Related Research Articles

The Ganges is a trans-boundary river of Asia which flows through India and Bangladesh. The 2,525 km (1,569 mi) river rises in the western Himalayas in the Indian state of Uttarakhand. It flows south and east through the Gangetic plain of North India, receiving the right-bank tributary, the Yamuna, which also rises in the western Indian Himalayas, and several left-bank tributaries from Nepal that account for the bulk of its flow. In West Bengal state, India, a feeder canal taking off from its right bank diverts 50% of its flow southwards, artificially connecting it to the Hooghly River. The Ganges continues into Bangladesh, its name changing to the Padma. It is then joined by the Jamuna, the lower stream of the Brahmaputra, and eventually the Meghna, forming the major estuary of the Ganges Delta, and emptying into the Bay of Bengal. The Ganges–Brahmaputra–Meghna system is the second-largest river on earth by discharge.
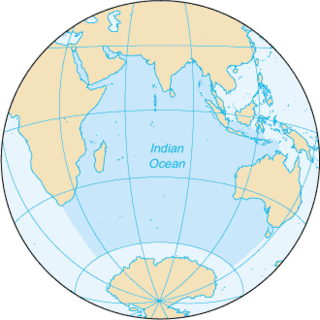
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering 70,560,000 km2 (27,240,000 sq mi) or ~20% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by the Southern Ocean, or Antarctica, depending on the definition in use. Along its core, the Indian Ocean has large marginal, or regional seas, such as the Arabian Sea, Laccadive Sea, Bay of Bengal and Andaman Sea.

The Bay of Bengal is the northeastern part of the Indian Ocean. Geographically, it is positioned between the Indian subcontinent and the Indochinese peninsula, located below the Bengal region. It is the largest water region called a bay in the world.

The Godavari is India's second longest river after the Ganga river and drains the third largest basin in India, covering about 10% of India's total geographical area. Its source is in Trimbakeshwar, Nashik, Maharashtra. It flows east for 1,465 kilometres (910 mi), draining the states of Maharashtra (48.6%), Telangana (18.8%), Andhra Pradesh (4.5%), Chhattisgarh (10.9%) and Odisha (5.7%). The river ultimately empties into the Bay of Bengal through an extensive network of distributaries. Measuring up to 312,812 km2 (120,777 sq mi), it forms one of the largest river basins in the Indian subcontinent, with only the Ganga and Indus rivers having a larger drainage basin. In terms of length, catchment area and discharge, the Godavari is the largest in peninsular India, and had been dubbed as the Dakshina Ganga.

Sewerage is the infrastructure that conveys sewage or surface runoff using sewers. It encompasses components such as receiving drains, manholes, pumping stations, storm overflows, and screening chambers of the combined sewer or sanitary sewer. Sewerage ends at the entry to a sewage treatment plant or at the point of discharge into the environment. It is the system of pipes, chambers, manholes, etc. that conveys the sewage or storm water.

The Satluj River is the longest of the five rivers that flow through the historic crossroads region of Punjab in northern India and Pakistan. The Sutlej River is also known as Satadru. It is the easternmost tributary of the Indus River. The Bhakra Dam is built around the river Sutlej to provide irrigation and other facilities to the states of Punjab, Rajasthan and Haryana.

The Daman Ganga also called Dawan River is a river in western India. The river's headwaters are on the western slope of the Western Ghats range, and it flows west into the Arabian Sea. The river flows through Maharashtra and Gujarat states, as well as the Union territory of Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu. The industrial towns of Vapi, Dadra and Silvassa lie on the north bank of the river, and the town of Daman occupies both banks of the river's estuary.

The Cooum river, or simply Koovam, is one of the shortest classified rivers draining into the Bay of Bengal. This river is about 72 km (45 mi) in length, flowing 32 km (20 mi) in the city of Chennai and the rest in rural part. The river is highly polluted in the urban area (Chennai). Along with the Adyar River running parallel to the south and the Kosasthalaiyar River, the river trifurcates the city of Chennai and separates Northern Chennai from Central Chennai. It is also sometimes known as Thiruvallikenni river

The Indian River Lagoon is a grouping of three lagoons: the Mosquito Lagoon, the Banana River, and the Indian River, on the Atlantic Coast of Florida; one of the most biodiverse estuaries in the Northern Hemisphere and is home to more than 4,300 species of plants and animals.

Palk Bay is a semi-enclosed shallow water body between the southeast coast of India and Sri Lanka, with a water depth maximum of 13 m. Palk Bay is located between 8° 50′ and 10° North latitudes and 78° 50′ and 80° 30′ East longitudes. The width of the bay ranges from 57 to 107 km and the length is around 150 km. It is one of the major sinks for sediments along with the Gulf of Mannar. Sediments discharged by rivers and transported by the surf currents as littoral drift settle in this sink. Few scientists have tried to understand the wave characteristics within the Palk Bay.
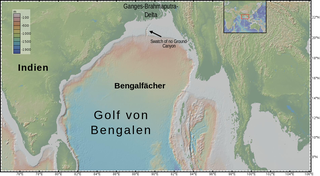
The Bengal Fan, also known as the Ganges Fan, is the largest submarine fan on Earth.

