
Lower shoreface refers to the portion of the seafloor, and the sedimentary depositional environment, that lies below the everyday wave base. [1]

Lower shoreface refers to the portion of the seafloor, and the sedimentary depositional environment, that lies below the everyday wave base. [1]
The wave base is the maximum depth at which a water wave's passage causes significant water motion. [1]
In this portion of the coastal marine environment, only the larger waves produced during storms have the power to agitate the seafloor.

Between storms, finer grained sediments accumulate on the seafloor, but during storms those sediments get suspended and moved around, resulting in a sedimentary structure form described as hummocky cross-stratification. [1]

Sedimentary rocks are types of rock that are formed by the accumulation or deposition of sediments, ie. mineral or organic particles, at Earth's surface, followed by cementation. Sedimentation is the collective name for processes that cause these particles to settle in place. The particles that form a sedimentary rock are called sediment, and may be composed of geological detritus (minerals) or biological detritus. The geological detritus originated from weathering and erosion of existing rocks, or from the solidification of molten lava blobs erupted by volcanoes. The geological detritus is transported to the place of deposition by water, wind, ice or mass movement, which are called agents of denudation. Biological detritus was formed by bodies and parts of dead aquatic organisms, as well as their fecal mass, suspended in water and slowly piling up on the floor of water bodies. Sedimentation may also occur as dissolved minerals precipitate from water solution.

Sediment is a solid material that is transported to a new location where it is deposited. It occurs naturally and, through the processes of weathering and erosion, is broken down and subsequently transported by the action of wind, water, or ice or by the force of gravity acting on the particles. For example, sand and silt can be carried in suspension in river water and on reaching the sea bed deposited by sedimentation; if buried, they may eventually become sandstone and siltstone through lithification.

Coastal erosion is the loss or displacement of land, or the long-term removal of sediment and rocks along the coastline due to the action of waves, currents, tides, wind-driven water, waterborne ice, or other impacts of storms. The landward retreat of the shoreline can be measured and described over a temporal scale of tides, seasons, and other short-term cyclic processes. Coastal erosion may be caused by hydraulic action, abrasion, impact and corrosion by wind and water, and other forces, natural or unnatural.

Deposition is the geological process in which sediments, soil and rocks are added to a landform or landmass. Wind, ice, water, and gravity transport previously weathered surface material, which, at the loss of enough kinetic energy in the fluid, is deposited, building up layers of sediment.

Upper shoreface refers to the portion of the seafloor that is shallow enough to be agitated by everyday wave action, the wave base.
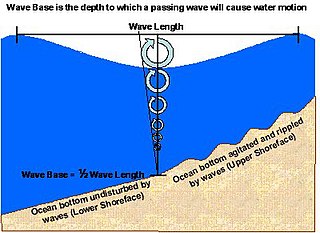
The wave base, in physical oceanography, is the maximum depth at which a water wave's passage causes significant water motion. At water depths deeper than the wave base, bottom sediments and the seafloor are no longer stirred by the wave motion above.
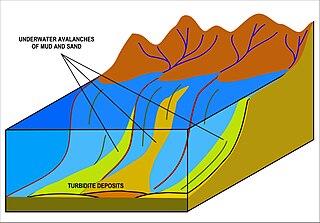
A turbidite is the geologic deposit of a turbidity current, which is a type of amalgamation of fluidal and sediment gravity flow responsible for distributing vast amounts of clastic sediment into the deep ocean.

A turbidity current is most typically an underwater current of usually rapidly moving, sediment-laden water moving down a slope; although current research (2018) indicates that water-saturated sediment may be the primary actor in the process. Turbidity currents can also occur in other fluids besides water.

Tempestites are storm deposits that can be recognized throughout the geologic record. They are studied in the scientific disciplines of sedimentary geology and paleotempestology. The deposits derive their meaning from the word tempest, a violent storm. Tempestites are preserved within a multitude of sedimentary environments including delta systems, estuarian systems, coastal environments, deep sea environments, and fresh water lacustrine environments. Tempesites most often form in wave-dominated delta systems and preserve, within the sedimentary record, evidence of events and processes below fair weather wave base and above storm weather wave base. They are commonly characterized by hummocky cross-stratified beds that have an erosive base, and can form under combined flow regimes. This erosive base is often seen in the form of gutter casts.

Sedimentary exhalative deposits are zinc-lead deposits originally interpreted to have been formed by discharge of metal-bearing basinal fluids onto the seafloor resulting in the precipitation of mainly stratiform ore, often with thin laminations of sulfide minerals. SEDEX deposits are hosted largely by clastic rocks deposited in intracontinental rifts or failed rift basins and passive continental margins. Since these ore deposits frequently form massive sulfide lenses, they are also named sediment-hosted massive sulfide (SHMS) deposits, as opposed to volcanic-hosted massive sulfide (VHMS) deposits. The sedimentary appearance of the thin laminations led to early interpretations that the deposits formed exclusively or mainly by exhalative processes onto the seafloor, hence the term SEDEX. However, recent study of numerous deposits indicates that shallow subsurface replacement is also an important process, in several deposits the predominant one, with only local if any exhalations onto the seafloor. For this reason, some authors prefer the term clastic-dominated zinc-lead deposits. As used today, therefore, the term SEDEX is not to be taken to mean that hydrothermal fluids actually vented into the overlying water column, although this may have occurred in some cases.

