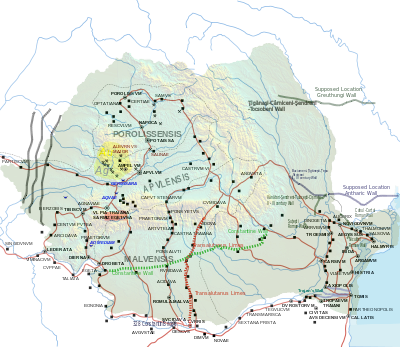
Dacia was the land inhabited by the Dacians, its core in Transylvania, stretching to the Danube in the south, the Black Sea in the east, and the Tisza in the west. The Carpathian Mountains were located in the middle of Dacia. It thus roughly corresponds to present-day Romania, as well as parts of Moldova, Bulgaria, Serbia, Hungary, Slovakia, and Ukraine.
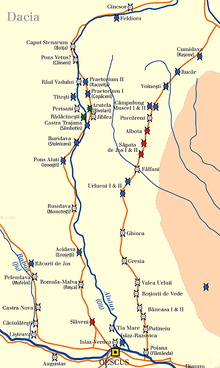
Romula or Malva was an ancient city in Roman Dacia, later the village of Reşca, Dobrosloveni Commune, Olt County, Romania. It was the capital of Dacia Malvensis, one of the three subdivisions of the province of Dacia.

Trajan's Wall is the name used for several linear earthen fortifications (valla) found across Eastern Europe, Moldova, Romania, and Ukraine. Contrary to the name and popular belief, the ramparts were not built by Romans during Trajan's reign, but during other imperial periods. Furthermore, the association with the Roman Emperor may be a recent scholarly invention, only entering the imagination of the locals with the national awakening of the 19th century. Medieval Moldavian documents referred to the earthworks as Troian, likely in reference to a mythological hero in the Romanian and Slavic folklore. The other major earthen fortification in Romania, Brazda lui Novac, is also named after a mythological hero.

Porolissum was an ancient Roman city in Dacia. Established as a military fort in 106 during Trajan's Dacian Wars, the city quickly grew through trade with the native Dacians and became the capital of the province Dacia Porolissensis in 124. The site is one of the largest and best-preserved archaeological sites in modern-day Romania. It is 8 km away from the modern city of Zalău, in Moigrad-Porolissum village, Mirsid Commune, Sălaj County.
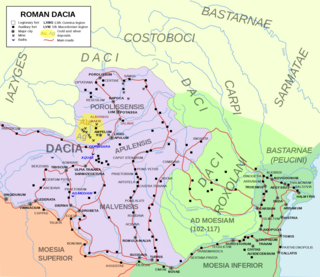
Located in Roman province of Dacia, present-day Romania, the Limes Porolissensis was a frontier of the Roman empire in Dacia Porolissensis, the northernmost of the three Dacian provinces. It was a defensive line dating from the 2nd century AD after the Conquest of Dacia. The frontier was a complex network of over 100 observation towers, fortlets, walls and forts disposed in a line over 200 km from the Apuseni Mountains to the Eastern Carpathians, following the highland chain of the Meseș Mountains.

The Moesian Limes is the modern term given to a linked series of Roman forts on the northern frontier of the Roman province of Moesia along the Danube between the Black Sea shore and Pannonia and dating from the 1st century AD. It was the eastern section of the so-called Danubian Limes and protected the Roman provinces of Upper and Lower Moesia south of the river. The eastern section is often called the limes Scythiae minoris as it was located in the late Roman province of Scythia Minor.

The Limes Alutanus was a fortified eastern border of the ancient Roman province of Dacia built by the Roman emperor Hadrian to stop invasions and raids from the east.

Brazda lui Novac is a Roman frontier system (limes) in present-day Romania, known also as Constantine's Wall. It is believed by some historians to border Ripa Gothica.

Acidava (Acidaua) was a Dacian and later Roman town and fort on the Olt river near the lower Danube. The settlement's remains are located in today's Enoşeşti, Olt County, Oltenia, Romania.
Amutria was a Dacian town close to the Danube and included in the Roman road network, after the conquest of Dacia.

Cumidava was originally a Dacian settlement, and later a Roman military camp on the site of the modern city of Râșnov in Romania.

Capidava was originally an important Geto-Dacian centre on the right bank of the Danube. After the Roman conquest, it became a civil and military centre in the province of Moesia Inferior and part of the defensive frontier system of the Moesian Limes along the Danube.

Arutela was an ancient Roman fort in the Roman province of Dacia today near the town Călimănești. It lies on the left bank of the Olt River. It was part of the Roman frontier system of the Limes Alutanus,

Castra Buridava was a fort in the Roman province of Dacia, part of the frontier system of the Limes Alutanus, and near the Dacian and Roman town of Buridava.

Cumidava was a fort in the Roman province of Dacia Apulensis. It is located at 4 km (2.5 mi) northwest of the city Râșnov, Romania near the city of Vulcan. The site is located on the middle terrace of Bârsa River.
Jidava was a fort in the Roman province of Dacia 4 km southwest of the town of Campulung, Romania. It was built around 190–211 AD as part of the frontier system of the Limes Transalutanus located approximately 20 km south of the Rucÿr-Bran pass.
Caput Stenarum was a fort in the Roman province of Dacia in the 2nd century AD. It is located 700 m east of the village Boița in Romania at the northern exit of the Olt gorge.
The castra of Drumul Carului was a fort in the Roman province of Dacia near Moieciu, Romania.

Praetorium I (Copăceni) was a fort in the Roman province of Dacia near the present village of Copăceni, Racovița, Vâlcea, Romania. It was part of the Roman frontier system of the Limes Alutanus along the Olt (river). It was built in 138 and reinforced with two towers two years later.

The Dacian Limes is the generic modern term given to a collection of ramparts and linked series of Roman forts on the frontiers of the Roman province of Dacia dating from the early 2nd century AD. They ran for about 1,000 km and included the: