
Calligra Suite is a graphic art and office suite by KDE. It is available for desktop PCs, tablet computers, and smartphones. It contains applications for word processing, spreadsheets, presentation, databases, vector graphics, and digital painting.

Knoppix, stylized KNOPPIX, is an operating system based on Debian designed to be run directly from a CD / DVD or a USB flash drive. It was first released in 2000 by German Linux consultant Klaus Knopper, and was one of the first popular live distributions. Knoppix is loaded from the removable medium and decompressed into a RAM drive. The decompression is transparent and on-the-fly.

c't – Magazin für Computertechnik is a German computer magazine, published by the Heinz Heise publishing house.

LinuxTag was an annual Free and Open Source Software (FOSS) conference and exposition with an emphasis on Linux but also BSD descendants located in Germany. The name is a compound with the German Tag meaning "Day", as it was initially a single day conference, but soon extended to multiple days, then always including a weekend. LinuxTag was the world's largest FLOSS conference and exhibition for years and aimed to provide a comprehensive overview of the Linux and Free Software market as well to promote contacts between users and developers. With this broad approach LinuxTag was one of the most important events of this kind.
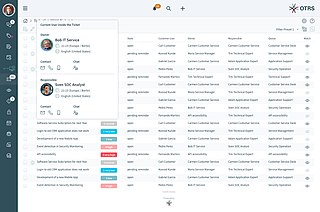
OTRS is a service management suite. The suite contains an agent portal, admin dashboard and customer portal. In the agent portal, teams process tickets and requests from customers. There are various ways in which this information, as well as customer and related data can be viewed. As the name implies, the admin dashboard allows system administrators to manage the system: Options are many, but include roles and groups, process automation, channel integration, and CMDB/database options. The third component, the customer portal, is much like a customizable webpage where information can be shared with customers and requests can be tracked on the customer side.

Georg C. F. Greve is a software developer, physicist, author and currently co-founder and president at Vereign. He has been working on technology politics since he founded the Free Software Foundation Europe (FSFE) in 2001.

Linux Format is the UK's first Linux-specific magazine, and as of 2013 was the best-selling Linux title in the UK. It is also exported to many countries worldwide. It is published by Future plc. Linux Format is commonly abbreviated to LXF, and issues are referred to with LXF as a prefix followed by the issue number.

Jon "maddog" Hall is the board chair for the Linux Professional Institute.

Free and open-source software (FOSS) is a term used to refer to groups of software consisting of both free software and open-source software, where anyone is freely licensed to use, copy, study, and change the software in any way, and the source code is publicly available so that people are encouraged to improve the design of the software. This is in contrast to proprietary software, where the software is under restrictive copyright or licensing and the source code is hidden from the users.

Trisquel is a computer operating system, a Linux distribution, derived from another distribution, Ubuntu. The project aims for a fully free software system without proprietary software or firmware and uses a version of Ubuntu's modified kernel, with the non-free code removed. Trisquel relies on user donations. Its logo is a triskelion, a Celtic symbol. Trisquel is listed by the Free Software Foundation as a distribution that contains only free software.
Video Disk Recorder (VDR) is an open-source application for Linux designed to allow any computer to function as a digital video recorder, in order to record and replay TV programming using the computer's hard drive. The computer needs to be equipped with a digital TV tuner card. VDR can also operate as an mp3 player and DVD player using available plugins. VDR uses drivers from the LinuxTV project. VDR was originally written by Klaus-Peter Schmidinger, one of the founders of CadSoft Computer GmbH and original developer of the EAGLE electronic design application. The software was originally hosted on CadSoft's server.

Elektor, also known as Elektor Magazine, is a monthly magazine about all aspects of electronics, originally published in the Netherlands as Elektronica Wereld in 1961 and latterly Elektuur in 1964, and now published worldwide in many languages including English, German, Dutch, French, Greek, Spanish, Swedish, Portuguese and Italian with distribution in over 50 countries. The English language edition of Elektor was launched in 1975 and is read worldwide.

Ubuntu User is a paper magazine that was launched by Linux New Media AG in May 2009.

Widelands is a free and open-source, slow-paced real-time strategy video game under the GNU General Public License. Widelands takes many ideas from and is quite similar to The Settlers and The Settlers II. It remains a work-in-progress game, with development still required in graphics and bug-fixing. The game runs on several operating systems such as AmigaOS 4, Linux, BSD, Mac OS X, and Windows.

The Open Source Business Alliance - Bundesverband für digitale Souveränität e.V. is a German non-profit that operates Europe's biggest network of companies and organizations developing, building and using open source software.
Caldera was a US-based software company founded in 1994 to develop Linux- and DOS-based operating system products.
Long-term support (LTS) is a product lifecycle management policy in which a stable release of computer software is maintained for a longer period of time than the standard edition. The term is typically reserved for open-source software, where it describes a software edition that is supported for months or years longer than the software's standard edition.

BlueSpice is free wiki software based on the MediaWiki engine and licensed with the GNU General Public License. It is especially developed for businesses as an enterprise wiki distribution for MediaWiki and used in over 150 countries.

Computec Media GmbH is a German computer media company headquartered in Fürth. It is a subsidiary of the Swiss Marquard Media Group. The company publishes multiple magazines and websites related to computers, video gaming and media.
