A carbonate platform is a sedimentary body which possesses topographic relief, and is composed of autochthonic calcareous deposits. Platform growth is mediated by sessile organisms whose skeletons build up the reef or by organisms which induce carbonate precipitation through their metabolism. Therefore, carbonate platforms can not grow up everywhere: they are not present in places where limiting factors to the life of reef-building organisms exist. Such limiting factors are, among others: light, water temperature, transparency and pH-Value. For example, carbonate sedimentation along the Atlantic South American coasts takes place everywhere but at the mouth of the Amazon River, because of the intense turbidity of the water there. Spectacular examples of present-day carbonate platforms are the Bahama Banks under which the platform is roughly 8 km thick, the Yucatan Peninsula which is up to 2 km thick, the Florida platform, the platform on which the Great Barrier Reef is growing, and the Maldive atolls. All these carbonate platforms and their associated reefs are confined to tropical latitudes. Today's reefs are built mainly by scleractinian corals, but in the distant past other organisms, like archaeocyatha or extinct cnidaria were important reef builders.

In geology, cross-bedding, also known as cross-stratification, is layering within a stratum and at an angle to the main bedding plane. The sedimentary structures which result are roughly horizontal units composed of inclined layers. The original depositional layering is tilted, such tilting not being the result of post-depositional deformation. Cross-beds or "sets" are the groups of inclined layers, which are known as cross-strata.
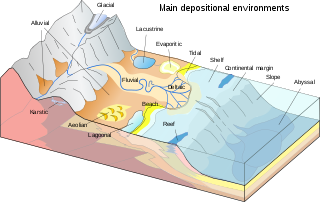
In geology, depositional environment or sedimentary environment describes the combination of physical, chemical, and biological processes associated with the deposition of a particular type of sediment and, therefore, the rock types that will be formed after lithification, if the sediment is preserved in the rock record. In most cases, the environments associated with particular rock types or associations of rock types can be matched to existing analogues. However, the further back in geological time sediments were deposited, the more likely that direct modern analogues are not available.
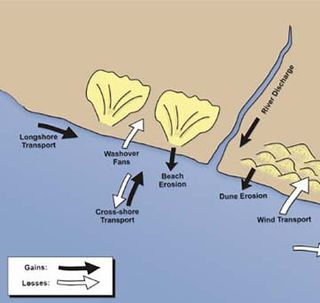
Sedimentary budgets are a coastal management tool used to analyze and describe the different sediment inputs (sources) and outputs (sinks) on the coasts, which is used to predict morphological change in any particular coastline over time. Within a coastal environment the rate of change of sediment is dependent on the amount of sediment brought into the system versus the amount of sediment that leaves the system. These inputs and outputs of sediment then equate to the total balance of the system and more than often reflect the amounts of erosion or accretion affecting the morphology of the coast.

Marine sediment, or ocean sediment, or seafloor sediment, are deposits of insoluble particles that have accumulated on the seafloor. These particles either have their origins in soil and rocks and have been transported from the land to the sea, mainly by rivers but also by dust carried by wind and by the flow of glaciers into the sea, or they are biogenic deposits from marine organisms or from chemical precipitation in seawater, as well as from underwater volcanoes and meteorite debris.

Coastal engineering is a branch of civil engineering concerned with the specific demands posed by constructing at or near the coast, as well as the development of the coast itself.

Sedimentary structures include all kinds of features in sediments and sedimentary rocks, formed at the time of deposition.

Hummocky cross-stratification is a type of sedimentary structure found in sandstones. It is a form of cross-bedding usually formed by the action of large storms, such as hurricanes. It takes the form of a series of "smile"-like shapes, crosscutting each other. It is only formed at a depth of water below fair-weather wave base and above storm-weather wave base. They are not related to "hummocks" except in shape.

In geology, lamination is a small-scale sequence of fine layers that occurs in sedimentary rocks. Laminae are normally smaller and less pronounced than bedding. Lamination is often regarded as planar structures one centimetre or less in thickness, whereas bedding layers are greater than one centimetre. However, structures from several millimetres to many centimetres have been described as laminae. A single sedimentary rock can have both laminae and beds.

A contourite is a sedimentary deposit commonly formed on continental rises in lower slope settings, although it may occur anywhere that is below the storm wave base. Countourites are produced by thermohaline-induced deepwater bottom currents and may be influenced by wind or tidal forces. The geomorphology of contourite deposits is mainly influenced by the deepwater bottom-current velocity, sediment supply, and seafloor topography.