, which owns and maintains the line until 2061 and charges tolls to train companies. Trains on this line depart Paris from Gare Montparnasse.

The LGV Bretagne-Pays de la Loire is a French high-speed rail line running between Connerré, Sarthe near Le Mans and Cesson-Sévigné, Ille-et-Vilaine near Rennes.

The TGV Duplex is a French high-speed train of the TGV family, manufactured by Alstom, and operated by the French national railway company SNCF. They were the first TGV trainsets to use bi-level passenger carriages with a seating capacity of 508 passengers, increasing capacity on busy high-speed lines. While the TGV Duplex started as a small component of the TGV fleet, it has become one of the system's workhorses.
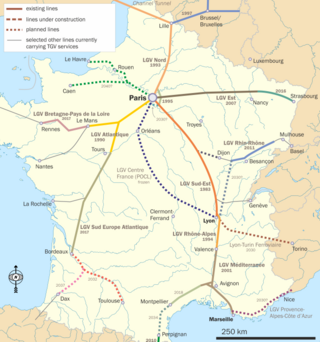
The LGV Bordeaux–Toulouse is a 222 kilometre (138 mi) long future French high-speed rail line reserved for passenger traffic between Bordeaux and Toulouse. Its dual aim is:

Champagne-Ardenne TGV station is a railway station located in Bezannes, France that opened in 2007 along with the first phase of the LGV Est, a high-speed rail line running from Paris to Strasbourg. It is situated about five kilometres south of Reims; the station is a stop for TGV, Ouigo and TER Grand Est services.

TGV Lyria is the brand name used for TGV railway lines connecting France and Switzerland. Lyria is also a corporation that runs the service using the staff of the SNCF in France and Swiss Federal Railways (SBB CFF FFS) in Switzerland – the staff consists of one French and one Swiss train manager on the whole journey.

The Renfe Class 100 is a high-speed train used for AVE services by the Renfe Operadora, in Spain. It was the first high-speed train put into service in Spain, in 1992.

France has a large network of high-speed rail lines. As of June 2021, the French high-speed rail network comprises 2,800 km (1,740 mi) of tracks, making it one of the largest in Europe and the world. As of early 2023, new lines are being constructed or planned. The first French high-speed railway, the LGV Sud-Est, linking the suburbs of Paris and Lyon, opened in 1981 and was at that time the only high-speed rail line in Europe.
Ouigo is a French low-cost service range of both conventional and high-speed trains. The literal translation of Ouigo from French to English is "yes go"; the name is also a play on words with the English homonym "we go." It is composed of two different services: Ouigo Grande Vitesse, which is a brand of SNCF operating high-speed trains; and Ouigo Vitesse Classique, a brand under which Oslo, a subsidiary of SNCF, operates conventional speed trains.

Avelia Euroduplex, more commonly known as just Euroduplex or TGV 2N2 in France, is a high-speed double-decker train manufactured by Alstom. It is primarily operated by the French national railway company SNCF, and also in operation with the Moroccan national railway company ONCF. It is the 3rd generation of the TGV Duplex.

TER Nouvelle-Aquitaine is the regional rail network serving the region of Nouvelle-Aquitaine, southwestern France. It is operated by the French national railway company SNCF. It was formed in 2017 from the previous TER networks TER Aquitaine, TER Limousin and TER Poitou-Charentes, after the respective regions were merged.



