The Indus River Delta forms where the Indus River flows into the Arabian Sea, mostly in the southern Sindh province of Pakistan with a small portion in the Kutch Region of India. The delta covers an area of about 41,440 km2, and is approximately 210 km (130 mi) across where it meets the sea. The active part of the delta is 6,000 km2 in area (2,300 sq mi). The climate is arid, the region only receives between 25 and 50 centimetres of rainfall in a normal year. The delta is home to the largest arid mangrove forests in the world, as well as many birds, fish and the Indus dolphin.

Kerala is situated between the Lakshadweep Sea to the west and the Western Ghats to the east. Kerala's coast runs some 580 km in length, while the state itself varies between 35–120 km in width. Geologically, pre-Cambrian and Pleistocene formations comprise the bulk of Kerala's terrain. The topography consists of a hot and wet coastal plain gradually rising in elevation to the high hills and mountains of the Western Ghats. Kerala lies between northern latitude of 8°.17'.30" N and 12°. 47'.40" N and east longitudes 74°.27'.47" E and 77°.37'.12" E. Kerala's climate is mainly wet and maritime tropical, heavily influenced by the seasonal heavy rains brought up by the monsoon.

The ongoing pollution of the Ganges, the largest river in the Indian subcontinent, poses a significant threat to human health and the environment. The river, which is severely polluted with human waste and industrial contaminants, provides water to about 40% of India's population across 11 states, serving an estimated population of 500 million people, more than any other river in the world.

Drought has resulted in millions of deaths in India over the years. Indian agriculture is heavily dependent on the country's climate: a favorable monsoon is critical to securing water for irrigating India's crops. In parts of India, failure of the monsoons causes water shortages, resulting in poor yields. This is particularly true of major drought-prone regions southeastern Maharashtra, northern Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Odisha, Gujarat, Telangana, and Rajasthan.

Water resources in India includes information on precipitation, surface and groundwater storage and hydropower potential. India experiences an average precipitation of 1,170 millimetres (46 in) per year, or about 4,000 cubic kilometres (960 cu mi) of rains annually or about 1,720 cubic metres (61,000 cu ft) of fresh water per person every year. India accounts for 18% of the world's population and about 4% of the world's water resources. One of the proposed solutions to solve the country's water woes is the Indian rivers interlinking project. Some 80 percent of its area experiences rains of 750 millimetres (30 in) or more a year. However, this rain is not uniform in time or geography. Most of the rains occur during its monsoon seasons, with the northeast and north receiving far more rain than India's west and south. Other than rains, the melting of snow over the Himalayas after the winter season feeds the northern rivers to varying degrees. The southern rivers, however, experience more flow variability over the year. For the Himalayan basin, this leads to flooding in some months and water scarcity in others. Despite an extensive river system, safe clean drinking water as well as irrigation water supplies for sustainable agriculture are in shortage across India, in part because it has, as yet, harnessed a small fraction of its available and recoverable surface water resource. India harnessed 761 cubic kilometres (183 cu mi) (20 percent) of its water resources in 2010, part of which came from unsustainable use of groundwater. Of the water it withdrew from its rivers and groundwater wells, India dedicated about 688 cubic kilometres (165 cu mi) to irrigation, 56 cubic kilometres (13 cu mi) to municipal and drinking water applications and 17 cubic kilometres (4.1 cu mi) to industry.

A river is a natural flowing watercourse, usually a freshwater stream, flowing on the Earth's land surface or inside caves towards another waterbody at a lower elevation, such as an ocean, sea, bay, lake, wetland, or another river. In some cases, a river flows into the ground or becomes dry at the end of its course without reaching another body of water. Small rivers can be referred to by names such as creek, brook, and rivulet. There are no official definitions for the generic term river as applied to geographic features, although in some countries or communities, a stream is defined by its size. Many names for small rivers are specific to geographic location; examples are "run" in some parts of the United States, "burn" in Scotland and Northeast England, and "beck" in Northern England. Sometimes a river is defined as being larger than a creek, but not always; the language is vague.

The Koyna Hydroelectric Project is the second largest hydroelectric power plant in India, just after the Tehri Dam Project. It is a complex project with four dams including the largest dam on the Koyna River, Maharashtra, hence the name Koyna Hydroelectric Project. The project site is in Satara district.

Water pollution is a major environmental issue in India. The largest source of water pollution in India is untreated sewage. Other sources of pollution include agricultural runoff and unregulated small-scale industry. Most rivers, lakes and surface water in India are polluted due to industries, untreated sewage and solid wastes. Although the average annual precipitation in India is about 4000 billion cubic metres, only about 1122 billion cubic metres of water resources are available for utilization due to lack of infrastructure. Much of this water is unsafe, because pollution degrades water quality. Water pollution severely limits the amount of water available to Indian consumers, its industry and its agriculture.
References
- ↑ Banerjee, Ananda (2015-05-25). "India's misunderstood rivers". www.livemint.com. HT Media Ltd. Retrieved 2015-08-22.
The Indian subcontinent is home to seven major river systems with more than 400 rivers.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 Kumar, Rakesh; Singh, R.D.; Sharma, K.D. (2005-09-10). "Water Resources of India" (PDF). Current Science. Bangalore: Current Science Association. 89 (5): 794–811. Retrieved 2013-10-13.