
Manaslu is the eighth-highest mountain in the world at 8,163 metres (26,781 ft) above sea level. It is in the Mansiri Himal, part of the Nepalese Himalayas, in west-central Nepal. Manaslu means "mountain of the spirit" and the word is derived from the Sanskrit word manasa, meaning "intellect" or "soul". Manaslu was first climbed on May 9, 1956, by Toshio Imanishi and Gyalzen Norbu, members of a Japanese expedition. It is said that, given the many unsuccessful attempts by the British to climb Everest before Nepali Tenzing Norgay and New Zealander Edmund Hillary, "just as the British consider Everest their mountain, Manaslu has always been a Japanese mountain".

Valley of Flowers National Park is an Indian national park which was established in 1982. It is located in Chamoli in the state of Uttarakhand and is known for its meadows of endemic alpine flowers and the variety of flora. This richly diverse area is also home to rare and endangered animals, including the Asiatic black bear, snow leopard, musk deer, brown bear, red fox and blue sheep. Birds found in the park include Himalayan monal pheasant and other high altitude birds.

Papaver is a genus of 70–100 species of frost-tolerant annuals, biennials, and perennials native to temperate and cold regions of Eurasia, Africa and North America. It is the type genus of the poppy family, Papaveraceae.

Gypsophila is a genus of flowering plants in the carnation family, Caryophyllaceae. They are native to Eurasia, Africa, Australia, and the Pacific Islands. Turkey has a particularly high diversity of Gypsophila taxa, with about 35 endemic species. Some Gypsophila are introduced species in other regions.

The Papaveraceae are an economically important family of about 42 genera and approximately 775 known species of flowering plants in the order Ranunculales, informally known as the poppy family. The family is cosmopolitan, occurring in temperate and subtropical climates, but almost unknown in the tropics. Most are herbaceous plants, but a few are shrubs and small trees. The family currently includes two groups that have been considered to be separate families: Fumariaceae and Pteridophyllaceae.

Meconopsis is a genus of flowering plants in the poppy family Papaveraceae. It was created by French botanist Viguier in 1814 for the species known by the common name Welsh poppy, which Carl Linnaeus had described as Papaver cambricum. The genus name means "poppy-like". Himalayan species discovered later were also placed in Meconopsis. In the 21st century, it was discovered that the Himalayan species were less closely related to the Welsh poppy, which has been restored to Papaver. All species now placed in Meconopsis are native to the Himalayas and surrounding regions. They have attractive, usually blue flowers.

Papaver cambricum, synonym Meconopsis cambrica, the Welsh poppy, is a perennial flowering plant in the poppy family Papaveraceae. It has yellow to orange flowers and is widely grown as a garden plant. It is a native of damp, rocky sites in upland areas of Western Europe from the British Isles to the Iberian Peninsula. It has been used since 2006 as the basis for the logo of the political party Plaid Cymru.

Meconopsis napaulensis, the Nepal poppy or satin poppy, is a plant of the family Papaveraceae. The plant contains beta-carbolines, which act as a psychedelic drug. However, its phytochemistry remains predominantly unstudied.
Meconopsis villosa, the Himalayan woodland-poppy, is an ornamental poppy, which is native of Nepal. The species was placed in the genus Cathcartia erected by J.D. Hooker to honour J.F. Cathcart, an Indian civil servant and amateur botanist who collected and hired native artists to illustrate the flowers of the Himalayas. It was transferred to Meconopsis by George Taylor in 1934. In 2017, it was suggested that the genus Cathcartia should be revived, and this species again treated as Cathcartia villosa.
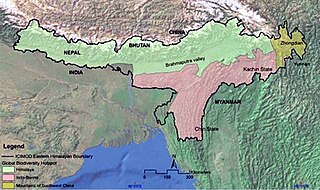
The Eastern Himalayas extend from eastern Nepal across Northeast India, Bhutan, the Tibet Autonomous Region to Yunnan in China and northern Myanmar. The climate of this region is influenced by the monsoon of South Asia from June to September. It is a biodiversity hotspot, with notable biocultural diversity.

The Western Himalayan alpine shrub and meadows is a montane grasslands and shrublands ecoregion of Nepal, India, and Tibet, which lies between the tree line and snow line in the western portion of the Himalaya Range.

The Eastern Himalayan alpine shrub and meadows is a montane grasslands and shrublands ecoregion of Bhutan, China, India, Myanmar, and Nepal, which lies between the tree line and snow line in the eastern portion of the Himalaya Range.

Meconopsis grandis, the Himalayan blue poppy, is a species of flowering plant in the poppy family Papaveraceae, native to China (Yunnan), Bhutan, North East India and Nepal.

The Northwestern Himalayan alpine shrub and meadows is a montane grasslands and shrublands ecoregion of the elevations of the northwestern Himalaya of China, India, and Pakistan.

Meconopsis manasluensis is a red-flowered Himalayan poppy belonging to Meconopsis subg. Discogyne, which forms a natural grouping of 6 or 7 species within the genus all characterised by a stylar disc surmounting the ovary. As reflected by the species etymology, M. manasluensis is endemic to the vicinity of the Manaslu Himal of Gorkha district, central Nepal, where it grows at high elevation and so far remains known only from its type collection locality.
Meconopsis bella is commonly known as the pretty blue poppy. M. bella is a species of the genus Meconopsis which is found from central Nepal to southeastern Tibet. It is a herbaceous flowering plant and is a part of the poppy family Papaveraceae. This plant is also referred to as Meconopsis bella prain, since it was aptly names by the botanist Prain.

Meconopsis horridula, the prickly blue poppy, is a flowering plant from the family Papaveraceae. It is an endangered species that grows in high altitudes. The height of the plant varies from 20 cm to 1m. It is a monocarpic, dicot plant.
Meconopsis lancifolia is a plant species in the genus Meconopsis, in the family Papaveraceae. M. lancifolia is monocarpic, meaning that it flowers only once before dying.
Solms-laubachia himalayensis is a flowering plant in the family Brassicaceae. The specific epithet himalayensis is from the Latin, meaning "Himalayan".
Cathcartia is a small genus of flowering plants in the family Papaveraceae, native to China, Nepal, the eastern Himalayas, and northern Myanmar. Chloroplast DNA evidence supports a split of Cathcartia from the blue poppy genus Meconopsis in an effort to resolve longstanding taxonomic difficulties in the Himalayan poppies.















