See also
Helicopters and rotorcraft | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Helicopters |
| |||||
| Rotorcraft |
| |||||
| Hazards |
| |||||
| Related | ||||||
| NATO reporting name | Common name |
|---|---|
| Haitun | Harbin Z-9 |
| Halo | Mil Mi-26 |
| Hare | Mil Mi-1 |
| Harke | Mil Mi-10 |
| Harp | Kamov Ka-20 |
| Hat | Kamov Ka-10 |
| Havoc | Mil Mi-28 |
| Haze | Mil Mi-14 |
| Helix | Kamov Ka-27/29/32 |
| Hen | Kamov Ka-15 |
| Hermit | Mil Mi-34 |
| Hind | Mil Mi-24 |
| Hip | Mil Mi-8/9/17 |
| Hog | Kamov Ka-18 |
| Hokum | Kamov Ka-50/52 |
| Homer | Mil V-12 |
| Hoodlum | Kamov Ka-26/126 |
| Hook | Mil Mi-6 |
| Hoop | Kamov Ka-22 |
| Hoplite | Mil Mi-2 |
| Hormone | Kamov Ka-25 |
| Horse | Yakovlev Yak-24 |
| Hound | Mil Mi-4 |

The Kosovo War was an armed conflict in Kosovo that started 28 February 1998 and lasted until 11 June 1999. It was fought by the forces of the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, which controlled Kosovo before the war, and the Kosovo Albanian rebel group known as the Kosovo Liberation Army (KLA). The conflict ended when the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) intervened by beginning air strikes in March 1999 which resulted in Yugoslav forces withdrawing from Kosovo.

The North Atlantic Treaty Organization, also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance among 28 European countries and 2 North American countries. Established in the aftermath of World War II, the organization implements the North Atlantic Treaty, signed 4 April 1949.
NATO reporting names are code names for military equipment from Russia, China, and historically, the Eastern Bloc. They provide unambiguous and easily understood English words in a uniform manner in place of the original designations, which either may have been unknown to the Western world at the time or easily confused codes. For example, the Russian bomber jet Tupolev Tu-160 is simply called "Blackjack".

The Warsaw Treaty Organization (WTO), officially the Treaty of Friendship, Cooperation and Mutual Assistance, commonly known as the Warsaw Pact (WP), was a collective defense treaty signed in Warsaw, Poland, between the Soviet Union and seven other Eastern Bloc socialist republics of Central and Eastern Europe in May 1955, during the Cold War. The Warsaw Pact was the military complement to the Council for Mutual Economic Assistance (CoMEcon), the regional economic organization for the socialist states of Central and Eastern Europe. The Warsaw Pact was created in reaction to the integration of West Germany into NATO in 1955 as per the London and Paris Conferences of 1954.

Jens Stoltenberg is a Norwegian politician who is serving as the 13th secretary general of NATO since 2014. A member of the Labour Party, he previously served as the 34th prime minister of Norway from 2000 to 2001 and again from 2005 until 2013.

The North Atlantic Treaty Organisation (NATO) carried out an aerial bombing campaign against the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia during the Kosovo War. The air strikes lasted from 24 March 1999 to 10 June 1999. The bombings continued until an agreement was reached that led to the withdrawal of Yugoslav armed forces from Kosovo, and the establishment of the United Nations Interim Administration Mission in Kosovo, a UN peacekeeping mission in Kosovo. The official NATO operation code name was Operation Allied Force whereas the United States called it Operation Noble Anvil; in Yugoslavia the operation was incorrectly called Merciful Angel as a result of a misunderstanding or mistranslation.

Supreme Headquarters Allied Powers Europe (SHAPE) is the headquarters of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization's Allied Command Operations (ACO). Since 1967 it has been located in Casteau, north of the Belgian city of Mons, but it had previously been located, from 1953, at Rocquencourt, next to Versailles, France. From 1951 to 2003, SHAPE was the headquarters of Allied Command Europe (ACE). Since 2003 it has been the headquarters of Allied Command Operations, controlling all NATO operations worldwide.

Killed in action (KIA) is a casualty classification generally used by militaries to describe the deaths of their own personnel at the hands of enemy or hostile forces. The United States Department of Defense, for example, says that those declared KIA did not need to have fired their weapons, but only to have been killed due to hostile attack. KIAs include those killed by friendly fire in the midst of combat, but not from incidents such as accidental vehicle crashes, murder or other non-hostile events or terrorism. KIA can be applied both to front-line combat troops and to naval, air and support troops. Someone who is killed in action during a particular event is denoted with a † (dagger) beside their name to signify their death in that event or events.

