High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), formerly referred to as high-pressure liquid chromatography, is a technique in analytical chemistry used to separate, identify, and quantify specific components in mixtures. The mixtures can originate from food, chemicals, pharmaceuticals, biological, environmental and agriculture, etc., which have been dissolved into liquid solutions.
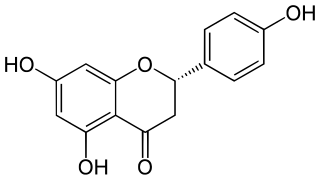
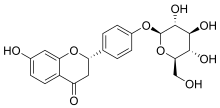
Naringenin is a flavanone from the flavonoid group of polyphenols. It is commonly found in citrus fruits, especially as the predominant flavonone in grapefruit.
Chiral column chromatography is a variant of column chromatography that is employed for the separation of chiral compounds, i.e. enantiomers, in mixtures such as racemates or related compounds. The chiral stationary phase (CSP) is made of a support, usually silica based, on which a chiral reagent or a macromolecule with numerous chiral centers is bonded or immobilized.

Daidzein is a naturally occurring compound found exclusively in soybeans and other legumes and structurally belongs to a class of compounds known as isoflavones. Daidzein and other isoflavones are produced in plants through the phenylpropanoid pathway of secondary metabolism and are used as signal carriers, and defense responses to pathogenic attacks. In humans, recent research has shown the viability of using daidzein in medicine for menopausal relief, osteoporosis, blood cholesterol, and lowering the risk of some hormone-related cancers, and heart disease. Despite the known health benefits, the use of both puerarin and daidzein is limited by their poor bioavailability and low water solubility.
Nanchang District is one of six urban districts of Wuxi, Jiangsu province, China.
Mixed-mode chromatography (MMC), or multimodal chromatography, refers to chromatographic methods that utilize more than one form of interaction between the stationary phase and analytes in order to achieve their separation. What is distinct from conventional single-mode chromatography is that the secondary interactions in MMC cannot be too weak, and thus they also contribute to the retention of the solutes.

Piceid is a stilbenoid glucoside and is a major resveratrol derivative in grape juices. It can be found in the bark of Picea sitchensis. It can also be isolated from Reynoutria japonica, the Japanese knotweed.
Shō-saiko-tō (小柴胡湯), also known as minor bupuleurum formula and xiǎocháihútāng (XCHT), is a herbal supplement, believed to enhance liver health. Sho-Saiko-To is a widely used prescription drug in China and is a listed formula in China and Japan as a Kampo medicine. There are currently ongoing clinical trials for Sho-Saiko-To at University of California, San Diego and Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center. The active ingredients of sho-saiko-to discovered so far include baicalin, baicalein, glycyrrhizin, saikosaponins, ginsenosides, wogonin, and gingerol.

Leonurine is a pseudoalkaloid that has been isolated from Leonotis leonurus, Leonotis nepetifolia, Leonurus japonicus, Leonurus cardiaca (motherwort), Leonurus sibiricus, as well as other plants of family Lamiaceae. Leonurine is easily extracted into water.

Salidroside (rhodioloside) is a glucoside of tyrosol found in the plant Rhodiola rosea. It has been studied, along with rosavin, as one of the potential compounds responsible for the putative antidepressant and anxiolytic actions of this plant. Salidroside may be more active than rosavin, even though many commercially marketed Rhodiola rosea extracts are standardized for rosavin content rather than salidroside.

Orientin is a flavone, a chemical flavonoid-like compound. It is the 8-C glucoside of luteolin.

Butin is a flavanone, a type of flavonoid. The compound can be found in the seeds of Vernonia anthelmintica (Asteraceae) and in the wood of Dalbergia odorifera (Fabaceae).
A chromatography detector is a device that detects and quantifies separated compounds as they elute from the chromatographic column. These detectors are integral to various chromatographic techniques, such as gas chromatography, liquid chromatography, and high-performance liquid chromatography, and supercritical fluid chromatography among others. The main function of a chromatography detector is to translate the physical or chemical properties of the analyte molecules into measurable signal, typically electrical signal, that can be displayed as a function of time in a graphical presentation, called a chromatograms. Chromatograms can provide valuable information about the composition and concentration of the components in the sample.

Huáng bǎi, huáng bó or huáng bò is one of the fifty fundamental herbs of traditional Chinese medicine. Known also as Cortex Phellodendri, it is the bark of one of two species of Phellodendron tree: Phellodendron amurense or Phellodendron chinense.

Countercurrent chromatography is a form of liquid–liquid chromatography that uses a liquid stationary phase that is held in place by inertia of the molecules composing the stationary phase accelerating toward the center of a centrifuge due to centripetal force and is used to separate, identify, and quantify the chemical components of a mixture. In its broadest sense, countercurrent chromatography encompasses a collection of related liquid chromatography techniques that employ two immiscible liquid phases without a solid support. The two liquid phases come in contact with each other as at least one phase is pumped through a column, a hollow tube or a series of chambers connected with channels, which contains both phases. The resulting dynamic mixing and settling action allows the components to be separated by their respective solubilities in the two phases. A wide variety of two-phase solvent systems consisting of at least two immiscible liquids may be employed to provide the proper selectivity for the desired separation.

Smilax glabra, sarsaparilla, is a plant species in the genus Smilax. It is native to China, the Himalayas, and Indochina.
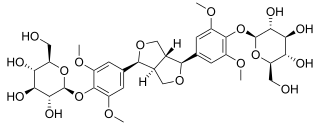
Eleutheroside D is an eleutheroside. An eleutheroside is a compound found in Eleutherococcus senticosus, the Siberian ginseng. Chemically, it is a dimer of sinapyl alcohol glucoside, and is an optical isomer of Eleutheroside E. Eleutheroside D and E are thought to be the most pharmacologically active out of the eleutherosides.

Phillyrin is an endophytic fungal isolate with anti-obesity activity. It can be produced by Colletotrichum gloeosporioides, an endophytic fungus isolated from Forsythia suspensa. It can also be prepared directly from Forsythia suspensa.

Pholiota adiposa is a slimy, scaly, yellow-brown mushroom. It is edible, and found in North America, Europe, and Asia. It grows parasitically or saprotrophically, most often on beech species, fruiting in bunches between August and November. Several compounds produced by this mushroom, for example methyl gallate, are of interest for their medicinal properties.
A phosphate phosphite is a chemical compound or salt that contains phosphate and phosphite anions (PO33- and PO43-). These are mixed anion compounds or mixed valence compounds. Some have third anions.