
Opabinia regalis is an extinct, stem group arthropod found in the Middle Cambrian Burgess Shale Lagerstätte of British Columbia. Opabinia was a soft-bodied animal, measuring up to 7 cm in body length, and its segmented trunk had flaps along the sides and a fan-shaped tail. The head shows unusual features: five eyes, a mouth under the head and facing backwards, and a clawed proboscis that probably passed food to the mouth. Opabinia probably lived on the seafloor, using the proboscis to seek out small, soft food. Fewer than twenty good specimens have been described; 3 specimens of Opabinia are known from the Greater Phyllopod bed, where they constitute less than 0.1% of the community.

Dinocaridida is a proposed fossil taxon of basal arthropods that flourished in the Cambrian period with occasional Ordovician and Devonian records. Characterized by a pair of frontal appendages and series of body flaps, the name of Dinocaridids refers to the suggested role of some of these members as the largest marine predators of their time. Dinocaridids are occasionally referred to as the 'AOPK group' by some literatures, as the group compose of Radiodonta, Opabiniidae, and the "gilled lobopodians" Pambdelurion and Kerygmachelidae. It is most likely paraphyletic, with Kerygmachelidae and Pambdelurion more basal than the clade compose of Opabiniidae, Radiodonta and other arthropods.

Anomalocaris is an extinct genus of radiodont, an order of early-diverging stem-group arthropods.

Peytoia is a genus of hurdiid radiodont, an early diverging order of stem-group arthropods, that lived in the Cambrian period, containing two species, Peytoia nathorsti from the Miaolingian of Canada and Peytoia infercambriensis from Poland, dating to Cambrian Stage 3. Its two frontal appendages had long bristle-like spines, it had no fan tail, and its short stalked eyes were behind its large head.

Anomalocarididae is an extinct family of Cambrian radiodonts, a group of stem-group arthropods.

Peytoia infercambriensis is a species of hurdiid radiodont in the genus Peytoia.
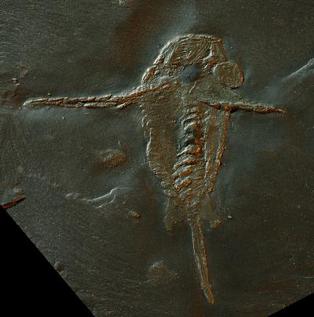
Schinderhannes bartelsi is a species of hurdiid radiodont (anomalocaridid) known from one specimen from the lower Devonian Hunsrück Slates. Its discovery was astonishing because previously, radiodonts were known only from exceptionally well-preserved fossil beds (Lagerstätten) from the Cambrian, 100 million years earlier.

Radiodonta is an extinct order of stem-group arthropods that was successful worldwide during the Cambrian period. They may be referred to as radiodonts, radiodontans, radiodontids, anomalocarids, or anomalocaridids, although the last two originally refer to the family Anomalocarididae, which previously included all species of this order but is now restricted to only a few species. Radiodonts are distinguished by their distinctive frontal appendages, which are morphologically diverse and used for a variety of functions. Radiodonts included the earliest large predators known, but they also included sediment sifters and filter feeders. Some of the most famous species of radiodonts are the Cambrian taxa Anomalocaris canadensis, Hurdia victoria, Peytoia nathorsti, Titanokorys gainessii, Cambroraster falcatus and Amplectobelua symbrachiata, the Ordovician Aegirocassis benmoulai and the Devonian Schinderhannes bartelsi.

Hurdia is an extinct genus of hurdiid radiodont that lived 505 million years ago during the Cambrian Period. Fossils have been found in North America, China and the Czech Republic.

Caryosyntrips ("nutcracker") is an extinct genus of stem-arthropod which known from Canada, United States and Spain during the middle Cambrian.
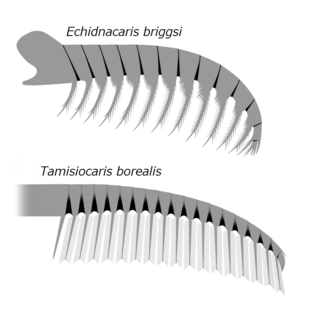
Tamisiocarididae is a family of radiodonts, extinct marine animals related to arthropods, that bore finely-spined appendages that were presumably used in filter-feeding. When first discovered, the clade was named Cetiocaridae after a speculative evolution artwork, Bearded Ceticaris by John Meszaros, that depicted a hypothetical filter-feeding radiodont at a time before any were known to exist. However, the family name was not valid according to the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature, as no real genus named "Cetiocaris" exists, and in 2019 it was formally replaced by the name Tamisiocarididae, after the only valid genus of the clade at the time. The family is only known from Series 2 of the Cambrian, unlike other radiodont families, which persisted longer into the Cambrian. All known species would have lived in tropical or subtropical waters, suggesting a preference for warmer waters.