The Partnership for Peace (PfP) is a North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) program aimed at creating trust between NATO and other states in Europe and the former Soviet Union; 20 states are members. It was first discussed by the Bulgarian Society Novae, after being proposed as an American initiative at the meeting of NATO defense ministers in Travemünde, Germany, on October 20–21, 1993, and formally launched on January 10–11, 1994 at the NATO summit in Brussels, Belgium. According to declassified U.S. State Department records, President Bill Clinton characterized the Partnership for Peace as a "track that will lead to NATO membership" and that "does not draw another line dividing Europe a few hundred miles to the east."
The NATO Medal is an international military decoration which is awarded to various militaries of the world under the authority of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO). It is manufactured by Eekelers-Centini Intl, of Hemiksem, Belgium.

Major non-NATO ally (MNNA) is a designation given by the United States government to close allies that have strategic working relationships with the US Armed Forces but are not members of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO). While the status does not automatically include a mutual defense pact with the United States, it still confers a variety of military and financial advantages that otherwise are not obtainable by non-NATO countries.

The 2008 Bucharest Summit or the 20th NATO Summit was a NATO summit organized in the Palace of the Parliament, Bucharest, Romania on 2 – 4 April 2008. Among other business, Croatia and Albania were invited to join the Alliance. The Former Yugoslav Republic Of Macedonia was not invited due to its ongoing naming dispute with Greece. Georgia and Ukraine had hoped to join the NATO Membership Action Plan, but, while welcoming the two countries’s aspirations for membership and agreeing that "these countries will become members of NATO", the NATO members decided to review their request in December 2008.

NATO is a military alliance of twenty-eight European and two North American countries that constitutes a system of collective defense. The process of joining the alliance is governed by Article 10 of the North Atlantic Treaty, which allows for the invitation of "other European States" only, and by subsequent agreements. Countries wishing to join must meet certain requirements and complete a multi-step process involving political dialogue and military integration. The accession process is overseen by the North Atlantic Council, NATO's governing body.

NATO is an international alliance that consists of 30 member states from Europe, North America, and Asia. It was established at the signing of the North Atlantic Treaty on 4 April 1949. Article Five of the treaty states that if an armed attack occurs against one of the member states, it shall be considered an attack against all members, and other members shall assist the attacked member, with armed forces if necessary.

Relations between Ukraine and the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) started in 1992. Ukraine applied to begin a NATO Membership Action Plan (MAP) in 2008. Plans for NATO membership were shelved by Ukraine following the 2010 presidential election in which Viktor Yanukovych, who preferred to keep the country non-aligned, was elected President. Amid the Euromaidan unrest, Yanukovych fled Ukraine in February 2014. The interim Yatseniuk Government which came to power initially said, with reference to the country's non-aligned status, that it had no plans to join NATO. However, following the Russian military invasion in Ukraine and parliamentary elections in October 2014, the new government made joining NATO a priority. On 21 February 2019, the Constitution of Ukraine was amended, the norms on the strategic course of Ukraine for membership in the European Union and NATO are enshrined in the preamble of the Basic Law, three articles and transitional provisions.
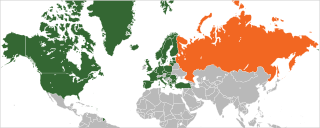
Relations between the NATO military alliance and the Russian Federation were established in 1991 within the framework of the North Atlantic Cooperation Council. In 1994, Russia joined the Partnership for Peace program, and since that time, NATO and Russia have signed several important agreements on cooperation.

The secretary general of NATO is the chief civil servant of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO). The officeholder is an international diplomat responsible for coordinating the workings of the alliance, leading NATO's international staff, chairing the meetings of the North Atlantic Council and most major committees of the alliance, with the notable exception of the NATO Military Committee, as well as acting as NATO's spokesperson. The secretary general does not have a military command role; political, military and strategic decisions ultimately rest with the member states. Together with the chairman of the NATO Military Committee and the supreme allied commander, the officeholder is one of the foremost officials of NATO.

NATO maintains foreign relations with many non-member countries across the globe. NATO runs a number of programs which provide a framework for the partnerships between itself and these non-member nations, typically based on that country's location. These include the Euro-Atlantic Partnership Council and the Partnership for Peace.