See also
| By state | ||
|---|---|---|
| By capital | ||
| Stations |
| |
| Related articles | ||
This is a list of former railway operating companies operating in Australia. For former Government authorities, see List of former government railway authorities of Australia.

Rail transport in Australia is a component of the Australian transport system. It is to a large extent state-based, as each state largely has its own operations, with the interstate network being developed ever since Australia's federation in 1901. As of 2022, the Australian rail network consists of a total of 32,929 kilometres (20,461 mi) of track built to three major track gauges: 18,007 kilometres (11,189 mi) of standard gauge, 2,685 kilometres (1,668 mi) of broad gauge, and 11,914 kilometres (7,403 mi) of narrow gauge lines. Additionally, about 1,400 kilometres (870 mi) of 610 mm / 2 ft gauge lines support the sugar-cane industry. 3,488 kilometres (2,167 mi), around 11 per cent of the Australian heavy railways network route-kilometres are electrified.

The Australian state of New South Wales has an extensive network of railways, which were integral to the growth and development of the state. The vast majority of railway lines were government built and operated, but there were also several private railways, some of which operate to this day.
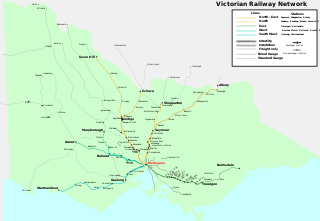
Rail transport in the Australian state of Victoria is provided by a number of railway operators who operate over the government-owned railway lines. The network consists of 2,357 km of Victorian broad gauge lines, and 1,912 km of standard gauge freight and interstate lines; the latter increasing with gauge conversion of the former. Historically, a few experimental 762 mm gauge lines were built, along with various private logging, mining and industrial railways. The rail network radiates from the state capital, Melbourne, with main interstate links to Sydney and to Adelaide, as well as major lines running to regional centres, upgraded as part of the Regional Fast Rail project.

The rail network in Adelaide, South Australia, consists of four lines and 89 stations, totalling 132 km (82 mi). It is operated by Keolis Downer under contract from the Government of South Australia, and is part of the citywide Adelaide Metro public transport system.
Australians generally assumed in the 1850s that railways would be built by the private sector. Private companies built railways in the then colonies of Victoria, opened in 1854, and New South Wales, where the company was taken over by the government before completion in 1855, due to bankruptcy. South Australia's railways were government owned from the beginning, including a horse-drawn line opened in 1854 and a steam-powered line opened in 1856. In Victoria, the private railways were soon found not to be financially viable, and existing rail networks and their expansion were taken over by the colony. Government ownership also enabled railways to be built to promote development, even if not apparently viable in strictly financial terms. The railway systems spread from the colonial capitals, except in cases where geography dictated a choice of an alternate port.

The Victorian Railways (VR), trading from 1974 as VicRail, was the state-owned operator of most rail transport in the Australian state of Victoria from 1859 to 1983. The first railways in Victoria were private companies, but when these companies failed or defaulted, the Victorian Railways was established to take over their operations. Most of the lines operated by the Victorian Railways were of 5 ft 3 in. However, the railways also operated up to five 2 ft 6 in narrow gauge lines between 1898 and 1962, and a 4 ft 8+1⁄2 instandard gauge line between Albury and Melbourne from 1961.

The first railway in colonial South Australia was a line from the port of Goolwa on the River Murray to an ocean harbour at Port Elliot, which first operated in December 1853, before its completion in May 1854.

