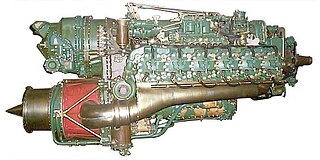
The Napier Nomad is a British diesel aircraft engine designed and built by Napier & Son in 1949. They combined a piston engine with a turbine to recover energy from the exhaust and thereby improve fuel economy. Two versions were tested, the complex Nomad I which used two propellers, each driven by the mechanically independent stages, and the Nomad II, using the turbo-compound principle, coupled the two parts to drive a single propeller. The Nomad II had the lowest specific fuel consumption figures seen up to that time. Despite this the Nomad project was cancelled in 1955 having spent £5.1 million on development, as most interest had passed to turboprop designs.
The Soloviev D-25V is a Soviet gas-turbine turboshaft engine for use in large helicopters. Designed and originally manufactured by the Soloviev Design Bureau the engine has been in production since May 1960. The power unit consists of two engines coupled to a gearbox weighing 3,200 kg (7,050 lb).

The Kuznetsov NK-12 is a Soviet turboprop engine of the 1950s, designed by the Kuznetsov design bureau. The NK-12 drives two large four-bladed contra-rotating propellers, 5.6 m (18 ft) diameter (NK-12MA), and 6.2 m (20 ft) diameter (NK-12MV). It is the most powerful turboprop engine to enter service.

The Napier Gazelle is a turboshaft helicopter engine that was manufactured by D. Napier & Son in the mid-1950s. In 1961 production was nominally transferred to a joint venture with Rolls-Royce called Napier Aero Engines Limited. But the venture closed two years later.

The General Electric T700 and CT7 are a family of turboshaft and turboprop engines in the 1,500–3,000 shp (1,100–2,200 kW) class.

The Turbomeca Astazou is a highly successful series of turboprop and turboshaft engines, first run in 1957. The original version weighed 110 kg (243 lb) and developed 240 kW (320 shp) at 40,000 rpm. It was admitted for aviation service on May 29, 1961, after a 150-hour test run. The main developing engineer was G. Sporer. It was named after two summits of the Pyrenees.

The Turbomeca Artouste is an early French turboshaft engine, first run in 1947. Originally conceived as an auxiliary power unit (APU), it was soon adapted to aircraft propulsion, and found a niche as a powerplant for turboshaft-driven helicopters in the 1950s. Artoustes were licence-built by Bristol Siddeley in the UK, Hindustan Aeronautics Limited in India, and developed by Continental CAE in the US as the Continental T51. Two major versions of the Artouste were produced. The Artouste II family, mainly used in the Aérospatiale Alouette II helicopter, had a one-stage centrifugal compressor and a two-stage turbine, with gearbox-limited power of 300 kW (400 hp). The Artouste III family, mainly used in Aérospatiale's Alouette III and Lama helicopters, had a two-stage axial-centrifugal compressor and a three-stage turbine, with gearbox-limited power of 420–440 kW (560–590 hp).

The Turbomeca Turmo is a family of French turboshaft engines manufactured for helicopter use. Developed from the earlier Turbomeca Artouste, later versions delivered up to 1,300 kW (1,700 shp). A turboprop version was developed for use with the Bréguet 941 transport aircraft.

The Honeywell T55 is a turboshaft engine used on American helicopters and fixed-wing aircraft since the 1950s, and in unlimited hydroplanes since the 1980s. As of 2021, more than 6,000 of these engines have been built. It is produced by Honeywell Aerospace, a division of Honeywell based in Scottsdale, Arizona, and was originally designed by the Turbine Engine Division of Lycoming Engines in Stratford, Connecticut, as a scaled-up version of the smaller Lycoming T53. The T55 serves as the engine on several major applications including the CH-47-Chinook, the Bell 309, and the Piper PA-48 Enforcer. The T55 also serves as the core of the Lycoming ALF 502 turbofan. Since the T55 was first developed, progressive increases in airflow, overall pressure ratio, and turbine inlet temperature have more than tripled the power output of the engine.

The Pratt & Whitney Canada PT6T Twin-Pac is a turboshaft engine designed for helicopters. Manufactured by Pratt & Whitney Canada, its first application was in the Bell 212 and UH-1N Twin Huey helicopter family. The PT6T Twin-Pac consists of two PT6A power turbines driving a common output reduction gearbox, producing up to 2,000 hp at 6,000 rpm. The engine is designated T400 by the U.S. military.

The Boeing T50 was a small turboshaft engine produced by Boeing. It was the first turboshaft engine to ever power a helicopter: a modified Kaman K-225 in 1951. Based on Boeing's earlier Model 500 gas generator, the T50's main application was in the QH-50 DASH helicopter drone of the 1950s. An up-rated version designated Model 550 was developed to power the QH-50D and was given the military designation T50-BO-12.

The Allison T38 was an early turboprop engine developed by Allison Engine Company during the late 1940s. The T38 became the basis for the very successful family of Allison T56 turboprop engine.
The Boeing T60 was a family of small turboshaft/turboprop engines produced by Boeing, based on Boeing's earlier Model 500 gas generator and Model 502 (T50) turboshaft engines.

The Continental CAE T51 was a small turboshaft engine produced by Continental Aviation and Engineering (CAE) under license from Turbomeca. A development of the Artouste, it was followed by three additional turboshaft engines, the T72, the T65, and the T67. However, none of these engines, including the T51, entered full production. CAE abandoned turboshaft development in 1967 after the XT67 lost to the Pratt & Whitney Canada PT6T (T400) to power the Bell UH-1N Twin Huey.

The Solar T62 Titan is an American gas turbine engine used mainly as a aircraft auxiliary power unit (APU), conventional power generator, turboprop engine for fixed-wing aircraft or turboshaft engine for helicopters. A new turbine version was developed as the Solar T66.

The Klimov TV2-117 is a Soviet gas-turbine turboshaft engine intended for helicopter use. Designed in the early 1960s by the Isotov Design Bureau the engine became the first purpose built gas turbine engine for helicopter use by the Soviet Union with previous helicopter turbines being adapted aeroplane powerplants. It was later produced by Klimov, production ending in 1997.

The Klimov GTD-350 is a Soviet gas-turbine turboshaft engine intended for helicopter use. Designed in the early 1960s by the Isotov Design Bureau the engine was later produced by Klimov and PZL, production ending in the late 1990s.

The Ivchenko AI-24 turboprop aircraft engine was designed and developed in the late-1950s by the Ivchenko design bureau and manufactured thereafter by Motor Sich. It was designed to power Antonov's successful An-24, An-26 and An-30 aircraft series.
The Ivchenko AI-8 is an aircraft auxiliary power unit developed and produced by Ivchenko-Progress and Motor Sich.

The BMW 6012 was a German turboshaft and gas generator engine. Designed in the late-1950s by BMW the engine powered the Dornier Do 32 helicopter and was also used as an auxiliary power unit (APU).

















