Related Research Articles

Yemen, officially the Republic of Yemen, is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula, and borders Saudi Arabia to the north and Oman to the northeast and shares maritime borders with Eritrea, Djibouti and Somalia. Yemen is the second-largest Arab sovereign state in the Arabian Peninsula, occupying 555,000 square kilometres, with a coastline stretching about 2,000 kilometres. Its constitutionally stated capital, and largest city, is Sanaa. As of 2023, Yemen has an estimated population of 34.2 million.

Taiz is a city in southwestern Yemen. It is located in the Yemeni highlands, near the port city of Mocha on the Red Sea, at an elevation of about 1,400 metres (4,600 ft) above sea level. It is the capital of Taiz Governorate. In 2019, the city had an estimated population of just over 370.000, making it the third largest city in Yemen.
Yemenia is the flag carrier of Yemen, based in Sanaa. It operates scheduled domestic and international passenger flights to destinations in Africa and the Middle East out of its hubs at Aden International Airport, and to a lesser extent Seiyun Airport.

The Mutawakkilite Kingdom of Yemen, also known as the Kingdom of Yemen or simply as Yemen, or, retrospectively, as North Yemen, was a state that existed between 1918 and 1962 in the northwestern part of what is now Yemen. Its capital was Sana'a until 1948, then Taiz. From 1962 to 1970, it maintained control over portions of Yemen until its final defeat in the North Yemen Civil War. Yemen was admitted to the United Nations on 30 September 1947.
The Nasserist Unionist People's Organisation is a Nasserist political party in Yemen.

Taiz is a governorate of Yemen. The governorate's capital is Taiz, which is the third-largest city in Yemen. Today it is among the most important commercial centres in Yemen, owing to its proximity to rich farmland in the nation and to the important Red Sea port of Mocha. It also has an international airport, Taiz International Airport, with numerous services within Yemen and to neighbouring countries.

Sharʿab as-Salam District is a district of the Taiz Governorate, Yemen. In 2003, the district had a population of 146,650.
Vehicle registration plates of Yemen started in 1993. The current version started in 2007.

On 26 March 2015, Saudi Arabia, leading a coalition of nine countries from West Asia and North Africa, launched an intervention in the Yemeni Civil War in response to calls from the president of Yemen Abdrabbuh Mansur Hadi for military support after he was ousted by the Houthi movement. The conflict ignited between the government forces, the Houthi rebels and other armed groups after the draft constitution and power-sharing arrangements collapsed, despite progress in the political transition led by the United Nations at that time, leading to an escalation of violence in mid-2014. The Houthis and allied units of the armed forces seized control of Sana’a and other parts of the country in September 2014 and in the following months. This prompted President Hadi to ask Saudi Arabia to intervene against the Iranian-backed Houthis.

The siege of Taiz is an ongoing, protracted military confrontation between opposing Yemeni forces in the city of Taiz for control of the city and surrounding area. The battle began one month after the start of the Yemeni Civil War.

The Houthi–Saudi Arabian conflict is an ongoing armed conflict between the Royal Saudi Armed Forces and Iran-backed Yemeni Houthi forces that has been taking place in the Arabian Peninsula, including the southern Saudi regions of Asir, Jizan, and Najran, and northern Yemeni governorates of Saada, Al Jawf, and Hajjah, since the onset of the Saudi Arabian-led intervention in Yemen in 2015.
A Saudi Arabian-led military intervention in Yemen began in 2015, in an attempt to influence the outcome of the Yemeni Civil War. Saudi Arabia, spearheading a coalition of nine Arab states, began carrying out airstrikes in neighbouring Yemen and imposing an aerial and naval blockade on 26 March 2015, heralding a military intervention code-named Operation Decisive Storm. More than 130 health facilities(2019) in Yemen have been destroyed by a series of airstrikes conducted by the Saudi Arabian-led coalition since March 2015. Many of these have been public health hospitals staffed or supported by Doctors Without Borders (MSF). Critics of the assaults say the airstrikes are war crimes in violation of the protections of health care facilities afforded by the internationally recognized rules of war and have called for independent investigations.
Human rights violations, committed by all warring parties, have been widespread throughout the Yemeni Civil War. This includes the two main groups involved in the ongoing conflict: forces loyal to the current Yemeni president, Abdrabbuh Mansur Hadi, and Houthis and other forces supporting Ali Abdullah Saleh, the former Yemeni president. Al-Qaeda in the Arabian Peninsula and the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant have also carried out attacks in Yemen. The Saudi-led coalition war crimes, backed by the United States and other nations, has also been accused of violating human rights and breaking international law, especially in regards to airstrikes that repeatedly hit civilian targets.