Western Australian Government Railways (WAGR) was the operator of railway services in the state of Western Australia between October 1890 and June 2003. Owned by the state government, it was renamed a number of times to reflect extra responsibility for tram and ferry operations that it assumed and later relinquished. Westrail was the trading name of WAGR from September 1975 until December 2000, when the WAGR's freight division and the Westrail name and logo were privatised. Its freight operations were privatised in December 2000 with the remaining passenger operations transferred to the Public Transport Authority in July 2003.
The history of the Railways on the West Coast of Tasmania has fascinated enthusiasts from around the world, because of the combination of the harsh terrain in which the railways were created, and the unique nature of most of the lines.
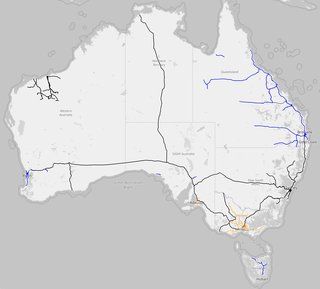
Rail gauges in Australia display significant variations, which has presented an extremely difficult problem for rail transport on the Australian continent since the 19th century. As of 2022, there are 11,914 kilometres (7,403 mi) of narrow-gauge railways, 18,007 kilometres (11,189 mi) of standard gauge railways and 2,685 kilometres (1,668 mi) of broad gauge railways. In the 19th century, each of the colonies of Australia adopted their own gauges.

Southern & Silverton Rail was an Australian rail operator founded in 1886 as the Silverton Tramway Company. The company operated the 1067 mm Silverton Tramway, conveying silver-lead-zinc concentrates 58 kilometres from Broken Hill to the South Australian border. In 1970, its main line was bypassed by the newly standardised, government-funded line from Broken Hill to Port Pirie. It then diversified to operating hook-and-pull services and in the mid-1990s rebranded to Silverton Rail. In 2006, it was purchased by South Spur Rail Services and rebranded again as Southern & Silverton Rail, before both entities were sold to Coote Industrial. In June 2010 it was sold to Qube Logistics and absorbed into that brand.

Railways in Western Australia were developed in the 19th century both by the Government of Western Australia and a number of private companies. Today passenger rail services are controlled by the Public Transport Authority through Transperth, which operates public transport in Perth, and Transwa, which operates country passenger services. Journey Beyond operates the Indian Pacific.

The rail network in Queensland, Australia, was the first in the world to adopt 1,067 mm narrow gauge for a main line, and now the second largest narrow gauge network in the world, consists of:

Rail transport in Tasmania consists of a network of narrow gauge track of 1,067 mm reaching virtually all cities and major towns in the island state of Tasmania, Australia. Today, rail services are focused primarily on bulk freight, with no commercial passenger services being operated. The mainline railways of Tasmania are currently operated by TasRail, a Government of Tasmania-owned Corporation, who owns and maintains both rolling stock, locomotives, and track infrastructure.

The South Western Railway, also known as the South West Main Line, is the main railway route between Perth and Bunbury in Western Australia.
The Mount Dundas – Zeehan Railway was a railway line running 7 miles (11 km) from Dundas to Zeehan on the West Coast of Tasmania. It operated from 1892 until 1932, and the rails were removed in 1940.
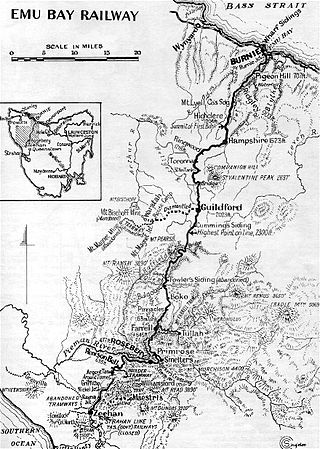
The Emu Bay Railway was a Tasmania, Australian railway company. The railway was significant during full operation, in that it linked the Tasmanian Government Railways system at Burnie with that at Zeehan that further linked to the Mount Lyell railway allowing connection through to Queenstown.

Zeehan railway station in Tasmania, was a major junction and railway yard for numerous different railway and tramway systems in western Tasmania in the town of Zeehan.
Transport in South Australia is provided by a mix of road, rail, sea and air transport. The capital city of Adelaide is the centre to transport in the state. With its population of 1.4 million people, it has the majority of the state's 1.7 million inhabitants. Adelaide has the state's major airport and sea port.