Lombok is an island in West Nusa Tenggara province, Indonesia. It forms part of the chain of the Lesser Sunda Islands, with the Lombok Strait separating it from Bali to the west and the Alas Strait between it and Sumbawa to the east. It is roughly circular, with a "tail" to the southwest, about 70 kilometres across and a total area of about 4,607.38 square kilometres including smaller offshore islands. The provincial capital and largest city on the island is Mataram.

Sumbawa is an Indonesian island, located in the middle of the Lesser Sunda Islands chain, with Lombok to the west, Flores to the east, and Sumba further to the southeast. Along with Lombok, it forms the province of West Nusa Tenggara, but there have been plans by the Indonesian government to split the island off into a separate province. Traditionally, the island is known as the source of sappanwood, as well as honey and sandalwood. Its savanna-like climate and vast grasslands are used to breed horses and cattle, as well as to hunt deer.

West Nusa Tenggara is a province of Indonesia. It comprises the western portion of the Lesser Sunda Islands, with the exception of Bali which is its own province. The province's land area is 19,931.45 km2. The two largest islands by far in the province are the smaller but much more populated Lombok in the west and the much larger in area but much less densely populated Sumbawa island in the east. Mataram, on Lombok, is the capital and largest city of the province. It shares maritime borders with Bali to the west and East Nusa Tenggara to the east.

Denpasar is the capital city of the province of Bali, Indonesia. Denpasar is the main gateway to the Bali island, the city is also a hub for other cities in the Lesser Sunda Islands.

Pasuruan is a city in East Java Province of Java, Indonesia. It had a population of 186,262 at the 2010 Census and 208,006 at the 2020 Census; the official estimate as at mid 2023 was 212,466.
East Jakarta is the largest of the five administrative cities which form the Special Capital Region of Jakarta, Indonesia. It had a population of 2,693,896 at the 2010 Census and 3,037,139 at the 2020 Census; the official estimate as at mid 2022 was 3,083,883, making it the most populous of the five administrative cities within Jakarta. East Jakarta is not self-governed and does not have a city council, hence it is not classified as a proper municipality.

Bondowoso Regency is a landlocked regency in East Java, Indonesia. It covers an area of 1,560.10 km2, and had a population of 736,772 at the 2010 Census and 776,151 at the 2020 Census; the official estimate as of mid-2023 was 796,911. The most common languages are Madurese and Javanese, although Madurese is the majority. The nearest large city is Surabaya, approximately five hour's drive away.

Cirebon Regency is a regency (kabupaten) of West Java Province of Indonesia. The town of Sumber is its capital. It covers 1,076.76 km2 and had a population of 2,068,116 at the 2010 census and 2,270,621 at the 2020 census; the official estimate as at mid 2023 was 2,360,441. These area and population figures exclude those of Cirebon City, which is an independent administration, although totally surrounded by the regency on its landward side.

Kediri is a city, located near the Brantas River in the province of East Java on the island of Java in Indonesia. It covers an area of 67.23 km2 and had a population of 268,950 at the 2010 Census and 286,796 at the 2020 Census; the official estimate as at mid 2023 was 298,830. It is one of two 'Daerah Tingkat II' that have the name 'Kediri'. The city is administratively separated from the Regency, of which it was formerly the capital.

Martapura is the capital of the Banjar Regency in South Kalimantan province, Indonesia. It is located close to the city of Banjarbaru and it consists of three districts within the Regency - Martapura, West Martapura and East Martapura, with a combined population at the 2020 Census of 169,356 people.

Sorong Regency is a regency of the Southwest Papua province of Indonesia. It covers an area of 13,075.28 km2, and had a population of 70,619 at the 2010 Census, and 118,679 at the 2020 Census; the official estimate as of mid-2023 was 129,963. Its administrative centre is the town of Aimas. Sorong Regency surrounds Sorong City (Kota) on the landward side; the city is administratively independent of the Regency and is not included in the above statistics; Sorong City has an airport, Sorong Airport, which also serves the Regency.

West Sumba Regency is a regency in East Nusa Tenggara Province of Indonesia. Established in 1958, the regency was considerably reduced on 2 January 2007 with the creation of new Regencies on Sumba Island under Law UU No.16 of that year. Its area is now 737.42 km2, and its population was 110,993 at the 2010 census and 145,097 at the 2020 Census; the official estimate as at mid 2023 was 152,414. It has its seat (capital) in (Kota) Waikabubak.

Sumbawa Besar is a town on the Indonesian island of Sumbawa, and is the second-biggest settlement on the island after Bima. It is the administrative capital of the Sumbawa Regency within the province of West Nusa Tenggara, and has a population of 56,337 inhabitants as of the 2010 census and 62,753 at the 2020 Census; the official estimate as at mid 2023 was 63,362.

West Lombok Regency is a regency of the Indonesian Province of West Nusa Tenggara. It is located on the island of Lombok and the administrative capital is the town of Gerung. The regency covers a land area of 922.91 km2 and had a population of 599,609 at the 2010 census and 721,481 at the 2020 census; the official estimate as at mid 2023 was 753,641.

East Lombok Regency is a regency of the Indonesian Province of West Nusa Tenggara. It is located on the island of Lombok, of which it comprises the eastern third ; the administrative capital is the town of Selong. The Regency covers an area of 1,605.55 km2 and had a population of 1,105,582 at the 2010 Census and 1,325,240 at the 2020 Census; the official estimate as at mid 2023 was 1,404.343.

Central Lombok Regency is a regency of the Indonesian Province of West Nusa Tenggara. It is located on the island of Lombok and the capital is Praya. It covers an area of 1,208.39 km2, and had a population of 859,309 at the 2010 census and 1,034,859 at the 2020 census; the official estimate as at mid 2023 was 1,099,211.
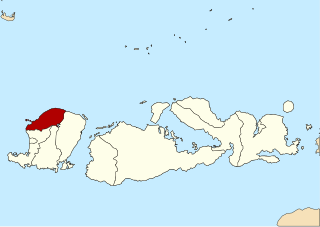
North Lombok Regency is a regency of the Indonesian Province of West Nusa Tenggara. It is located in the northwest of the island of Lombok and includes the offshore Gili Islands. The capital is Tanjung situated on the northwest coast of the island. The regency covers an area of 809.53 km2 and had a population of 200,072 at the 2010 Census and 247,400 at the 2020 Census; the official estimate as at mid 2023 was 265,500.

The Palembang metropolitan area, known locally as Patungraya Agung, is a metropolitan area in South Sumatra, Indonesia. It encompasses Palembang as the core city and parts of the three surrounding regencies: Banyuasin Regency, Ogan Ilir Regency, and Ogan Komering Ilir Regency. It is the second-largest metropolitan area in Sumatra with an estimated population of over 2.7 million.

The Semarang metropolitan area, known locally as Kedungsepur, is a metropolitan area anchored by the city of Semarang in Central Java, Indonesia. It additionally includes the city of Salatiga, as well as Demak Regency, Grobogan Regency, Kendal Regency, and Semarang Regency. It is the fourth most populous metropolitan area in Indonesia with an estimated population of about 6.2 million as at mid 2023.