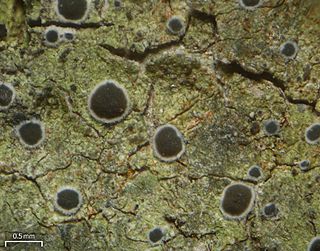
The Pilocarpaceae are a family of crustose lichens in the order Lecanorales. The species of this family have a cosmopolitan distribution and have been found in a variety of climatic regions. Pilocarpaceae was circumscribed by Alexander Zahlbruckner in Adolf Engler's influential 1905 work Die Natürlichen Pflanzenfamilien.

Porina is a genus of lichens in the family Trichotheliaceae. A 2020 estimate places about 145 species in the widespread genus.

Calopadia is a genus of foliicolous (leaf-dwelling) lichens in the family Pilocarpaceae. It was circumscribed by Czech lichenologist Antonín Vězda in 1986.

Byssoloma is a genus of leaf-dwelling lichens in the family Pilocarpaceae.
Badimia is a genus of foliicolous (leaf-inhabiting) lichens in the family Ramalinaceae.
Sporopodium is a genus of lichen-forming fungi in the family Pilocarpaceae.
Caprettia is a genus of lichenized fungi in the family Monoblastiaceae. The genus was circumscribed by Augusto Chaves Batista and Heraldo da Silva Maia in 1965, with Caprettia amazonensis assigned as the type species.
Aderkomyces is a genus of lichens in the family Gomphillaceae. It was circumscribed by Brazilian mycologist Augusto Chaves Batista in 1961.
Echinoplaca is a genus of lichens in the family Gomphillaceae.
Gyalectidium is a genus of lichen-forming fungi in the family Gomphillaceae. A 2020 estimates placed 52 species in the genus. The genus was circumscribed by Swiss lichenologist Johannes Müller Argoviensis in 1881. He included 3 species: G. xantholeucum, G. dispersum, and G. filicinum; the last of these is now the type species of the genus.

Astrothelium is a large genus of corticolous (bark-dwelling) lichens in the family Trypetheliaceae. The genus is characterized by a corticate thallus and diverse ascomata structures, which can be simple, aggregated, or forming pseudostromata. Astrothelium is also notable for the carbonized walls of its ascomata, the so-called textura intricata arrangement of cells in these walls, and various forms of distoseptate, transparent spores.
Pseudopyrenula is a genus of lichen-forming fungi in the family Trypetheliaceae.

Malmideaceae is a family of crustose and corticolous lichens in the order Lecanorales. It contains eight genera and about 70 species.
Antonín (Toni) Vězda was a Czech lichenologist. After completing a university education that was postponed by World War II, Vězda taught botany at the Czech University of Life Sciences. In 1958, he was dismissed from his university position as a result of the restrictions placed on academic freedoms by the communist regime in power. He eventually was hired as a lichen researcher by the Czechoslovak Academy of Sciences, who allowed him to work from his apartment, which served also as an office and herbarium.

Coenogonium is a genus of filamentous lichens in the monotypic family Coenogoniaceae. It has about 90 species. Most species are leaf-dwelling or grow on bark, although a few are known to grow on rocks under certain conditions, and some are restricted to growth on termite nests. The genus was circumscribed in 1820 by German naturalist Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg.
Eugeniella is a genus of mostly leaf-dwelling (foliicolous) lichens in the family Pilocarpaceae. It contains 13 species. The genus was circumscribed in 2008 by lichenologists Robert Lücking, Emmanuël Sérusiaux, and Klaus Kalb, with Eugeniella psychotriae assigned as the type species. This lichen was originally called Patellaria psychotriae by Johannes Müller Argoviensis in 1881. The seven species that were initially included in the genus had previously been placed in the genera Bacidia and Byssoloma. Several newly identified species from Australasia and Central and South America were later added. Most of the species grow on leaves, although four of the Australasian species grow on bark.
Brasilicia is a genus of leaf-dwelling lichens in the family Pilocarpaceae. It has 6 species. The genus was circumscribed in 2008 by lichenologists Robert Lücking, Klaus Kalb, and Emmanuël Sérusiaux, with B. brasiliensis assigned as the type species. The genus was originally circumscribed as monotypic; Edit Farkas transferred five species to Brasilicia from Bacidia in 2015.
Phylloblastia is a genus of foliicolous (leaf-dwelling) lichens in the family Verrucariaceae. The genus was circumscribed in 1921 by Finnish lichenologist Edvard August Vainio, with Phylloblastia dolichospora assigned as the type species.

Robert Lücking is a German lichenologist. He earned his master's and PhD from the University of Ulm, focusing on the taxonomy, ecology, and biodiversity of foliicolous lichens. He has received numerous awards for his work, including the Mason E. Hale Award for his doctoral thesis, the Augustin Pyramus de Candolle prize for his monograph, and the Tuckerman Award twice for his publications in The Bryologist. Since 2015, he has been serving as the curator of lichens, fungi, and bryophytes at the Berlin Botanical Garden and Botanical Museum, and several lichen species and a genus have been named in his honour.
Aspidothelium is a genus of lichen-forming fungi in the family Thelenellaceae. All species in the genus have a tropical distribution and are crustose with a chlorococcoid photobiont partner. Most Aspidothelium species are foliicolous (leaf-dwelling), although some corticolous (bark-dwelling) species are known, as well as a single saxicolous (rock-dwelling) member.






