Podolia Governorate was an administrative-territorial unit (guberniya) of the Southwestern Krai of the Russian Empire. It bordered Volhynian Governorate to the north, Kiev Governorate to the east, Kherson Governorate to the southeast, Bessarabia Governorate to the south, and Austria to the west. Its administrative centre was Kamenets-Podolsky (Kamianets-Podilskyi), which later moved to Vinnitsa (Vinnytsia). The governorate covered areas of Ukraine's partially Khmelnytskyi and most of Vinnytsia Oblasts, along with the fractionally recognised state of Transnistria.

Kherson Governorate, known until 1803 as Nikolayev Governorate, was an administrative-territorial unit (guberniya) of the Russian Empire, with its capital in Kherson. It encompassed 71,936 square kilometres (27,775 sq mi) in area and had a population of 2,733,612 inhabitants. At the time of the census in 1897, it bordered Podolia Governorate to the northwest, Kiev Governorate to the north, Poltava Governorate to the northeast, Yekaterinoslav Governorate to the east, Taurida Governorate to the southeast, Black Sea to the south, and Bessarabia Governorate to the west. It roughly corresponds to what is now most of Mykolaiv, Kirovohrad and Odesa Oblasts in Ukraine and some parts of Kherson and Dnipropetrovsk Oblasts.

The Vilna Governorate was a province (guberniya) of the Northwestern Krai of the Russian Empire. In 1897, the governorate covered an area of 41,907.9 square kilometres (16,180.7 sq mi) and had a population of 1,591,207 inhabitants. The governorate was defined by the Minsk Governorate to the south, the Grodno Governorate to the southwest, the Suwałki Governorate to the west, the Kovno and Courland Governorates to the north, and the Vitebsk Governorate to the east. The capital was located in Vilna (Vilnius). The city also served as the capital of Vilna Governorate-General, which existed until 1912. The area roughly corresponded to the Vilnius Region, which was later occupied by Germany, Bolsheviks, and Poland.

Volhynia Governorate, also known as Volyn Governorate, was an administrative-territorial unit (guberniya) of the Southwestern Krai of the Russian Empire. It consisted of an area of 71,736 square kilometres (27,697 sq mi) and a population of 2,989,482 inhabitants. The governorate bordered Grodno and Minsk Governorates to the north, Kiev Governorate to the east, Podolia Governorate to the south, Lublin and Siedlce Governorates, and after 1912, Kholm Governorate and Austria to the west. Its capital was in Novograd-Volynsky until 1804, and then Zhitomir. It corresponded to most of modern-day Volyn, Rivne and Zhytomyr Oblasts of Ukraine and some parts of Brest and Gomel Regions of Belarus.
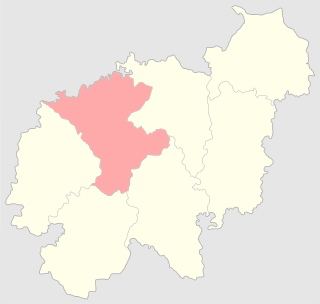
The Vilna uezd was a county (uezd) of the Vilna Governorate of the Russian Empire, with the administrative centre in Vilna. The uezd was bordered by the Sventsyany uezd to the east, the Oshmyany and Lida uezds to the south, the Troki uezd to the west, and the Vilkomir uezd of the Kovno Governorate to the north. The district covered the area of modern Vilnius County of Lithuania.

