Local government is a generic term for the lowest tiers of public administration within a particular sovereign state. This particular usage of the word government refers specifically to a level of administration that is both geographically localised and has limited powers. While in some countries, "government" is normally reserved purely for a national administration (government), the term local government is always used specifically in contrast to national government – as well as, in many cases, the activities of sub-national, first-level administrative divisions. Local governments generally act only within powers specifically delegated to them by law and/or directives of a higher level of government. In federal states, local government generally comprises a third or fourth tier of government, whereas in unitary states, local government usually occupies the second or third tier of government.
In many countries, a mayor is the highest-ranking official in a municipal government such as that of a city or a town. Worldwide, there is a wide variance in local laws and customs regarding the powers and responsibilities of a mayor as well as the means by which a mayor is elected or otherwise mandated. Depending on the system chosen, a mayor may be the chief executive officer of the municipal government, may simply chair a multi-member governing body with little or no independent power, or may play a solely ceremonial role. A mayor's duties and responsibilities may be to appoint and oversee municipal managers and employees, provide basic governmental services to constituents, and execute the laws and ordinances passed by a municipal governing body. Options for selection of a mayor include direct election by the public, or selection by an elected governing council or board.

A district is a type of administrative division that in some countries is managed by the local government. Across the world, areas known as "districts" vary greatly in size, spanning regions or counties, several municipalities, subdivisions of municipalities, school district, or political district.
Nonpartisan democracy is a system of representative government or organization such that universal and periodic elections take place without reference to political parties. Sometimes electioneering and even speaking about candidates may be discouraged, so as not to prejudice others' decisions or create a contentious atmosphere.

The administrative divisions of New York are the various units of government that provide local services in the U.S. State of New York. The state is divided into boroughs, counties, cities, towns, and villages. They are municipal corporations, chartered (created) by the New York State Legislature, as under the New York State Constitution the only body that can create governmental units is the state. All of them have their own governments, sometimes with no paid employees, that provide local services. Centers of population that are not incorporated and have no government or local services are designated hamlets. Whether a municipality is defined as a borough, city, town, or village is determined not by population or land area, but rather on the form of government selected by the residents and approved by the New York State Legislature. Each type of local government is granted specific home rule powers by the New York State Constitution. There are still occasional changes as a village becomes a city, or a village dissolves, each of which requires legislative action. New York also has various corporate entities that provide local services and have their own administrative structures (governments), such as school and fire districts. These are not found in all counties.

The Tasmanian Legislative Council is the upper house of the Parliament of Tasmania in Australia. It is one of the two chambers of the Parliament, the other being the House of Assembly. Both houses sit in Parliament House in the state capital, Hobart. Members of the Legislative Council are often referred to as MLCs.

The Council of the District of Columbia is the legislative branch of the government of the District of Columbia. As permitted in the United States Constitution, the district is not part of any U.S. state and is overseen directly by the federal government.

A Member of the Legislative Assembly (MLA) is a representative elected by the voters of an electoral district (constituency) to the legislature of State government in the Indian system of government. From each constituency, the people elect one representative who then becomes a member of the Legislative Assembly (MLA). Each state has between seven and nine MLAs for every Member of Parliament (MP) that it has in the Lok Sabha, the lower house of India's bicameral parliament. There are also members in three unicameral legislatures in Union Territories: the Delhi Legislative Assembly, Jammu and Kashmir Legislative Assembly and the Puducherry Legislative Assembly. Only a Member of the Legislative Assembly can work as a minister for more than 6 months. If a non-Member of the Legislative Assembly becomes a Chief Minister or a minister, he must become an MLA within 6 months to continue in the job. Only a Member of the Legislative Assembly can become a Speaker of the Legislature.
A capital district, capital region or capital territory is normally a specially designated administrative division where a country's seat of government is located. As such, in a federal model of government, no state or territory has any political or economic advantage relative to the others because of the national capital lying within its borders. A capital territory can be a specific form of federal district.

The government of the Philippines has three interdependent branches: the legislative, executive, and judicial branches. The Philippines is governed as a unitary state under a presidential representative and democratic constitutional republic in which the president functions as both the head of state and the head of government of the country within a pluriform multi-party system.
A municipal council is the legislative body of a municipality or local government area. Depending on the location and classification of the municipality it may be known as a city council, town council, town board, community council, rural council, village council, or board of aldermen.

The government of the U.S. State of Oklahoma, established by the Oklahoma Constitution, is a republican democracy modeled after the federal government of the United States. The state government has three branches: the executive, legislative, and judicial. Through a system of separation of powers or "checks and balances," each of these branches has some authority to act on its own, some authority to regulate the other two branches, and has some of its own authority, in turn, regulated by the other branches.

The Buffalo Common Council is the legislative branch of the city of Buffalo, New York government. It is a representative assembly, with one elected member from each of nine districts: Niagara, Delaware, Masten, Ellicott, Lovejoy, Fillmore, North, University, and South. In the past, the Common Council also had as many as five at-large members and a Council President who were elected citywide. Each council seat is elected for a four-year term, with elections occurring during off-years, between mid-term elections and presidential elections.
Sangguniang Panlalawigan, commonly known as the Provincial Board, are the legislatures in Philippine provinces. They are the legislative branches of the provinces, and their powers and responsibilities are defined by the Local Government Code of 1991. Along with the provincial governor, the executive branch of the province, they form the province's government.
The Sangguniang Bayan is the local legislative branch of the municipal governments in the Philippines. It is responsible for passing ordinances and resolutions for the administration of a municipality. Its powers are defined by the Local Government Code, passed by Congress in 1991.

The government of Indiana is established and regulated by the Constitution of Indiana. The state-level government consists of three branches: the judicial branch, the legislative branch, and the executive branch. The three branches share power and jointly govern the state of Indiana. County and local governments are also constitutional bodies with limited authority to levy taxes, pass legislation, and create and maintain local public infrastructure.

The Bangkok Metropolitan Administration (BMA) is the local government of Bangkok, which includes the capital of the Kingdom of Thailand. The government is composed of two branches: the executive and the legislative. The administration's roles are to formulate and implement policies to manage Bangkok. Its purview includes transport services, urban planning, waste management, housing, roads and highways, security services, and the environment.

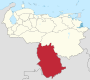
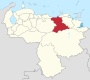
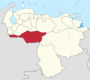
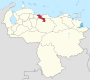
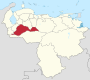
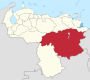
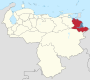
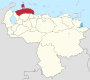
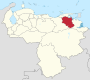
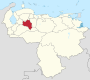
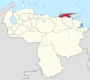
Venezuela is a federal state that is divided into states, and these into autonomous municipalities and these in turn into parishes. In total, the country has 1,136 parishes that make up the 335 municipalities.

In the year 2000, Rwanda began a decentralization process by adopting a National Decentralization Policy. The policy's objective were to promote good governance, to reduce poverty and to promote efficient, effective, and accountable service delivery.

Brisbane City Council (BCC) is the democratic executive local government authority for the City of Brisbane, the capital city of the state of Queensland, Australia. The largest City Council in Australia by population and area, BCC's jurisdiction includes 26 wards and 27 elected councillors covering 1,338 km2 (517 sq mi). BCC is overseen by the Lord Mayor of Brisbane, Adrian Schrinner, and the Council of Brisbane and the Civic Cabinet. The council's CEO is Colin Jensen, supported by EO Ainsley Gold.