
The Zambezi is the fourth-longest river in Africa, the longest east-flowing river in Africa and the largest flowing into the Indian Ocean from Africa. Its drainage basin covers 1,390,000 km2 (540,000 sq mi), slightly less than half of the Nile's. The 2,574 km (1,599 mi) river rises in Zambia and flows through eastern Angola, along the north-eastern border of Namibia and the northern border of Botswana, then along the border between Zambia and Zimbabwe to Mozambique, where it crosses the country to empty into the Indian Ocean.

The Kafue River is the longest river lying wholly within Zambia at about 1,576 kilometres (979 mi) long. Its water is used for irrigation and for hydroelectric power. It is the largest tributary of the Zambezi, and of Zambia's principal rivers, it is the most central and the most urban. More than 50% of Zambia's population live in the Kafue River Basin and of these around 65% are urban.

Kafue National Park is the largest national park in Zambia, covering an area of about 22,400 km2. It is the second largest national park in Africa and is home to 152 different species of mammals. There are also 515 bird species, 70 reptile species, 58 species of fish and 36 amphibious species.

South Luangwa National Park is in eastern Zambia, the southernmost of three national parks in the valley of the Luangwa River. It is a world-renowned wildlife haven which is known to locals simply as "the South Park." Concentrations of game along the meandering Luangwa River and its lagoons are amongst the most intense in Africa. The river teems with hippo and crocodile and provides a lifeline for one of the greatest diversities of habitat and wildlife, supporting more than 60 species of mammals and over 400 species of birds. It marks the end of the Great Rift Valley.

Mana Pools National Park is a 219,600-hectare (543,000-acre) wildlife conservation area and national park in northern Zimbabwe. It is a region of the lower Zambezi in Zimbabwe where the floodplain turns into a broad expanse of lakes after each rainy season. As the lakes gradually dry up and recede, the region attracts many large animals in search of water, making it one of Africa's most renowned game-viewing regions.
Luambe National Park is located in the Eastern Province of Zambia. The park is situated north-east of the famous South Luangwa National Park, and south of the North Luangwa National Park. Like its neighbours, it is located in the Luangwa River rift valley.

Lukanga Swamp is a major wetland in the Central Province of Zambia, about 50 km west of Kabwe. Its permanently swampy area consists of a roughly circular area with a diameter of 40 to 50 km covering 1850 km2, plus roughly 250 km2 in the mouths of and along rivers discharging into it such as the Lukanga River from the north-east, plus another 500 km2 either side of the Kafue River to the west and north-west, making 2600 km2 in total. It contains many lagoons such as Lake Chiposhye and Lake Suye but few large channels, and its average depth is only 1.5 m.

Sioma Ngwezi National Park is a 5,000-square-kilometre park in the south west corner of Zambia. It is undeveloped and rarely visited, lacking roads and being off the usual tourist tracks, but this may change in the future.

The wildlife of Malawi is composed of the flora and fauna of the country. Malawi is a landlocked country in southeastern Africa, with Lake Malawi taking up about a third of the country's area. It has around 187 species of mammal, some 648 species of birds have been recorded in the country and around 500 species of fish, many of them endemic, are found in its lakes and rivers. About 20% of the country has been set aside as national parks and game and forest reserves.

The wildlife of Mozambique consists of the flora and fauna of this country in southeastern Africa. Mozambique has a range of different habitat types and an ecologically rich and diverse wildlife. This includes 236 species of mammal, 740 species of bird and 5,692 species of vascular plant. The Maputaland-Pondoland-Albany hotspot, with significantly high levels of biodiversity, stretches from the southern tip of Mozambique into northeastern South Africa.

The wildlife of Zambia refers to the natural flora and fauna of Zambia. This article provides an overview, and outline of the main wildlife areas or regions, and compact lists of animals focusing on prevalence and distribution in the country rather than on taxonomy. More specialized articles on particular groups are linked from here.

The Zambezian flooded grasslands is an ecoregion of southern and eastern Africa that is rich in wildlife.
The biomes and ecoregions in the ecology of Zambia are described, listed and mapped here, following the World Wildlife Fund's classification scheme for terrestrial ecoregions, and the WWF freshwater ecoregion classification for rivers, lakes and wetlands. Zambia is in the Zambezian region of the Afrotropical biogeographic realm. Three terrestrial biomes are well represented in the country . The distribution of the biomes and ecoregions is governed mainly by the physical environment, especially climate.

The Central Zambezian miombo woodlands ecoregion spans southern central Africa. Miombo woodland is the predominant plant community. It is one of the largest ecoregions on the continent, and home to a great variety of wildlife, including many large mammals.
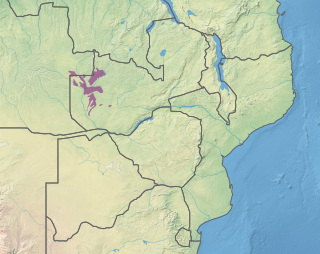
The Zambezian dry evergreen forest, also known as the Zambezian Cryptosepalum dry forest, is a tropical dry broadleaf forest ecoregion of Southern Africa. It consists of several areas of thick forest in western Zambia and adjacent Angola. It is one of the largest areas of tropical evergreen forest outside the equatorial zone.

Bwabwata National Park is a protected area in northeastern Namibia that was established in 2007 and covers 6,274 km2 (2,422 sq mi). It was created by merging Namibia's Caprivi Game Park and Mahango Game Park. It is situated in the Zambezi and Kavango East regions, extending along the Caprivi Strip. It is bounded by the Okavango River to the west and the Kwando River to the east. Angola lies to the north and Botswana to the south.

The Zambezian and mopane woodlands is a tropical and subtropical grasslands, savannas, and shrublands ecoregion of southeastern Africa.

Mudumu is a National Park in Caprivi Region of north-eastern Namibia. Established in 1990, the park covers an area of 737 square kilometres (285 sq mi). The Kwando River forms the western border with Botswana. Various communal area conservancies and community forests surround Mudumu National Park.
The Cheringoma Plateau is a low plateau in Sofala Province of Mozambique. It lies mostly within Cheringoma, Muanza, and Marromeu districts.

The Southern miombo woodlands is a tropical grasslands and woodlands ecoregion extending across portions of Malawi, Mozambique, Zambia, and Zimbabwe.


