Amplectobeluidae is a clade of Cambrian radiodonts. It currently includes five definitive genera, Amplectobelua, Lyrarapax, Ramskoeldia, Guanshancaris and a currently unnamed genus from the lower Cambrian aged Sirius Passet site in Greenland. There is also a potential fifth genus, Houcaris, but that genus has become problematic in terms of its taxonomic placement.

Hurdiidae is an extinct cosmopolitan family of radiodonts, a group of stem-group arthropods, which lived during the Paleozoic Era. It is the most long-lived radiodont clade, lasting from the Cambrian period to the Devonian period.

Ramskoeldia is a genus of amplectobeluid radiodont described in 2018. It was the second genus of radiodont found to possess gnathobase-like structures and an atypical oral cone after Amplectobelua. It was discovered in the Chengjiang biota of China, the home of numerous radiodontids such as Amplectobelua and Lyrarapax.

Ursulinacaris is a genus of hurdiid radiodont from the Cambrian of North America. It contains one known species, Ursulinacaris grallae. It was described in 2019, based on fossils of the frontal appendages discovered in the 1990s and thereafter. The endites of Ursulinacaris were very slender, unlike other hurdiids such as Peytoia or Hurdia. It was initially reported as the first hurdiid with paired endites, but Moysiuk & Caron (2021) suggested that it is actually the preservation of the fossils and thus no paired endites.

Kylinxia is a genus of extinct arthropod described in 2020. It was described from six specimens discovered in Yu'anshan Formation in southern China. The specimens are assigned to one species Kylinxia zhangi. Dated to 518 million years, the fossils falls under the Cambrian period. Announcing the discovery on 4 November 2020 at a press conference, Zeng Han of the Nanjing Institute of Geology and Paleontology, said that the animal "bridges the evolutionary gap from Anomalocaris to true arthropods and forms a key ‘missing link’ in the origin of arthropods," which was "predicted by Darwin’s evolutionary theory." The same day the formal description was published in Nature.

Houcaris is a possibly paraphyletic radiodont genus, tentatively assigned to either Amplectobeluidae, Anomalocarididae or Tamisiocarididae, known from Cambrian Series 2 of China and the United States. It contains two species, Houcaris saron and Houcaris magnabasis, both of which were originally named as species of the related genus Anomalocaris. The genus Houcaris was established for the two species in 2021 and honors Hou Xianguang, who had discovered and named the type species Anomalocaris saron in 1995 along with his colleagues Jan Bergström and Per E. Ahlberg.

Laminacaris is a genus of extinct stem-group arthropods (Radiodonta) that lived during the Cambrian period. It is monotypic with a single species Laminacaris chimera, the fossil of which was described from the Chengjiang biota of China in 2018. Around the same time, two specimens that were similar or of the same species were discovered at the Kinzers Formation in Pennsylvania, USA. The first specimens from China were three frontal appendages, without the other body parts.
Innovatiocaris is a genus of radiodont of uncertain family from the early Cambrian Chengjiang Lagerstätte of Yunnan Province, China. The genus contains two named species, I. maotianshanensis, known from a nearly complete individual measuring over 14.6 cm (5.7 in) and isolated frontal appendages, and I.? multispiniformis, known from a complete frontal appendage.
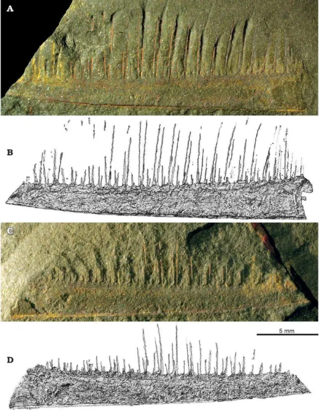
Pseudoangustidontus is a genus of hurdiid radiodont from the Lower Ordovician of Morocco. This genus is known from two described species, P. duplospineus and P. izidigua, with some specimens that are hard to determine which species to belong to. This animal is only known from the Fezouata Formation, a fossil site in Morocco that is of Lagerstätte status, meaning that the fossils from this site are exceptionally preserved. Because of its partial remains, its classification was debated, but with more complete fossils it is identified as radiodont frontal appendage.




