The Southern Transitional Council is a political organization in South Yemen representing the interests of Southern Yemenis in the wake of Yemen's ongoing civil war. The 26 members of the STC include the governors of five southern governorates and two government ministers. It was formed by a faction of the Southern Movement, also known as al-Hirak al-Janoubi. The Southern Movement was established in 2007, during the term of former president Ali Abdullah Saleh, and it has called for and worked toward the separation of southern Yemen from the rest of the nation.
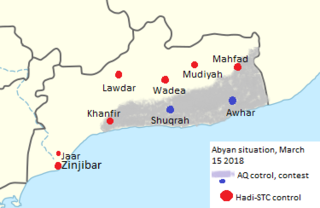
The Abyan conflict was a series of clashes between forces of AQAP loyal to Yemeni president Abdrabbuh Mansur Hadi, and forces loyal to Southern Movement for the control of Abyan between 2016 and 2018.

The Yemeni National Resistance is an elite formation of approximately 3,000-10,000 previous members of Yemeni Republican Guard and Central Security Organization commanded by Tareq Saleh, nephew of former Yemeni President Ali Abdullah Saleh, and loyal to Hadi-led government fighting against the Houthi movement in the 2015 Yemen Civil War.

The first confirmed case relating to the COVID-19 pandemic in Yemen was announced on 10 April 2020 with an occurrence in Hadhramaut. Organizations called the news a "devastating blow" and a "nightmare scenario" given the country's already dire humanitarian situation.
On 30 December 2020, a plane carrying members of the recently formed Yemeni government landed at Aden International Airport in the southwest of Yemen. As passengers disembarked, there were explosions and gunfire, leaving 28 people dead and 107 others injured. None of the passengers were hurt in the attack and the Yemeni cabinet members were quickly transported to Mashiq Palace for safety.
Bushra al-Maqtari is a Yemeni writer and activist. She came to prominence as an anti-government protest leader in her hometown of Taiz during the 2011 Yemeni Revolution. As a writer, she is best known for her 2012 novel Behind the Sun and her 2018 nonfiction work What You Have Left Behind: Voices from the Land of the Forgotten War.
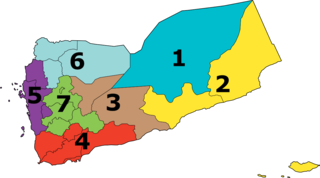
The Fourth Military Region is a military region of Armed Forces of Yemen. Its headquarters locates in Aden city, the interim capital of Yemen.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 "List of Hospitals in Yemen". UAE Medical Insurance. Retrieved April 20, 2020.
- 1 2 "Yemen Facts and Figures" (PDF). International Committee of the Red Cross. Retrieved April 20, 2020.
- ↑ See Wikipedia:WikiProject Hospitals/Tutorials#Notability for a description criteria for a notable hospital.
- ↑ "اسواق عدن". اسواق عدن (in Arabic). Retrieved 2023-05-31.
- ↑ "اسواق عدن". اسواق عدن (in Arabic). Retrieved 2023-05-31.
- ↑ "المستشفيات السعودية » مستشفى عدن العام ومركز القلب" (in Arabic). Retrieved 2023-05-31.
- ↑ "اسواق عدن". اسواق عدن (in Arabic). Retrieved 2023-05-31.
- ↑ "اسواق عدن". اسواق عدن (in Arabic). Retrieved 2023-05-31.
- ↑ The Lancet. Little, Brown. 2002. p. 1889. Retrieved 11 July 2011.
- ↑ "Nuclear Medicine at Al=Thawra Hospital" (PDF). IAEA. 2009. Retrieved September 22, 2020.
- 1 2 "Yemen Health Facilities Face Indiscriminate Attacks in Taiz City". Relief Web. March 20, 2020. Retrieved September 23, 2020.
- ↑ "Yemen International Hospital Taiz". YIH Taiz. Retrieved September 23, 2020.
- ↑ Michael, Maggie (May 15, 2020). "Coronavirus spreads in Yemen with health system in shambles". Associated Press.
In the first week of May, a surge of patients entered the Kuwait Hospital, the sole fully operating COVID-19 treatment center in the capital, said four officials.
- ↑ Maan A. Bari Qasem Saleh and Ahmed Mohamed Makki. Mental health in Yemen, Obstacles and challenges (PDF). Cambridge University Press.