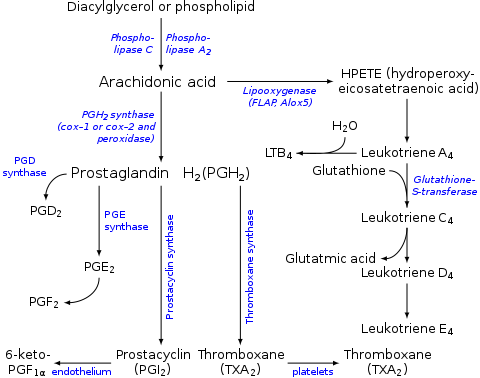
Leukotrienes are a family of eicosanoid inflammatory mediators produced in leukocytes by the oxidation of arachidonic acid (AA) and the essential fatty acid eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) by the enzyme arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase.

Angiogenin (Ang) also known as ribonuclease 5 is a small 123 amino acid protein that in humans is encoded by the ANG gene. Angiogenin is a potent stimulator of new blood vessels through the process of angiogenesis. Ang hydrolyzes cellular RNA, resulting in modulated levels of protein synthesis and interacts with DNA causing a promoter-like increase in the expression of rRNA. Ang is associated with cancer and neurological disease through angiogenesis and through activating gene expression that suppresses apoptosis.

Leukotriene C4 (LTC4) is a leukotriene. LTC4 has been extensively studied in the context of allergy and asthma. In cells of myeloid origin such as mast cells, its biosynthesis is orchestrated by translocation to the nuclear envelope along with co-localization of cytosolic phospholipase A2 (cPLA2), Arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase (5-LO), 5-lipoxygenase-activating protein (FLAP) and LTC4 synthase (LTC4S), which couples glutathione to an LTA4 intermediate. The MRP1 transporter then secretes cytosolic LTC4 and cell surface proteases further metabolize it by sequential cleavage of the γ-glutamyl and glycine residues off its glutathione segment, generating the more stable products LTD4 and LTE4. All three leukotrienes then bind at different affinities to two G-protein coupled receptors: CYSLTR1 and CYSLTR2, triggering pulmonary vasoconstriction and bronchoconstriction.

Leukotriene A4 hydrolase, also known as LTA4H is a human gene. The protein encoded by this gene is a bifunctional enzyme which converts leukotriene A4 to leukotriene B4 and acts as an aminopeptidase.

Cysteinyl leukotriene receptor 1, also termed CYSLTR1, is a receptor for cysteinyl leukotrienes (LT). CYSLTR1, by binding these cysteinyl LTs contributes to mediating various allergic and hypersensitivity reactions in humans as well as models of the reactions in other animals.

Glycylpeptide N-tetradecanoyltransferase 1 also known as myristoyl-CoA:protein N-myristoyltransferase 1 (NMT-1) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the NMT1 gene. It belongs to the protein N-terminal methyltransferase and glycylpeptide N-tetradecanoyltransferase family of enzymes.
Regulator of G-protein signaling 19 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RGS19 gene.
Glutathione S-transferase Mu 4 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the GSTM4 gene.

Microsomal glutathione S-transferase 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MGST1 gene.

Pancreatic secretory granule membrane major glycoprotein GP2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GP2 gene.

PGDS protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HPGDS gene.

In molecular biology the MAPEG family of proteins are a group of membrane associated proteins with highly divergent functions. Included are the 5-lipoxygenase-activating protein, leukotriene C4 synthase, which catalyzes the production of leukotriene C4 (LTC4) from leukotriene A4 (LTA4), and microsomal glutathione S-transferase II (GST-II), which also produces LTC4 from LTA4.

Aquaporin-5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the AQP5 gene.

FK506-binding protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FKBP2 gene.
Alpha-1,3-mannosyl-glycoprotein 2-beta-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MGAT1 gene.

FRAS1-related extracellular matrix protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FREM2 gene.

Microsomal glutathione S-transferase 2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MGST2 gene.

Microsomal prostaglandin E synthase-1 (mPGES-1) or Prostaglandin E synthase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PTGES gene.

Microsomal glutathione S-transferase 3 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MGST3 gene.
Eoxins are proposed to be a family of proinflammatory eicosanoids. They are produced by human eosinophils, mast cells, the L1236 Reed–Sternberg cell line derived from Hodgkin's lymphoma, and certain other tissues. These cells produce the eoxins by initially metabolizing arachidonic acid, an omega-6 (ω-6) fatty acid, via any enzyme possessing 15-lipoxygenase activity. The product of this initial metabolic step, 15(S)-hydroperoxyeicosatetraenoic acid, is then converted to a series of eoxins by the same enzymes that metabolize the 5-lipoxygenase product of arachidonic acid metabolism, i.e. 5-Hydroperoxy-eicosatetraenoic acid to a series of leukotrienes. That is, the eoxins are 14,15-disubstituted analogs of the 5,6-disubstituted leukotrienes.