The Balta uezd was a county (uezd) of the Podolian Governorate of the Russian Empire. It bordered the Olgopol and Gaysin uezds to the north, the Uman uezd of the Kiev Governorate to the northeast, the Kherson Governorate's Elisavetgrad uezd to the east, and Ananev uezd to the south, and the Orgeev uezd of the Bessarabia Governorate to the west. Its administrative centre was Balta.
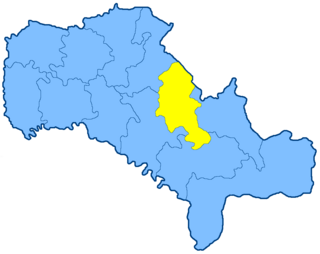
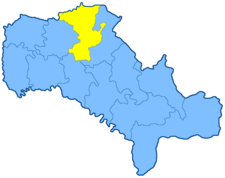
The Bratslav uezd was a county (uezd) of the Podolian Governorate of the Russian Empire. It bordered the Lipovets uezd of the Kiev Governorate to the north, the Gaysin uezd to the east, the Olgopol uezd to the south, the Yampol uezd to the southwest, and the Vinnitsa uezd to the north. The Bratslav uezd was eponymously named for its administrative center, Bratslav.
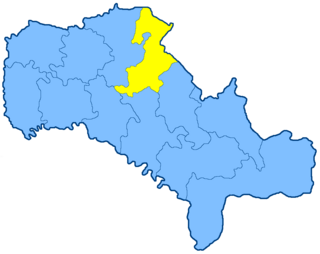
The Vinnitsa uezd was a county (uezd) of the Podolian Governorate of the Russian Empire. The uezd bordered the Zhitomir uezd of the Volhynian Governorate to the north, the Berdichev uezd of the Kiev Governorate to the northeast, the Bratslav uezd to the east, the Yampol uezd to the south, and the Litin uezd to the west. The administrative centre of the county was Vinnitsa. The county composed most of Vinnytsia Raion of contemporary Ukraine.
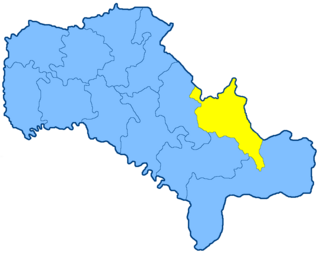
The Gaysin uezd was a county (uezd) of the Podolian Governorate of the Russian Empire, with its administrative centre in Gaysin. The area of the Gaysin uezd covered the area of modern-day Haisyn Raion.

The Kamenets-Podolsky uezd was a county (uezd) of the Podolian Governorate of the Russian Empire. The uezd bordered the Proskurov uezd to the north, the Ushitsa uezd to the east, the Khotin uezd to the south, and Austria to the west. Its administrative centre of the county was Kamenets-Podolsky. The county covered most of the area of Kamianets-Podilskyi Raion.
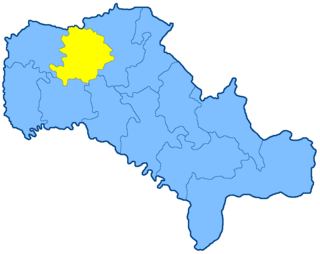
The Letichev uezd was a county (uezd) of the Podolian Governorate of the Russian Empire. The uezd bordered the Starokonstantinov uezd of the Volhynian Governorate, the Litin uezd to the east, the Mogilev uezd to the southeast, the Ushitsa uezd to the south, and the Proskurov uezd to the west. The area of the uezd encompassed most of Khmelnytskyi Raion of Ukraine. The administrative centre of the county was Letichev.

The Mogilev uezd was a county (uezd) of the Podolia Governorate of the Russian Empire. It bordered the Letichev and Litin uezds to the north, the Yampol uezd to the east, the Soroka uezd to the south, and the Ushitsa uezd to the west. The administrative centre of the county was Mogilev-Podolsky. The uezd included most of Mohyliv-Podilskyi and Zhmerynka Raions of Ukraine.
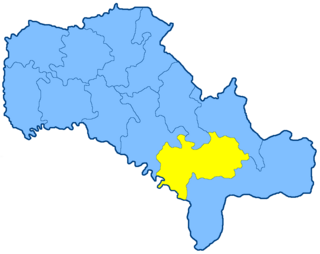
The Olgopol uezd was a county (uezd) of the Podolia Governorate of the Russian Empire, with its administrative centre in Olgopol. It bordered the Bratslav and Gaysin uezds to the north, the Balta uezd, the Orgeev uezd of the Bessarabia Governorate to the south, the Yampol uezd to the west.

The Proskurov uezd was a county (uezd) of the Podolia Governorate of the Russian Empire, with its administrative centre in Proskurov. It border the Starokonstantinov uezd of the Volhynian Governorate to the north, the Letichev uezd to the east, the Kamenets-Podolsky uezd to the south, and Austria to the west. The area of the uezd covered most of Ukraine's Khmelnytskyi Raion.

The Yampol uezd was a county (uezd) of the Podolia Governorate of the Russian Empire. It bordered the Vinnitsa uezd to the north, the Bratslav and Olgopol uezds to the east, the Soroka uezd to the south, and the Mogilev uezd to the west. The district was eponymously named for its administrative center, Yampol.
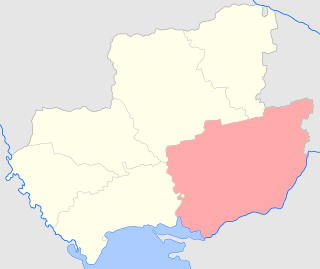
The Kherson uezd was a county (uezd) of the Kherson Governorate of the Russian Empire, and then of the Ukrainian People's Republic and the Ukrainian SSR until the administrative reform of 1923. The uezd bordered the Odessa uezd to the west, the Elisavetgrad uezd to the northwest, the Aleksandriya uezd to the north, the Verkhnedneprovsk and Yekaterinoslav uezds of the Yekaterinoslav Governorate to the east, the Melitopol and Dneprovsk uezds of the Taurida Governorate, and the Black Sea to the south. The district was eponymously named for its administrative center, Kherson.

The Aleksandriya uezd was a county (uezd) of the Kherson Governorate of the Russian Empire. It bordered the Chigirin uezd of the Kiev Governorate to the north, the Kremenchug uezd to the northeast, the Verkhnedneprovsk uezd of the Yekaterinoslav Governorate to the east, the Kherson uezd to the south, and the Elisavetgrad uezd to the west. The Aleksandriya uezd was eponymously named for its administrative center, Aleksandriya.

The Elisavetgrad uezd was a county (uezd) of the Kherson Governorate of the Russian Empire, with its administrative center in Yelisavetgrad. It bordered the Zvenigorodka and Chigirin uezds of the Kiev Governorate to the north, the Aleksandriya uezd to the east, the Kherson uezd to the south, and the Ananev uezd to the west. The uezd corresponded to Kirovohrad and Mykolaiv Oblasts. Most of the land was owned by the noble Skarzynski family until 1909.

The Odessa uezd was a county (uezd) of the Kherson Governorate of the Russian Empire. The uezd bordered the Tiraspol and Ananev uezds to the north, the Elisavetgrad uezd to the northeast, the Kherson uezd to the east, the Black Sea to the south, and the Akkerman uezd of the Bessarabia Governorate to the west. The administrative centre of the county was Odessa (Odesa).
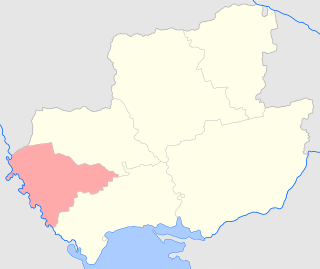
The Tiraspol uezd was a county (uezd) of the Kherson Governorate of the Russian Empire. The uezd bordered the Balta uezd of the Podolia Governorate to the north, the Ananev uezd to the east, the Odessa uezd to the south, and the Akkerman and Bendery uezd of the Bessarabia Governorate to the west. The administrative centre of the county was Tiraspol. The area of the Tiraspol uezd corresponded to most of Odesa Oblast and the breakaway territory of Transnistria, which is a part of Moldova.